Zheyuan Bai
and Other Contributors
MoRAgent: Parameter Efficient Agent Tuning with Mixture-of-Roles
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Despite recent advancements of fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) to facilitate agent tasks, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methodologies for agent remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce three key strategies for PEFT in agent tasks: 1) Inspired by the increasingly dominant Reason+Action paradigm, we first decompose the capabilities necessary for the agent tasks into three distinct roles: reasoner, executor, and summarizer. The reasoner is responsible for comprehending the user's query and determining the next role based on the execution trajectory. The executor is tasked with identifying the appropriate functions and parameters to invoke. The summarizer conveys the distilled information from conversations back to the user. 2) We then propose the Mixture-of-Roles (MoR) framework, which comprises three specialized Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) groups, each designated to fulfill a distinct role. By focusing on their respective specialized capabilities and engaging in collaborative interactions, these LoRAs collectively accomplish the agent task. 3) To effectively fine-tune the framework, we develop a multi-role data generation pipeline based on publicly available datasets, incorporating role-specific content completion and reliability verification. We conduct extensive experiments and thorough ablation studies on various LLMs and agent benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed method. This project is publicly available at https://mor-agent.github.io.
Pangu Light: Weight Re-Initialization for Pruning and Accelerating LLMs
May 26, 2025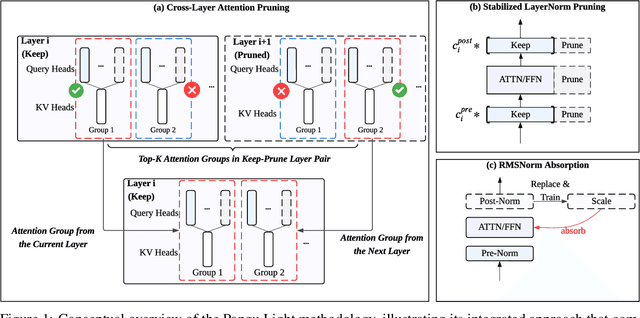

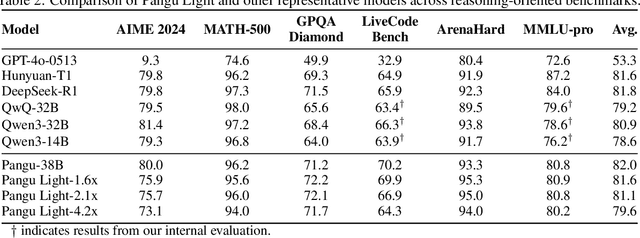
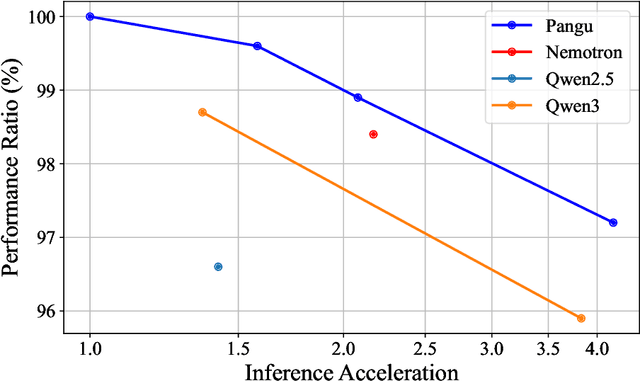
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) deliver state-of-the-art capabilities across numerous tasks, but their immense size and inference costs pose significant computational challenges for practical deployment. While structured pruning offers a promising avenue for model compression, existing methods often struggle with the detrimental effects of aggressive, simultaneous width and depth reductions, leading to substantial performance degradation. This paper argues that a critical, often overlooked, aspect in making such aggressive joint pruning viable is the strategic re-initialization and adjustment of remaining weights to improve the model post-pruning training accuracies. We introduce Pangu Light, a framework for LLM acceleration centered around structured pruning coupled with novel weight re-initialization techniques designed to address this ``missing piece''. Our framework systematically targets multiple axes, including model width, depth, attention heads, and RMSNorm, with its effectiveness rooted in novel re-initialization methods like Cross-Layer Attention Pruning (CLAP) and Stabilized LayerNorm Pruning (SLNP) that mitigate performance drops by providing the network a better training starting point. Further enhancing efficiency, Pangu Light incorporates specialized optimizations such as absorbing Post-RMSNorm computations and tailors its strategies to Ascend NPU characteristics. The Pangu Light models consistently exhibit a superior accuracy-efficiency trade-off, outperforming prominent baseline pruning methods like Nemotron and established LLMs like Qwen3 series. For instance, on Ascend NPUs, Pangu Light-32B's 81.6 average score and 2585 tokens/s throughput exceed Qwen3-32B's 80.9 average score and 2225 tokens/s.
Rethinking Optimization and Architecture for Tiny Language Models
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:The power of large language models (LLMs) has been demonstrated through numerous data and computing resources. However, the application of language models on mobile devices is facing huge challenge on the computation and memory costs, that is, tiny language models with high performance are urgently required. Limited by the highly complex training process, there are many details for optimizing language models that are seldom studied carefully. In this study, based on a tiny language model with 1B parameters, we carefully design a series of empirical study to analyze the effect of each component. Three perspectives are mainly discussed, \ie, neural architecture, parameter initialization, and optimization strategy. Several design formulas are empirically proved especially effective for tiny language models, including tokenizer compression, architecture tweaking, parameter inheritance and multiple-round training. Then we train PanGu-$\pi$-1B Pro and PanGu-$\pi$-1.5B Pro on 1.6T multilingual corpora, following the established formulas. Experimental results demonstrate the improved optimization and architecture yield a notable average improvement of 8.87 on benchmark evaluation sets for PanGu-$\pi$-1B Pro. Besides, PanGu-$\pi$-1.5B Pro surpasses a range of SOTA models with larger model sizes, validating its superior performance. The code is available at https://github.com/YuchuanTian/RethinkTinyLM.
PanGu-$π$: Enhancing Language Model Architectures via Nonlinearity Compensation
Dec 27, 2023

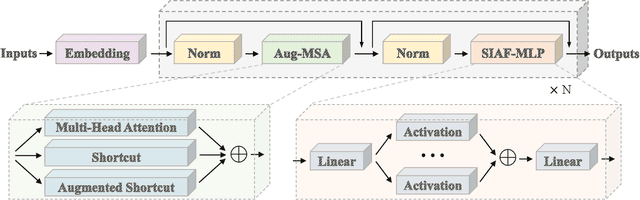

Abstract:The recent trend of large language models (LLMs) is to increase the scale of both model size (\aka the number of parameters) and dataset to achieve better generative ability, which is definitely proved by a lot of work such as the famous GPT and Llama. However, large models often involve massive computational costs, and practical applications cannot afford such high prices. However, the method of constructing a strong model architecture for LLMs is rarely discussed. We first analyze the state-of-the-art language model architectures and observe the feature collapse problem. Based on the theoretical analysis, we propose that the nonlinearity is also very important for language models, which is usually studied in convolutional neural networks for vision tasks. The series informed activation function is then introduced with tiny calculations that can be ignored, and an augmented shortcut is further used to enhance the model nonlinearity. We then demonstrate that the proposed approach is significantly effective for enhancing the model nonlinearity through carefully designed ablations; thus, we present a new efficient model architecture for establishing modern, namely, PanGu-$\pi$. Experiments are then conducted using the same dataset and training strategy to compare PanGu-$\pi$ with state-of-the-art LLMs. The results show that PanGu-$\pi$-7B can achieve a comparable performance to that of benchmarks with about 10\% inference speed-up, and PanGu-$\pi$-1B can achieve state-of-the-art performance in terms of accuracy and efficiency. In addition, we have deployed PanGu-$\pi$-7B in the high-value domains of finance and law, developing an LLM named YunShan for practical application. The results show that YunShan can surpass other models with similar scales on benchmarks.
Data-Free Distillation of Language Model by Text-to-Text Transfer
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (DFKD) plays a vital role in compressing the model when original training data is unavailable. Previous works for DFKD in NLP mainly focus on distilling encoder-only structures like BERT on classification tasks, which overlook the notable progress of generative language modeling. In this work, we propose a novel DFKD framework, namely DFKD-T$^{3}$, where the pretrained generative language model can also serve as a controllable data generator for model compression. This novel framework DFKD-T$^{3}$ leads to an end-to-end learnable text-to-text framework to transform the general domain corpus to compression-friendly task data, targeting to improve both the \textit{specificity} and \textit{diversity}. Extensive experiments show that our method can boost the distillation performance in various downstream tasks such as sentiment analysis, linguistic acceptability, and information extraction. Furthermore, we show that the generated texts can be directly used for distilling other language models and outperform the SOTA methods, making our method more appealing in a general DFKD setting. Our code is available at https://gitee.com/mindspore/models/tree/master/research/nlp/DFKD\_T3.
Multiscale Positive-Unlabeled Detection of AI-Generated Texts
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Recent releases of Large Language Models (LLMs), e.g. ChatGPT, are astonishing at generating human-like texts, but they may get misused for fake scholarly texts, fake news, fake tweets, et cetera. Previous works have proposed methods to detect these multiscale AI-generated texts, including simple ML classifiers, pretrained-model-based training-agnostic methods, and finetuned language classification models. However, mainstream detectors are formulated without considering the factor of corpus length: shorter corpuses are harder to detect compared with longer ones for shortage of informative features. In this paper, a Multiscale Positive-Unlabeled (MPU) training framework is proposed to address the challenge of multiscale text detection. Firstly, we acknowledge the human-resemblance property of short machine texts, and rephrase text classification as a Positive-Unlabeled (PU) problem by marking these short machine texts as "unlabeled" during training. In this PU context, we propose the length-sensitive Multiscale PU Loss, where we use a recurrent model in abstraction to estimate positive priors of scale-variant corpuses. Additionally, we introduce a Text Multiscaling module to enrich training corpuses. Experiments show that our MPU method augments detection performance on long AI-generated text, and significantly improves short-corpus detection of language model detectors. Language Models trained with MPU could outcompete existing detectors by large margins on multiscale AI-generated texts. The codes are available at https://github.com/mindspore-lab/mindone/tree/master/examples/detect_chatgpt and https://github.com/YuchuanTian/AIGC_text_detector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge