Zhonghua Wan
The Solution for Language-Enhanced Image New Category Discovery
Jul 06, 2024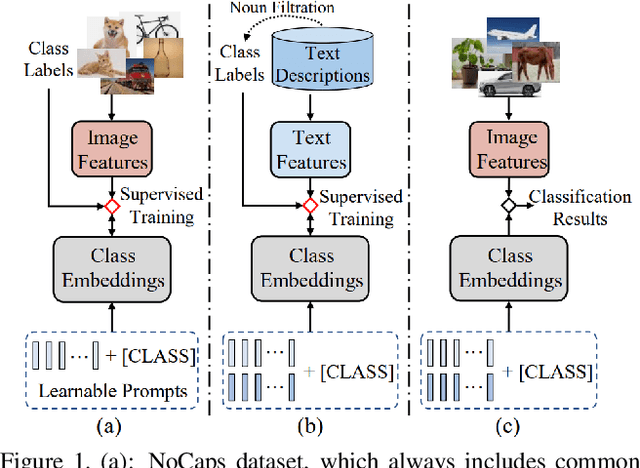
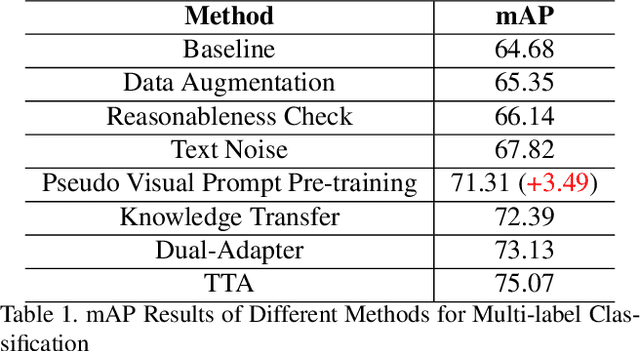
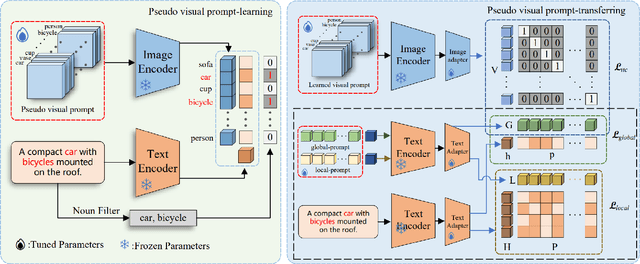
Abstract:Treating texts as images, combining prompts with textual labels for prompt tuning, and leveraging the alignment properties of CLIP have been successfully applied in zero-shot multi-label image recognition. Nonetheless, relying solely on textual labels to store visual information is insufficient for representing the diversity of visual objects. In this paper, we propose reversing the training process of CLIP and introducing the concept of Pseudo Visual Prompts. These prompts are initialized for each object category and pre-trained on large-scale, low-cost sentence data generated by large language models. This process mines the aligned visual information in CLIP and stores it in class-specific visual prompts. We then employ contrastive learning to transfer the stored visual information to the textual labels, enhancing their visual representation capacity. Additionally, we introduce a dual-adapter module that simultaneously leverages knowledge from the original CLIP and new learning knowledge derived from downstream datasets. Benefiting from the pseudo visual prompts, our method surpasses the state-of-the-art not only on clean annotated text data but also on pseudo text data generated by large language models.
The Solution for the AIGC Inference Performance Optimization Competition
Jul 06, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the rapid advancement of large-scale pre-trained language models based on transformer architectures has revolutionized natural language processing tasks. Among these, ChatGPT has gained widespread popularity, demonstrating human-level conversational abilities and attracting over 100 million monthly users by late 2022. Concurrently, Baidu's commercial deployment of the Ernie Wenxin model has significantly enhanced marketing effectiveness through AI-driven technologies. This paper focuses on optimizing high-performance inference for Ernie models, emphasizing GPU acceleration and leveraging the Paddle inference framework. We employ techniques such as Faster Transformer for efficient model processing, embedding layer pruning to reduce computational overhead, and FP16 half-precision inference for enhanced computational efficiency. Additionally, our approach integrates efficient data handling strategies using multi-process parallel processing to minimize latency. Experimental results demonstrate that our optimized solution achieves up to an 8.96x improvement in inference speed compared to standard methods, while maintaining competitive performance.
The Solution for the 5th GCAIAC Zero-shot Referring Expression Comprehension Challenge
Jul 06, 2024Abstract:This report presents a solution for the zero-shot referring expression comprehension task. Visual-language multimodal base models (such as CLIP, SAM) have gained significant attention in recent years as a cornerstone of mainstream research. One of the key applications of multimodal base models lies in their ability to generalize to zero-shot downstream tasks. Unlike traditional referring expression comprehension, zero-shot referring expression comprehension aims to apply pre-trained visual-language models directly to the task without specific training. Recent studies have enhanced the zero-shot performance of multimodal base models in referring expression comprehension tasks by introducing visual prompts. To address the zero-shot referring expression comprehension challenge, we introduced a combination of visual prompts and considered the influence of textual prompts, employing joint prediction tailored to the data characteristics. Ultimately, our approach achieved accuracy rates of 84.825 on the A leaderboard and 71.460 on the B leaderboard, securing the first position.
The Solution for the sequential task continual learning track of the 2nd Greater Bay Area International Algorithm Competition
Jul 06, 2024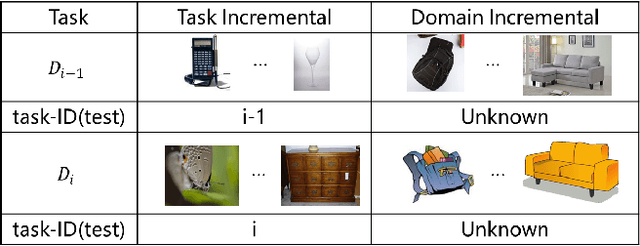
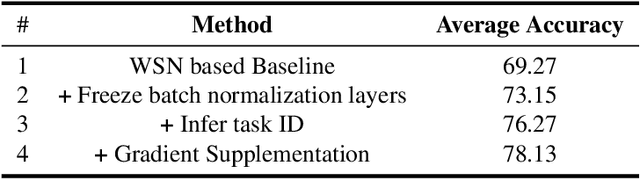
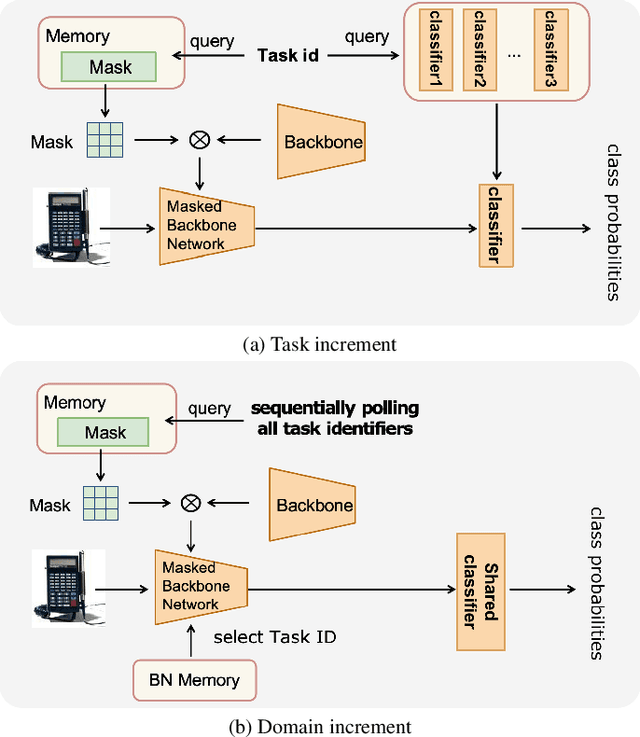
Abstract:This paper presents a data-free, parameter-isolation-based continual learning algorithm we developed for the sequential task continual learning track of the 2nd Greater Bay Area International Algorithm Competition. The method learns an independent parameter subspace for each task within the network's convolutional and linear layers and freezes the batch normalization layers after the first task. Specifically, for domain incremental setting where all domains share a classification head, we freeze the shared classification head after first task is completed, effectively solving the issue of catastrophic forgetting. Additionally, facing the challenge of domain incremental settings without providing a task identity, we designed an inference task identity strategy, selecting an appropriate mask matrix for each sample. Furthermore, we introduced a gradient supplementation strategy to enhance the importance of unselected parameters for the current task, facilitating learning for new tasks. We also implemented an adaptive importance scoring strategy that dynamically adjusts the amount of parameters to optimize single-task performance while reducing parameter usage. Moreover, considering the limitations of storage space and inference time, we designed a mask matrix compression strategy to save storage space and improve the speed of encryption and decryption of the mask matrix. Our approach does not require expanding the core network or using external auxiliary networks or data, and performs well under both task incremental and domain incremental settings. This solution ultimately won a second-place prize in the competition.
RCDN -- Robust X-Corner Detection Algorithm based on Advanced CNN Model
Jul 07, 2023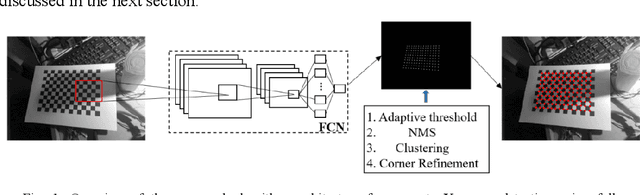
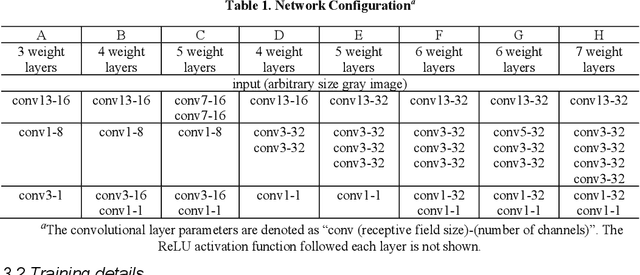
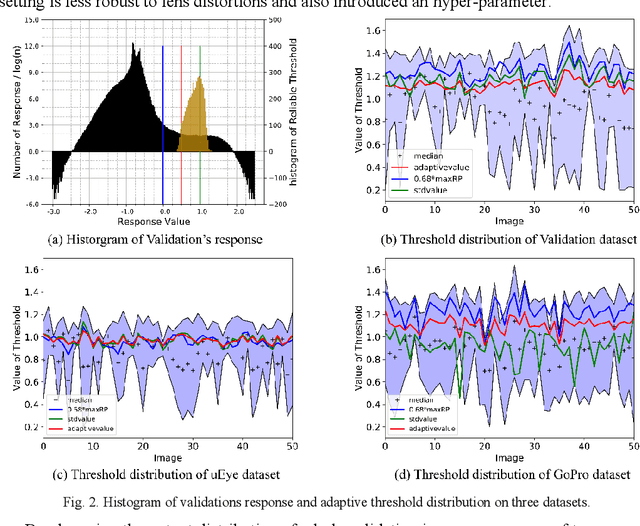

Abstract:Accurate detection and localization of X-corner on both planar and non-planar patterns is a core step in robotics and machine vision. However, previous works could not make a good balance between accuracy and robustness, which are both crucial criteria to evaluate the detectors performance. To address this problem, in this paper we present a novel detection algorithm which can maintain high sub-pixel precision on inputs under multiple interference, such as lens distortion, extreme poses and noise. The whole algorithm, adopting a coarse-to-fine strategy, contains a X-corner detection network and three post-processing techniques to distinguish the correct corner candidates, as well as a mixed sub-pixel refinement technique and an improved region growth strategy to recover the checkerboard pattern partially visible or occluded automatically. Evaluations on real and synthetic images indicate that the presented algorithm has the higher detection rate, sub-pixel accuracy and robustness than other commonly used methods. Finally, experiments of camera calibration and pose estimation verify it can also get smaller re-projection error in quantitative comparisons to the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge