Zihan Gao
Tears or Cheers? Benchmarking LLMs via Culturally Elicited Distinct Affective Responses
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Culture serves as a fundamental determinant of human affective processing and profoundly shapes how individuals perceive and interpret emotional stimuli. Despite this intrinsic link extant evaluations regarding cultural alignment within Large Language Models primarily prioritize declarative knowledge such as geographical facts or established societal customs. These benchmarks remain insufficient to capture the subjective interpretative variance inherent to diverse sociocultural lenses. To address this limitation, we introduce CEDAR, a multimodal benchmark constructed entirely from scenarios capturing Culturally \underline{\textsc{E}}licited \underline{\textsc{D}}istinct \underline{\textsc{A}}ffective \underline{\textsc{R}}esponses. To construct CEDAR, we implement a novel pipeline that leverages LLM-generated provisional labels to isolate instances yielding cross-cultural emotional distinctions, and subsequently derives reliable ground-truth annotations through rigorous human evaluation. The resulting benchmark comprises 10,962 instances across seven languages and 14 fine-grained emotion categories, with each language including 400 multimodal and 1,166 text-only samples. Comprehensive evaluations of 17 representative multilingual models reveal a dissociation between language consistency and cultural alignment, demonstrating that culturally grounded affective understanding remains a significant challenge for current models.
LocalBench: Benchmarking LLMs on County-Level Local Knowledge and Reasoning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely evaluated on macro-scale geographic tasks, such as global factual recall, event summarization, and regional reasoning. Yet, their ability to handle hyper-local knowledge remains poorly understood. This gap is increasingly consequential as real-world applications, from civic platforms to community journalism, demand AI systems that can reason about neighborhood-specific dynamics, cultural narratives, and local governance. Existing benchmarks fall short in capturing this complexity, often relying on coarse-grained data or isolated references. We present LocalBench, the first benchmark designed to systematically evaluate LLMs on county-level local knowledge across the United States. Grounded in the Localness Conceptual Framework, LocalBench includes 14,782 validated question-answer pairs across 526 U.S. counties in 49 states, integrating diverse sources such as Census statistics, local subreddit discourse, and regional news. It spans physical, cognitive, and relational dimensions of locality. Using LocalBench, we evaluate 13 state-of-the-art LLMs under both closed-book and web-augmented settings. Our findings reveal critical limitations: even the best-performing models reach only 56.8% accuracy on narrative-style questions and perform below 15.5% on numerical reasoning. Moreover, larger model size and web augmentation do not guarantee better performance, for example, search improves Gemini's accuracy by +13.6%, but reduces GPT-series performance by -11.4%. These results underscore the urgent need for language models that can support equitable, place-aware AI systems: capable of engaging with the diverse, fine-grained realities of local communities across geographic and cultural contexts.
Fast and Efficient: Mask Neural Fields for 3D Scene Segmentation
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:Understanding 3D scenes is a crucial challenge in computer vision research with applications spanning multiple domains. Recent advancements in distilling 2D vision-language foundation models into neural fields, like NeRF and 3DGS, enables open-vocabulary segmentation of 3D scenes from 2D multi-view images without the need for precise 3D annotations. While effective, however, the per-pixel distillation of high-dimensional CLIP features introduces ambiguity and necessitates complex regularization strategies, adding inefficiencies during training. This paper presents MaskField, which enables fast and efficient 3D open-vocabulary segmentation with neural fields under weak supervision. Unlike previous methods, MaskField distills masks rather than dense high-dimensional CLIP features. MaskFields employ neural fields as binary mask generators and supervise them with masks generated by SAM and classified by coarse CLIP features. MaskField overcomes the ambiguous object boundaries by naturally introducing SAM segmented object shapes without extra regularization during training. By circumventing the direct handling of high-dimensional CLIP features during training, MaskField is particularly compatible with explicit scene representations like 3DGS. Our extensive experiments show that MaskField not only surpasses prior state-of-the-art methods but also achieves remarkably fast convergence, outperforming previous methods with just 5 minutes of training. We hope that MaskField will inspire further exploration into how neural fields can be trained to comprehend 3D scenes from 2D models.
Multiplane Prior Guided Few-Shot Aerial Scene Rendering
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been successfully applied in various aerial scenes, yet they face challenges with sparse views due to limited supervision. The acquisition of dense aerial views is often prohibitive, as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) may encounter constraints in perspective range and energy constraints. In this work, we introduce Multiplane Prior guided NeRF (MPNeRF), a novel approach tailored for few-shot aerial scene rendering-marking a pioneering effort in this domain. Our key insight is that the intrinsic geometric regularities specific to aerial imagery could be leveraged to enhance NeRF in sparse aerial scenes. By investigating NeRF's and Multiplane Image (MPI)'s behavior, we propose to guide the training process of NeRF with a Multiplane Prior. The proposed Multiplane Prior draws upon MPI's benefits and incorporates advanced image comprehension through a SwinV2 Transformer, pre-trained via SimMIM. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that MPNeRF outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods applied in non-aerial contexts, by tripling the performance in SSIM and LPIPS even with three views available. We hope our work offers insights into the development of NeRF-based applications in aerial scenes with limited data.
* 17 pages, 8 figures, accepted at CVPR 2024
AIM 2022 Challenge on Instagram Filter Removal: Methods and Results
Oct 17, 2022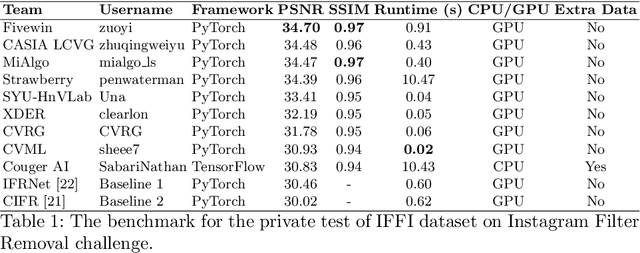

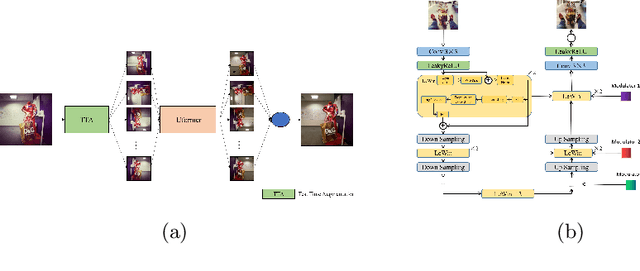
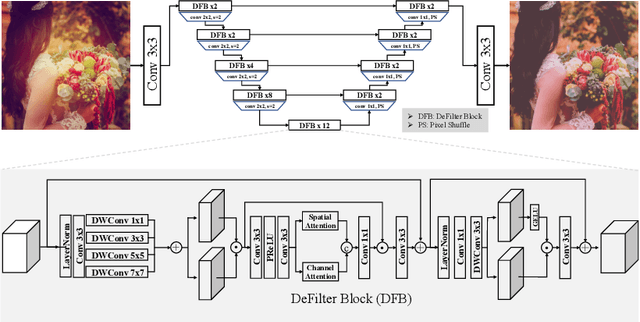
Abstract:This paper introduces the methods and the results of AIM 2022 challenge on Instagram Filter Removal. Social media filters transform the images by consecutive non-linear operations, and the feature maps of the original content may be interpolated into a different domain. This reduces the overall performance of the recent deep learning strategies. The main goal of this challenge is to produce realistic and visually plausible images where the impact of the filters applied is mitigated while preserving the content. The proposed solutions are ranked in terms of the PSNR value with respect to the original images. There are two prior studies on this task as the baseline, and a total of 9 teams have competed in the final phase of the challenge. The comparison of qualitative results of the proposed solutions and the benchmark for the challenge are presented in this report.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge