Traffic Data Imputation
Papers and Code
Spatial-Temporal Feedback Diffusion Guidance for Controlled Traffic Imputation
Jan 08, 2026Imputing missing values in spatial-temporal traffic data is essential for intelligent transportation systems. Among advanced imputation methods, score-based diffusion models have demonstrated competitive performance. These models generate data by reversing a noising process, using observed values as conditional guidance. However, existing diffusion models typically apply a uniform guidance scale across both spatial and temporal dimensions, which is inadequate for nodes with high missing data rates. Sparse observations provide insufficient conditional guidance, causing the generative process to drift toward the learned prior distribution rather than closely following the conditional observations, resulting in suboptimal imputation performance. To address this, we propose FENCE, a spatial-temporal feedback diffusion guidance method designed to adaptively control guidance scales during imputation. First, FENCE introduces a dynamic feedback mechanism that adjusts the guidance scale based on the posterior likelihood approximations. The guidance scale is increased when generated values diverge from observations and reduced when alignment improves, preventing overcorrection. Second, because alignment to observations varies across nodes and denoising steps, a global guidance scale for all nodes is suboptimal. FENCE computes guidance scales at the cluster level by grouping nodes based on their attention scores, leveraging spatial-temporal correlations to provide more accurate guidance. Experimental results on real-world traffic datasets show that FENCE significantly enhances imputation accuracy.
Modeling Information Blackouts in Missing Not-At-Random Time Series Data
Jan 06, 2026Large-scale traffic forecasting relies on fixed sensor networks that often exhibit blackouts: contiguous intervals of missing measurements caused by detector or communication failures. These outages are typically handled under a Missing At Random (MAR) assumption, even though blackout events may correlate with unobserved traffic conditions (e.g., congestion or anomalous flow), motivating a Missing Not At Random (MNAR) treatment. We propose a latent state-space framework that jointly models (i) traffic dynamics via a linear dynamical system and (ii) sensor dropout via a Bernoulli observation channel whose probability depends on the latent traffic state. Inference uses an Extended Kalman Filter with Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoothing, and parameters are learned via an approximate EM procedure with a dedicated update for detector-specific missingness parameters. On the Seattle inductive loop detector data, introducing latent dynamics yields large gains over naive baselines, reducing blackout imputation RMSE from 7.02 (LOCF) and 5.02 (linear interpolation + seasonal naive) to 4.23 (MAR LDS), corresponding to about a 64% reduction in MSE relative to LOCF. Explicit MNAR modeling provides a consistent but smaller additional improvement on real data (imputation RMSE 4.20; 0.8% RMSE reduction relative to MAR), with similar modest gains for short-horizon post-blackout forecasts (evaluated at 1, 3, and 6 steps). In controlled synthetic experiments, the MNAR advantage increases as the true missingness dependence on latent state strengthens. Overall, temporal dynamics dominate performance, while MNAR modeling offers a principled refinement that becomes most valuable when missingness is genuinely informative.
Network-Wide Traffic Volume Estimation from Speed Profiles using a Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network with Directed Spatial Attention
Dec 15, 2025Existing traffic volume estimation methods typically address either forecasting traffic on sensor-equipped roads or spatially imputing missing volumes using nearby sensors. While forecasting models generally disregard unmonitored roads by design, spatial imputation methods explicitly address network-wide estimation; yet this approach relies on volume data at inference time, limiting its applicability in sensor-scarce cities. Unlike traffic volume data, probe vehicle speeds and static road attributes are more broadly accessible and support full coverage of road segments in most urban networks. In this work, we present the Hybrid Directed-Attention Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network (HDA-STGNN), an inductive deep learning framework designed to tackle the network-wide volume estimation problem. Our approach leverages speed profiles, static road attributes, and road network topology to predict daily traffic volume profiles across all road segments in the network. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we perform extensive ablation studies that demonstrate the model's capacity to capture complex spatio-temporal dependencies and highlight the value of topological information for accurate network-wide traffic volume estimation without relying on volume data at inference time.
PAST: A Primary-Auxiliary Spatio-Temporal Network for Traffic Time Series Imputation
Nov 17, 2025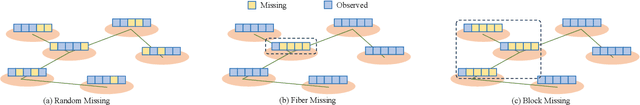
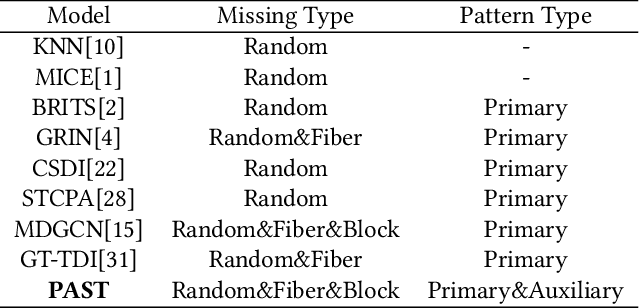
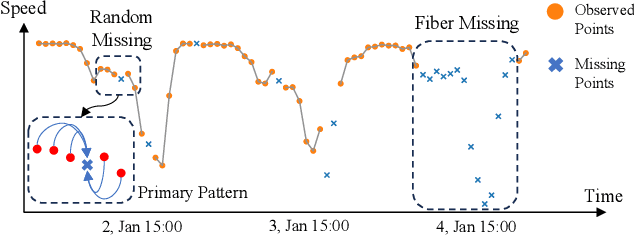
Traffic time series imputation is crucial for the safety and reliability of intelligent transportation systems, while diverse types of missing data, including random, fiber, and block missing make the imputation task challenging. Existing models often focus on disentangling and separately modeling spatial and temporal patterns based on relationships between data points. However, these approaches struggle to adapt to the random missing positions, and fail to learn long-term and large-scale dependencies, which are essential in extensive missing conditions. In this paper, patterns are categorized into two types to handle various missing data conditions: primary patterns, which originate from internal relationships between data points, and auxiliary patterns, influenced by external factors like timestamps and node attributes. Accordingly, we propose the Primary-Auxiliary Spatio-Temporal network (PAST). It comprises a graph-integrated module (GIM) and a cross-gated module (CGM). GIM captures primary patterns via dynamic graphs with interval-aware dropout and multi-order convolutions, and CGM extracts auxiliary patterns through bidirectional gating on embedded external features. The two modules interact via shared hidden vectors and are trained under an ensemble self-supervised framework. Experiments on three datasets under 27 missing data conditions demonstrate that the imputation accuracy of PAST outperforms seven state-of-the-art baselines by up to 26.2% in RMSE and 31.6% in MAE.
STAMImputer: Spatio-Temporal Attention MoE for Traffic Data Imputation
Jun 11, 2025Traffic data imputation is fundamentally important to support various applications in intelligent transportation systems such as traffic flow prediction. However, existing time-to-space sequential methods often fail to effectively extract features in block-wise missing data scenarios. Meanwhile, the static graph structure for spatial feature propagation significantly constrains the models flexibility in handling the distribution shift issue for the nonstationary traffic data. To address these issues, this paper proposes a SpatioTemporal Attention Mixture of experts network named STAMImputer for traffic data imputation. Specifically, we introduce a Mixture of Experts (MoE) framework to capture latent spatio-temporal features and their influence weights, effectively imputing block missing. A novel Low-rank guided Sampling Graph ATtention (LrSGAT) mechanism is designed to dynamically balance the local and global correlations across road networks. The sampled attention vectors are utilized to generate dynamic graphs that capture real-time spatial correlations. Extensive experiments are conducted on four traffic datasets for evaluation. The result shows STAMImputer achieves significantly performance improvement compared with existing SOTA approaches. Our codes are available at https://github.com/RingBDStack/STAMImupter.
Neural Canonical Polyadic Factorization for Traffic Analysis
Jun 18, 2025Modern intelligent transportation systems rely on accurate spatiotemporal traffic analysis to optimize urban mobility and infrastructure resilience. However, pervasive missing data caused by sensor failures and heterogeneous sensing gaps fundamentally hinders reliable traffic modeling. This paper proposes a Neural Canonical Polyadic Factorization (NCPF) model that synergizes low-rank tensor algebra with deep representation learning for robust traffic data imputation. The model innovatively embeds CP decomposition into neural architecture through learnable embedding projections, where sparse traffic tensors are encoded into dense latent factors across road segments, time intervals, and mobility metrics. A hierarchical feature fusion mechanism employs Hadamard products to explicitly model multilinear interactions, while stacked multilayer perceptron layers nonlinearly refine these representations to capture complex spatiotemporal couplings. Extensive evaluations on six urban traffic datasets demonstrate NCPF's superiority over six state-of-the-art baselines. By unifying CP decomposition's interpretable factor analysis with neural network's nonlinear expressive power, NCPF provides a principled yet flexible approaches for high-dimensional traffic data imputation, offering critical support for next-generation transportation digital twins and adaptive traffic control systems.
Improving Traffic Signal Data Quality for the Waymo Open Motion Dataset
Jun 08, 2025Datasets pertaining to autonomous vehicles (AVs) hold significant promise for a range of research fields, including artificial intelligence (AI), autonomous driving, and transportation engineering. Nonetheless, these datasets often encounter challenges related to the states of traffic signals, such as missing or inaccurate data. Such issues can compromise the reliability of the datasets and adversely affect the performance of models developed using them. This research introduces a fully automated approach designed to tackle these issues by utilizing available vehicle trajectory data alongside knowledge from the transportation domain to effectively impute and rectify traffic signal information within the Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD). The proposed method is robust and flexible, capable of handling diverse intersection geometries and traffic signal configurations in real-world scenarios. Comprehensive validations have been conducted on the entire WOMD, focusing on over 360,000 relevant scenarios involving traffic signals, out of a total of 530,000 real-world driving scenarios. In the original dataset, 71.7% of traffic signal states are either missing or unknown, all of which were successfully imputed by our proposed method. Furthermore, in the absence of ground-truth signal states, the accuracy of our approach is evaluated based on the rate of red-light violations among vehicle trajectories. Results show that our method reduces the estimated red-light running rate from 15.7% in the original data to 2.9%, thereby demonstrating its efficacy in rectifying data inaccuracies. This paper significantly enhances the quality of AV datasets, contributing to the wider AI and AV research communities and benefiting various downstream applications. The code and improved traffic signal data are open-sourced at https://github.com/michigan-traffic-lab/WOMD-Traffic-Signal-Data-Improvement
Filling the Missings: Spatiotemporal Data Imputation by Conditional Diffusion
Jun 08, 2025Missing data in spatiotemporal systems presents a significant challenge for modern applications, ranging from environmental monitoring to urban traffic management. The integrity of spatiotemporal data often deteriorates due to hardware malfunctions and software failures in real-world deployments. Current approaches based on machine learning and deep learning struggle to model the intricate interdependencies between spatial and temporal dimensions effectively and, more importantly, suffer from cumulative errors during the data imputation process, which propagate and amplify through iterations. To address these limitations, we propose CoFILL, a novel Conditional Diffusion Model for spatiotemporal data imputation. CoFILL builds on the inherent advantages of diffusion models to generate high-quality imputations without relying on potentially error-prone prior estimates. It incorporates an innovative dual-stream architecture that processes temporal and frequency domain features in parallel. By fusing these complementary features, CoFILL captures both rapid fluctuations and underlying patterns in the data, which enables more robust imputation. The extensive experiments reveal that CoFILL's noise prediction network successfully transforms random noise into meaningful values that align with the true data distribution. The results also show that CoFILL outperforms state-of-the-art methods in imputation accuracy. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/joyHJL/CoFILL.
MNT-TNN: Spatiotemporal Traffic Data Imputation via Compact Multimode Nonlinear Transform-based Tensor Nuclear Norm
Mar 29, 2025Imputation of random or non-random missing data is a long-standing research topic and a crucial application for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). However, with the advent of modern communication technologies such as Global Satellite Navigation Systems (GNSS), traffic data collection has outpaced traditional methods, introducing new challenges in random missing value imputation and increasing demands for spatiotemporal dependency modelings. To address these issues, we propose a novel spatiotemporal traffic imputation method, Multimode Nonlinear Transformed Tensor Nuclear Norm (MNT-TNN), grounded in the Transform-based Tensor Nuclear Norm (TTNN) optimization framework which exhibits efficient mathematical representations and theoretical guarantees for the recovery of random missing values. Specifically, we strictly extend the single-mode transform in TTNN to a multimode transform with nonlinear activation, effectively capturing the intrinsic multimode spatiotemporal correlations and low-rankness of the traffic tensor, represented as location $\times$ location $\times$ time. To solve the nonconvex optimization problem, we design a proximal alternating minimization (PAM) algorithm with theoretical convergence guarantees. We suggest an Augmented Transform-based Tensor Nuclear Norm Families (ATTNNs) framework to enhance the imputation results of TTNN techniques, especially at very high miss rates. Extensive experiments on real datasets demonstrate that our proposed MNT-TNN and ATTNNs can outperform the compared state-of-the-art imputation methods, completing the benchmark of random missing traffic value imputation.
A Double-Norm Aggregated Tensor Latent Factorization Model for Temporal-Aware Traffic Speed Imputation
Apr 24, 2025In intelligent transportation systems (ITS), traffic management departments rely on sensors, cameras, and GPS devices to collect real-time traffic data. Traffic speed data is often incomplete due to sensor failures, data transmission delays, or occlusions, resulting in missing speed data in certain road segments. Currently, tensor decomposition based methods are extensively utilized, they mostly rely on the $L_2$-norm to construct their learning objectives, which leads to reduced robustness in the algorithms. To address this, we propose Temporal-Aware Traffic Speed Imputation (TATSI), which combines the $L_2$-norm and smooth $L_1$ (${SL}_1$)-norm in its loss function, thereby achieving both high accuracy and robust performance in imputing missing time-varying traffic speed data. TATSI adopts a single latent factor-dependent, nonnegative, and multiplicative update (SLF-NMU) approach, which serves as an efficient solver for performing nonnegative latent factor analysis (LFA) on a tensor. Empirical studies on three real-world time-varying traffic speed datasets demonstrate that, compared with state-of-the-art traffic speed predictors, TATSI more precisely captures temporal patterns, thereby yielding the most accurate imputations for missing traffic speed data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge