Zhigang Zhang
MacFormer: Map-Agent Coupled Transformer for Real-time and Robust Trajectory Prediction
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:Predicting the future behavior of agents is a fundamental task in autonomous vehicle domains. Accurate prediction relies on comprehending the surrounding map, which significantly regularizes agent behaviors. However, existing methods have limitations in exploiting the map and exhibit a strong dependence on historical trajectories, which yield unsatisfactory prediction performance and robustness. Additionally, their heavy network architectures impede real-time applications. To tackle these problems, we propose Map-Agent Coupled Transformer (MacFormer) for real-time and robust trajectory prediction. Our framework explicitly incorporates map constraints into the network via two carefully designed modules named coupled map and reference extractor. A novel multi-task optimization strategy (MTOS) is presented to enhance learning of topology and rule constraints. We also devise bilateral query scheme in context fusion for a more efficient and lightweight network. We evaluated our approach on Argoverse 1, Argoverse 2, and nuScenes real-world benchmarks, where it all achieved state-of-the-art performance with the lowest inference latency and smallest model size. Experiments also demonstrate that our framework is resilient to imperfect tracklet inputs. Furthermore, we show that by combining with our proposed strategies, classical models outperform their baselines, further validating the versatility of our framework.
TENET: Transformer Encoding Network for Effective Temporal Flow on Motion Prediction
Jun 30, 2022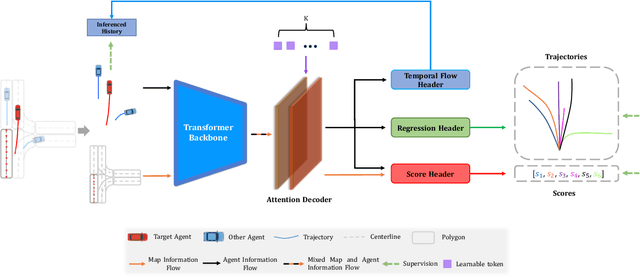
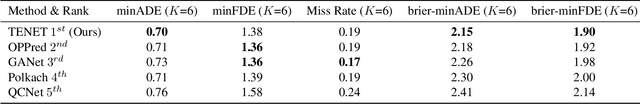
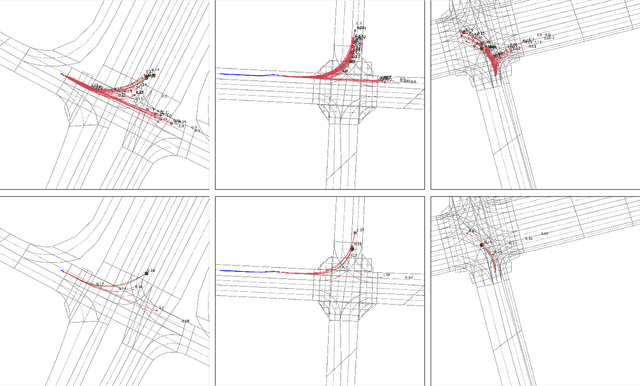
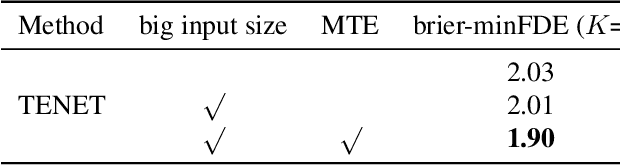
Abstract:This technical report presents an effective method for motion prediction in autonomous driving. We develop a Transformer-based method for input encoding and trajectory prediction. Besides, we propose the Temporal Flow Header to enhance the trajectory encoding. In the end, an efficient K-means ensemble method is used. Using our Transformer network and ensemble method, we win the first place of Argoverse 2 Motion Forecasting Challenge with the state-of-the-art brier-minFDE score of 1.90.
Accelerating Prostate Diffusion Weighted MRI using Guided Denoising Convolutional Neural Network: Retrospective Feasibility Study
Jun 30, 2020


Abstract:Purpose: To investigate feasibility of accelerating prostate diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) by reducing the number of acquired averages and denoising the resulting image using a proposed guided denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN). Materials and Methods: Raw data from the prostate DWI scans were retrospectively gathered (between July 2018 and July 2019) from six single-vendor MRI scanners. 118 data sets were used for training and validation (age: 64.3 +- 8 years) and 37 - for testing (age: 65.1 +- 7.3 years). High b-value diffusion-weighted (hb-DW) data were reconstructed into noisy images using two averages and reference images using all sixteen averages. A conventional DnCNN was modified into a guided DnCNN, which uses the low b-value DWI image as a guidance input. Quantitative and qualitative reader evaluations were performed on the denoised hb-DW images. A cumulative link mixed regression model was used to compare the readers scores. The agreement between the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps (denoised vs reference) was analyzed using Bland Altman analysis. Results: Compared to the DnCNN, the guided DnCNN produced denoised hb-DW images with higher peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity index and lower normalized mean square error (p < 0.001). Compared to the reference images, the denoised images received higher image quality scores (p < 0.0001). The ADC values based on the denoised hb-DW images were in good agreement with the reference ADC values. Conclusion: Accelerating prostate DWI by reducing the number of acquired averages and denoising the resulting image using the proposed guided DnCNN is technically feasible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge