Zhiquan Liu
Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
Osmosis Distillation: Model Hijacking with the Fewest Samples
Mar 05, 2026Abstract:Transfer learning is devised to leverage knowledge from pre-trained models to solve new tasks with limited data and computational resources. Meanwhile, dataset distillation has emerged to synthesize a compact dataset that preserves critical information from the original large dataset. Therefore, a combination of transfer learning and dataset distillation offers promising performance in evaluations. However, a non-negligible security threat remains undiscovered in transfer learning using synthetic datasets generated by dataset distillation methods, where an adversary can perform a model hijacking attack with only a few poisoned samples in the synthetic dataset. To reveal this threat, we propose Osmosis Distillation (OD) attack, a novel model hijacking strategy that targets deep learning models using the fewest samples. Comprehensive evaluations on various datasets demonstrate that the OD attack attains high attack success rates in hidden tasks while preserving high model utility in original tasks. Furthermore, the distilled osmosis set enables model hijacking across diverse model architectures, allowing model hijacking in transfer learning with considerable attack performance and model utility. We argue that awareness of using third-party synthetic datasets in transfer learning must be raised.
AgentSentry: Mitigating Indirect Prompt Injection in LLM Agents via Temporal Causal Diagnostics and Context Purification
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) agents increasingly rely on external tools and retrieval systems to autonomously complete complex tasks. However, this design exposes agents to indirect prompt injection (IPI), where attacker-controlled context embedded in tool outputs or retrieved content silently steers agent actions away from user intent. Unlike prompt-based attacks, IPI unfolds over multi-turn trajectories, making malicious control difficult to disentangle from legitimate task execution. Existing inference-time defenses primarily rely on heuristic detection and conservative blocking of high-risk actions, which can prematurely terminate workflows or broadly suppress tool usage under ambiguous multi-turn scenarios. We propose AgentSentry, a novel inference-time detection and mitigation framework for tool-augmented LLM agents. To the best of our knowledge, AgentSentry is the first inference-time defense to model multi-turn IPI as a temporal causal takeover. It localizes takeover points via controlled counterfactual re-executions at tool-return boundaries and enables safe continuation through causally guided context purification that removes attack-induced deviations while preserving task-relevant evidence. We evaluate AgentSentry on the \textsc{AgentDojo} benchmark across four task suites, three IPI attack families, and multiple black-box LLMs. AgentSentry eliminates successful attacks and maintains strong utility under attack, achieving an average Utility Under Attack (UA) of 74.55 %, improving UA by 20.8 to 33.6 percentage points over the strongest baselines without degrading benign performance.
Noise-Aware and Dynamically Adaptive Federated Defense Framework for SAR Image Target Recognition
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:As a critical application of computational intelligence in remote sensing, deep learning-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image target recognition facilitates intelligent perception but typically relies on centralized training, where multi-source SAR data are uploaded to a single server, raising privacy and security concerns. Federated learning (FL) provides an emerging computational intelligence paradigm for SAR image target recognition, enabling cross-site collaboration while preserving local data privacy. However, FL confronts critical security risks, where malicious clients can exploit SAR's multiplicative speckle noise to conceal backdoor triggers, severely challenging the robustness of the computational intelligence model. To address this challenge, we propose NADAFD, a noise-aware and dynamically adaptive federated defense framework that integrates frequency-domain, spatial-domain, and client-behavior analyses to counter SAR-specific backdoor threats. Specifically, we introduce a frequency-domain collaborative inversion mechanism to expose cross-client spectral inconsistencies indicative of hidden backdoor triggers. We further design a noise-aware adversarial training strategy that embeds $Γ$-distributed speckle characteristics into mask-guided adversarial sample generation to enhance robustness against both backdoor attacks and SAR speckle noise. In addition, we present a dynamic health assessment module that tracks client update behaviors across training rounds and adaptively adjusts aggregation weights to mitigate evolving malicious contributions. Experiments on MSTAR and OpenSARShip datasets demonstrate that NADAFD achieves higher accuracy on clean test samples and a lower backdoor attack success rate on triggered inputs than existing federated backdoor defenses for SAR target recognition.
GraphEdge: Dynamic Graph Partition and Task Scheduling for GNNs Computing in Edge Network
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:With the exponential growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, edge computing (EC) is gradually playing an important role in providing cost-effective services. However, existing approaches struggle to perform well in graph-structured scenarios where user data is correlated, such as traffic flow prediction and social relationship recommender systems. In particular, graph neural network (GNN)-based approaches lead to expensive server communication cost. To address this problem, we propose GraphEdge, an efficient GNN-based EC architecture. It considers the EC system of GNN tasks, where there are associations between users and it needs to take into account the task data of its neighbors when processing the tasks of a user. Specifically, the architecture first perceives the user topology and represents their data associations as a graph layout at each time step. Then the graph layout is optimized by calling our proposed hierarchical traversal graph cut algorithm (HiCut), which cuts the graph layout into multiple weakly associated subgraphs based on the aggregation characteristics of GNN, and the communication cost between different subgraphs during GNN inference is minimized. Finally, based on the optimized graph layout, our proposed deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based graph offloading algorithm (DRLGO) is executed to obtain the optimal offloading strategy for the tasks of users, the offloading strategy is subgraph-based, it tries to offload user tasks in a subgraph to the same edge server as possible while minimizing the task processing time and energy consumption of the EC system. Experimental results show the good effectiveness and dynamic adaptation of our proposed architecture and it also performs well even in dynamic scenarios.
AdaSin: Enhancing Hard Sample Metrics with Dual Adaptive Penalty for Face Recognition
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:In recent years, the emergence of deep convolutional neural networks has positioned face recognition as a prominent research focus in computer vision. Traditional loss functions, such as margin-based, hard-sample mining-based, and hybrid approaches, have achieved notable performance improvements, with some leveraging curriculum learning to optimize training. However, these methods often fall short in effectively quantifying the difficulty of hard samples. To address this, we propose Adaptive Sine (AdaSin) loss function, which introduces the sine of the angle between a sample's embedding feature and its ground-truth class center as a novel difficulty metric. This metric enables precise and effective penalization of hard samples. By incorporating curriculum learning, the model dynamically adjusts classification boundaries across different training stages. Unlike previous adaptive-margin loss functions, AdaSin introduce a dual adaptive penalty, applied to both the positive and negative cosine similarities of hard samples. This design imposes stronger constraints, enhancing intra-class compactness and inter-class separability. The combination of the dual adaptive penalty and curriculum learning is guided by a well-designed difficulty metric. It enables the model to focus more effectively on hard samples in later training stages, and lead to the extraction of highly discriminative face features. Extensive experiments across eight benchmarks demonstrate that AdaSin achieves superior accuracy compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
RVAFM: Re-parameterizing Vertical Attention Fusion Module for Handwritten Paragraph Text Recognition
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Handwritten Paragraph Text Recognition (HPTR) is a challenging task in Computer Vision, requiring the transformation of a paragraph text image, rich in handwritten text, into text encoding sequences. One of the most advanced models for this task is Vertical Attention Network (VAN), which utilizes a Vertical Attention Module (VAM) to implicitly segment paragraph text images into text lines, thereby reducing the difficulty of the recognition task. However, from a network structure perspective, VAM is a single-branch module, which is less effective in learning compared to multi-branch modules. In this paper, we propose a new module, named Re-parameterizing Vertical Attention Fusion Module (RVAFM), which incorporates structural re-parameterization techniques. RVAFM decouples the structure of the module during training and inference stages. During training, it uses a multi-branch structure for more effective learning, and during inference, it uses a single-branch structure for faster processing. The features learned by the multi-branch structure are fused into the single-branch structure through a special fusion method named Re-parameterization Fusion (RF) without any loss of information. As a result, we achieve a Character Error Rate (CER) of 4.44% and a Word Error Rate (WER) of 14.37% on the IAM paragraph-level test set. Additionally, the inference speed is slightly faster than VAN.
HNCSE: Advancing Sentence Embeddings via Hybrid Contrastive Learning with Hard Negatives
Nov 19, 2024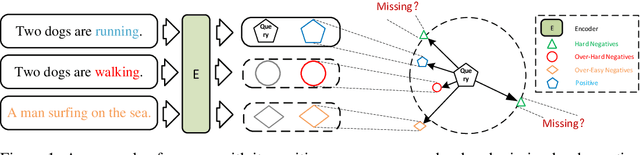
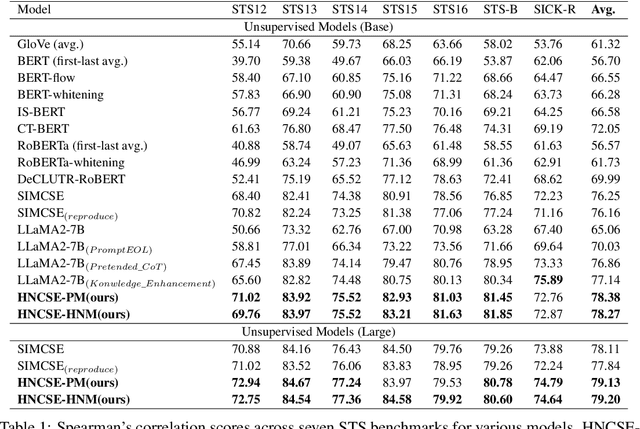
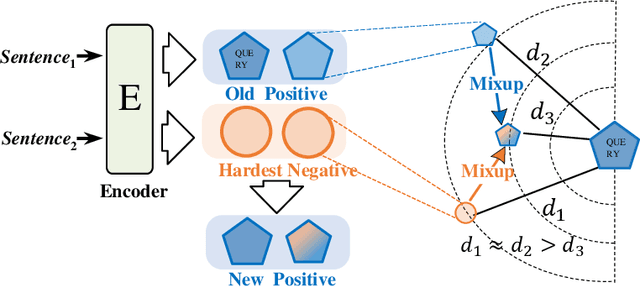
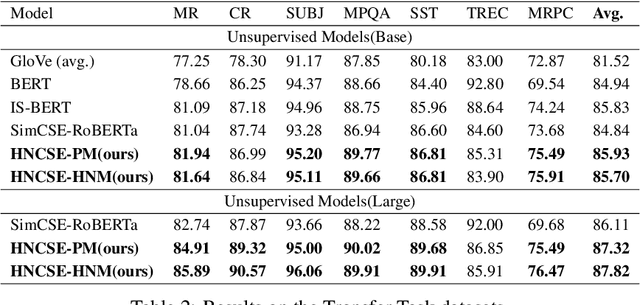
Abstract:Unsupervised sentence representation learning remains a critical challenge in modern natural language processing (NLP) research. Recently, contrastive learning techniques have achieved significant success in addressing this issue by effectively capturing textual semantics. Many such approaches prioritize the optimization using negative samples. In fields such as computer vision, hard negative samples (samples that are close to the decision boundary and thus more difficult to distinguish) have been shown to enhance representation learning. However, adapting hard negatives to contrastive sentence learning is complex due to the intricate syntactic and semantic details of text. To address this problem, we propose HNCSE, a novel contrastive learning framework that extends the leading SimCSE approach. The hallmark of HNCSE is its innovative use of hard negative samples to enhance the learning of both positive and negative samples, thereby achieving a deeper semantic understanding. Empirical tests on semantic textual similarity and transfer task datasets validate the superiority of HNCSE.
VSRQ: Quantitative Assessment Method for Safety Risk of Vehicle Intelligent Connected System
May 03, 2023



Abstract:The field of intelligent connected in modern vehicles continues to expand, and the functions of vehicles become more and more complex with the development of the times. This has also led to an increasing number of vehicle vulnerabilities and many safety issues. Therefore, it is particularly important to identify high-risk vehicle intelligent connected systems, because it can inform security personnel which systems are most vulnerable to attacks, allowing them to conduct more thorough inspections and tests. In this paper, we develop a new model for vehicle risk assessment by combining I-FAHP with FCA clustering: VSRQ model. We extract important indicators related to vehicle safety, use fuzzy cluster analys (FCA) combined with fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) to mine the vulnerable components of the vehicle intelligent connected system, and conduct priority testing on vulnerable components to reduce risks and ensure vehicle safety. We evaluate the model on OpenPilot and experimentally demonstrate the effectiveness of the VSRQ model in identifying the safety of vehicle intelligent connected systems. The experiment fully complies with ISO 26262 and ISO/SAE 21434 standards, and our model has a higher accuracy rate than other models. These results provide a promising new research direction for predicting the security risks of vehicle intelligent connected systems and provide typical application tasks for VSRQ. The experimental results show that the accuracy rate is 94.36%, and the recall rate is 73.43%, which is at least 14.63% higher than all other known indicators.
EViT: Privacy-Preserving Image Retrieval via Encrypted Vision Transformer in Cloud Computing
Aug 31, 2022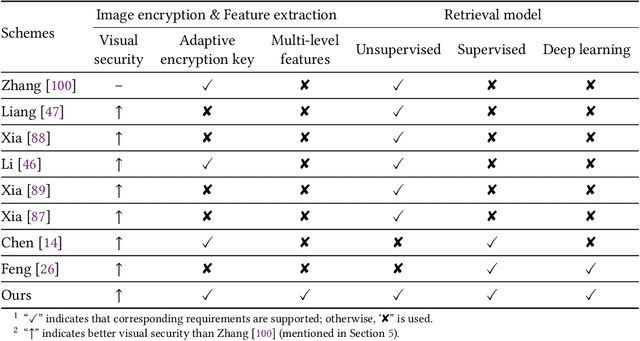


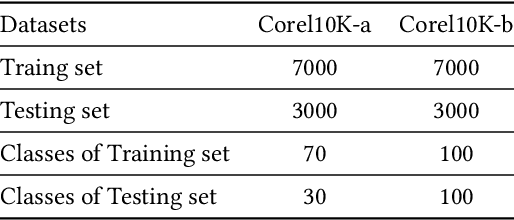
Abstract:Image retrieval systems help users to browse and search among extensive images in real-time. With the rise of cloud computing, retrieval tasks are usually outsourced to cloud servers. However, the cloud scenario brings a daunting challenge of privacy protection as cloud servers cannot be fully trusted. To this end, image-encryption-based privacy-preserving image retrieval schemes have been developed, which first extract features from cipher-images, and then build retrieval models based on these features. Yet, most existing approaches extract shallow features and design trivial retrieval models, resulting in insufficient expressiveness for the cipher-images. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm named Encrypted Vision Transformer (EViT), which advances the discriminative representations capability of cipher-images. First, in order to capture comprehensive ruled information, we extract multi-level local length sequence and global Huffman-code frequency features from the cipher-images which are encrypted by stream cipher during JPEG compression process. Second, we design the Vision Transformer-based retrieval model to couple with the multi-level features, and propose two adaptive data augmentation methods to improve representation power of the retrieval model. Our proposal can be easily adapted to unsupervised and supervised settings via self-supervised contrastive learning manner. Extensive experiments reveal that EViT achieves both excellent encryption and retrieval performance, outperforming current schemes in terms of retrieval accuracy by large margins while protecting image privacy effectively. Code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/onlinehuazai/EViT}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge