Zhihai Bi
ALORE: Autonomous Large-Object Rearrangement with a Legged Manipulator
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Endowing robots with the ability to rearrange various large and heavy objects, such as furniture, can substantially alleviate human workload. However, this task is extremely challenging due to the need to interact with diverse objects and efficiently rearrange multiple objects in complex environments while ensuring collision-free loco-manipulation. In this work, we present ALORE, an autonomous large-object rearrangement system for a legged manipulator that can rearrange various large objects across diverse scenarios. The proposed system is characterized by three main features: (i) a hierarchical reinforcement learning training pipeline for multi-object environment learning, where a high-level object velocity controller is trained on top of a low-level whole-body controller to achieve efficient and stable joint learning across multiple objects; (ii) two key modules, a unified interaction configuration representation and an object velocity estimator, that allow a single policy to regulate planar velocity of diverse objects accurately; and (iii) a task-and-motion planning framework that jointly optimizes object visitation order and object-to-target assignment, improving task efficiency while enabling online replanning. Comparisons against strong baselines show consistent superiority in policy generalization, object-velocity tracking accuracy, and multi-object rearrangement efficiency. Key modules are systematically evaluated, and extensive simulations and real-world experiments are conducted to validate the robustness and effectiveness of the entire system, which successfully completes 8 continuous loops to rearrange 32 chairs over nearly 40 minutes without a single failure, and executes long-distance autonomous rearrangement over an approximately 40 m route. The open-source packages are available at https://zhihaibi.github.io/Alore/.
Fast and Safe Trajectory Optimization for Mobile Manipulators With Neural Configuration Space Distance Field
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Mobile manipulators promise agile, long-horizon behavior by coordinating base and arm motion, yet whole-body trajectory optimization in cluttered, confined spaces remains difficult due to high-dimensional nonconvexity and the need for fast, accurate collision reasoning. Configuration Space Distance Fields (CDF) enable fixed-base manipulators to model collisions directly in configuration space via smooth, implicit distances. This representation holds strong potential to bypass the nonlinear configuration-to-workspace mapping while preserving accurate whole-body geometry and providing optimization-friendly collision costs. Yet, extending this capability to mobile manipulators is hindered by unbounded workspaces and tighter base-arm coupling. We lift this promise to mobile manipulation with Generalized Configuration Space Distance Fields (GCDF), extending CDF to robots with both translational and rotational joints in unbounded workspaces with tighter base-arm coupling. We prove that GCDF preserves Euclidean-like local distance structure and accurately encodes whole-body geometry in configuration space, and develop a data generation and training pipeline that yields continuous neural GCDFs with accurate values and gradients, supporting efficient GPU-batched queries. Building on this representation, we develop a high-performance sequential convex optimization framework centered on GCDF-based collision reasoning. The solver scales to large numbers of implicit constraints through (i) online specification of neural constraints, (ii) sparsity-aware active-set detection with parallel batched evaluation across thousands of constraints, and (iii) incremental constraint management for rapid replanning under scene changes.
Online Trajectory Optimization for Arbitrary-Shaped Mobile Robots via Polynomial Separating Hypersurfaces
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:An emerging class of trajectory optimization methods enforces collision avoidance by jointly optimizing the robot's configuration and a separating hyperplane. However, as linear separators only apply to convex sets, these methods require convex approximations of both the robot and obstacles, which becomes an overly conservative assumption in cluttered and narrow environments. In this work, we unequivocally remove this limitation by introducing nonlinear separating hypersurfaces parameterized by polynomial functions. We first generalize the classical separating hyperplane theorem and prove that any two disjoint bounded closed sets in Euclidean space can be separated by a polynomial hypersurface, serving as the theoretical foundation for nonlinear separation of arbitrary geometries. Building on this result, we formulate a nonlinear programming (NLP) problem that jointly optimizes the robot's trajectory and the coefficients of the separating polynomials, enabling geometry-aware collision avoidance without conservative convex simplifications. The optimization remains efficiently solvable using standard NLP solvers. Simulation and real-world experiments with nonconvex robots demonstrate that our method achieves smooth, collision-free, and agile maneuvers in environments where convex-approximation baselines fail.
FLORES: A Reconfigured Wheel-Legged Robot for Enhanced Steering and Adaptability
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Wheel-legged robots integrate the agility of legs for navigating rough terrains while harnessing the efficiency of wheels for smooth surfaces. However, most existing designs do not fully capitalize on the benefits of both legged and wheeled structures, which limits overall system flexibility and efficiency. We present FLORES (reconfigured wheel-legged robot for enhanced steering and adaptability), a novel wheel-legged robot design featuring a distinctive front-leg configuration that sets it beyond standard design approaches. Specifically, FLORES replaces the conventional hip-roll degree of freedom (DoF) of the front leg with hip-yaw DoFs, and this allows for efficient movement on flat surfaces while ensuring adaptability when navigating complex terrains. This innovative design facilitates seamless transitions between different locomotion modes (i.e., legged locomotion and wheeled locomotion) and optimizes the performance across varied environments. To fully exploit FLORES's mechanical capabilities, we develop a tailored reinforcement learning (RL) controller that adapts the Hybrid Internal Model (HIM) with a customized reward structure optimized for our unique mechanical configuration. This framework enables the generation of adaptive, multi-modal locomotion strategies that facilitate smooth transitions between wheeled and legged movements. Furthermore, our distinctive joint design enables the robot to exhibit novel and highly efficient locomotion gaits that capitalize on the synergistic advantages of both locomotion modes. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate FLORES's enhanced steering capabilities, improved navigation efficiency, and versatile locomotion across various terrains. The open-source project can be found at https://github.com/ZhichengSong6/FLORES-A-Reconfigured-Wheel-Legged-Robot-for-Enhanced-Steering-and-Adaptability.git.
Interactive Navigation for Legged Manipulators with Learned Arm-Pushing Controller
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Interactive navigation is crucial in scenarios where proactively interacting with objects can yield shorter paths, thus significantly improving traversal efficiency. Existing methods primarily focus on using the robot body to relocate large obstacles (which could be comparable to the size of a robot). However, they prove ineffective in narrow or constrained spaces where the robot's dimensions restrict its manipulation capabilities. This paper introduces a novel interactive navigation framework for legged manipulators, featuring an active arm-pushing mechanism that enables the robot to reposition movable obstacles in space-constrained environments. To this end, we develop a reinforcement learning-based arm-pushing controller with a two-stage reward strategy for large-object manipulation. Specifically, this strategy first directs the manipulator to a designated pushing zone to achieve a kinematically feasible contact configuration. Then, the end effector is guided to maintain its position at appropriate contact points for stable object displacement while preventing toppling. The simulations validate the robustness of the arm-pushing controller, showing that the two-stage reward strategy improves policy convergence and long-term performance. Real-world experiments further demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed navigation framework, which achieves shorter paths and reduced traversal time. The open-source project can be found at https://github.com/Zhihaibi/Interactive-Navigation-for-legged-manipulator.git.
Local Reactive Control for Mobile Manipulators with Whole-Body Safety in Complex Environments
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Mobile manipulators typically encounter significant challenges in navigating narrow, cluttered environments due to their high-dimensional state spaces and complex kinematics. While reactive methods excel in dynamic settings, they struggle to efficiently incorporate complex, coupled constraints across the entire state space. In this work, we present a novel local reactive controller that reformulates the time-domain single-step problem into a multi-step optimization problem in the spatial domain, leveraging the propagation of a serial kinematic chain. This transformation facilitates the formulation of customized, decoupled link-specific constraints, which is further solved efficiently with augmented Lagrangian differential dynamic programming (AL-DDP). Our approach naturally absorbs spatial kinematic propagation in the forward pass and processes all link-specific constraints simultaneously during the backward pass, enhancing both constraint management and computational efficiency. Notably, in this framework, we formulate collision avoidance constraints for each link using accurate geometric models with extracted free regions, and this improves the maneuverability of the mobile manipulator in narrow, cluttered spaces. Experimental results showcase significant improvements in safety, efficiency, and task completion rates. These findings underscore the robustness of the proposed method, particularly in narrow, cluttered environments where conventional approaches could falter. The open-source project can be found at https://github.com/Chunx1nZHENG/MM-with-Whole-Body-Safety-Release.git.
FRTree Planner: Robot Navigation in Cluttered and Unknown Environments with Tree of Free Regions
Oct 26, 2024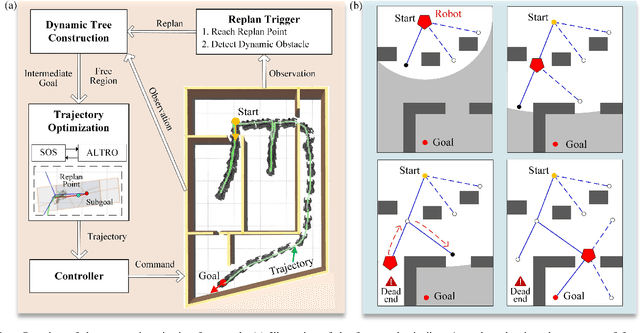
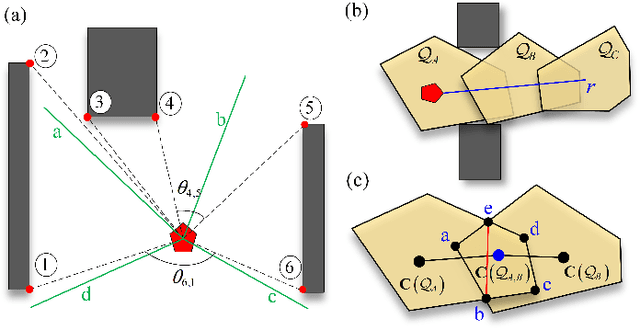
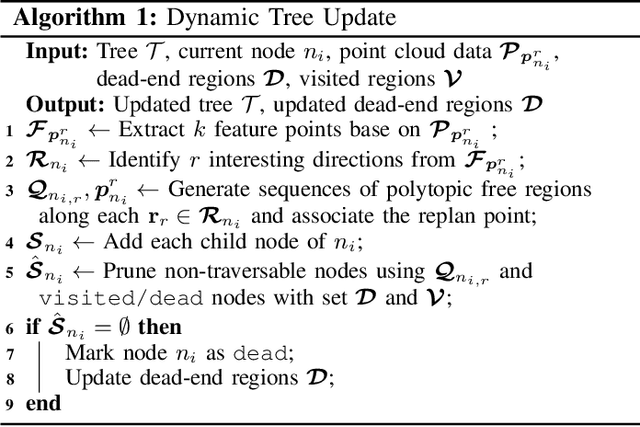
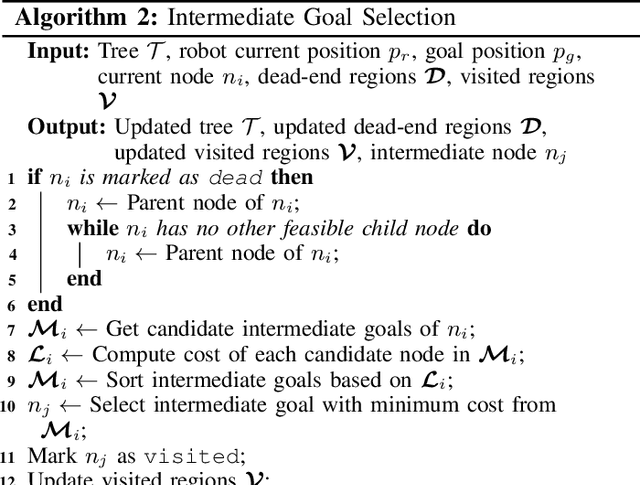
Abstract:In this work, we present FRTree planner, a novel robot navigation framework that leverages a tree structure of free regions, specifically designed for navigation in cluttered and unknown environments with narrow passages. The framework continuously incorporates real-time perceptive information to identify distinct navigation options and dynamically expands the tree toward explorable and traversable directions. This dynamically constructed tree incrementally encodes the geometric and topological information of the collision-free space, enabling efficient selection of the intermediate goals, navigating around dead-end situations, and avoidance of dynamic obstacles without a prior map. Crucially, our method performs a comprehensive analysis of the geometric relationship between free regions and the robot during online replanning. In particular, the planner assesses the accessibility of candidate passages based on the robot's geometries, facilitating the effective selection of the most viable intermediate goals through accessible narrow passages while minimizing unnecessary detours. By combining the free region information with a bi-level trajectory optimization tailored for robots with specific geometries, our approach generates robust and adaptable obstacle avoidance strategies in confined spaces. Through extensive simulations and real-world experiments, FRTree demonstrates its superiority over benchmark methods in generating safe, efficient motion plans through highly cluttered and unknown terrains with narrow gaps.
Dynamic models for Planar Peristaltic Locomotion of a Metameric Earthworm-like Robot
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:The development of versatile robots capable of traversing challenging and irregular environments is of increasing interest in the field of robotics, and metameric robots have been identified as a promising solution due to their slender, deformable bodies. Inspired by the effective locomotion of earthworms, earthworm-like robots capable of both rectilinear and planar locomotion have been designed and prototyped. While much research has focused on developing kinematic models to describe the planar locomotion of earthworm-like robots, the authors argue that the development of dynamic models is critical to improving the accuracy and efficiency of these robots. A comprehensive analysis of the dynamics of a metameric earthworm-like robot capable of planar motion is presented in this work. The model takes into account the complex interactions between the robot's deformable body and the forces acting on it and draws on the methods previously used to develop mathematical models of snake-like robots. The proposed model represents a significant advancement in the field of metameric robotics and has the potential to enhance the performance of earthworm-like robots in a variety of challenging environments, such as underground pipes and tunnels, and serves as a foundation for future research into the dynamics of soft-bodied robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge