Ricardo Otazo
Development of a Clinical Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer MR fingerprinting (CEST-MRF) Pulse Sequence and Reconstruction for Brain Tumor Quantification
Aug 18, 2021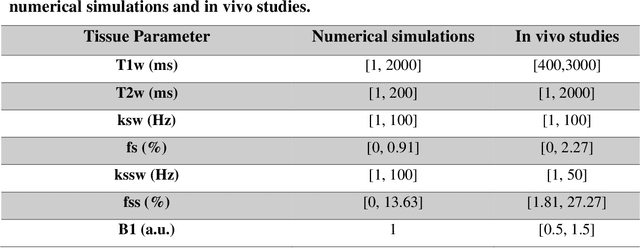



Abstract:Purpose: To develop a clinical chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance fingerprinting (CEST-MRF) pulse sequence and reconstruction method. Methods: The CEST-MRF pulse sequence was modified to conform to hardware limits on clinical scanners while keeping scan time $\leqslant$ 2 minutes. The measured data was reconstructed using a deep reconstruction network (DRONE) to yield the water relaxation and chemical exchange parameters. The feasibility of the 6 parameter DRONE reconstruction was tested in simulations in a digital brain phantom. A healthy subject was scanned with the CEST-MRF sequence and a conventional MRF sequence for comparison. The reproducibility was assessed via test-retest experiments and the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) calculated for white matter (WM) and grey matter (GM). The clinical utility of CEST-MRF was demonstrated in a brain metastasis patient in comparison to standard clinical imaging sequences. The tumor was segmented into edema, solid core and necrotic core regions and the CEST-MRF values compared to the contra-lateral side. Results: The 6 parameter DRONE reconstruction of the digital phantom yielded a mean absolute error of $\leqslant$ 6% for all parameters. The CEST-MRF parameters were in good agreement with those from a conventional MRF sequence and previous studies in the literature. The mean CCC for all 6 parameters was 0.79$\pm$0.02 in WM and 0.63$\pm$0.03 in GM. The CEST-MRF values in nearly all tumor regions were significantly different (p=0.001) from each other and the contra-lateral side. Conclusion: The clinical CEST-MRF sequence provides a method for fast simultaneous quantification of multiple tissue parameters in pathologies.
Accelerating Prostate Diffusion Weighted MRI using Guided Denoising Convolutional Neural Network: Retrospective Feasibility Study
Jun 30, 2020


Abstract:Purpose: To investigate feasibility of accelerating prostate diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) by reducing the number of acquired averages and denoising the resulting image using a proposed guided denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN). Materials and Methods: Raw data from the prostate DWI scans were retrospectively gathered (between July 2018 and July 2019) from six single-vendor MRI scanners. 118 data sets were used for training and validation (age: 64.3 +- 8 years) and 37 - for testing (age: 65.1 +- 7.3 years). High b-value diffusion-weighted (hb-DW) data were reconstructed into noisy images using two averages and reference images using all sixteen averages. A conventional DnCNN was modified into a guided DnCNN, which uses the low b-value DWI image as a guidance input. Quantitative and qualitative reader evaluations were performed on the denoised hb-DW images. A cumulative link mixed regression model was used to compare the readers scores. The agreement between the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps (denoised vs reference) was analyzed using Bland Altman analysis. Results: Compared to the DnCNN, the guided DnCNN produced denoised hb-DW images with higher peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity index and lower normalized mean square error (p < 0.001). Compared to the reference images, the denoised images received higher image quality scores (p < 0.0001). The ADC values based on the denoised hb-DW images were in good agreement with the reference ADC values. Conclusion: Accelerating prostate DWI by reducing the number of acquired averages and denoising the resulting image using the proposed guided DnCNN is technically feasible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge