Zhenfeng Fan
AIComposer: Any Style and Content Image Composition via Feature Integration
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Image composition has advanced significantly with large-scale pre-trained T2I diffusion models. Despite progress in same-domain composition, cross-domain composition remains under-explored. The main challenges are the stochastic nature of diffusion models and the style gap between input images, leading to failures and artifacts. Additionally, heavy reliance on text prompts limits practical applications. This paper presents the first cross-domain image composition method that does not require text prompts, allowing natural stylization and seamless compositions. Our method is efficient and robust, preserving the diffusion prior, as it involves minor steps for backward inversion and forward denoising without training the diffuser. Our method also uses a simple multilayer perceptron network to integrate CLIP features from foreground and background, manipulating diffusion with a local cross-attention strategy. It effectively preserves foreground content while enabling stable stylization without a pre-stylization network. Finally, we create a benchmark dataset with diverse contents and styles for fair evaluation, addressing the lack of testing datasets for cross-domain image composition. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, significantly improving the LPIPS score by 30.5% and the CSD metric by 18.1%. We believe our method will advance future research and applications. Code and benchmark at https://github.com/sherlhw/AIComposer.
MyPortrait: Morphable Prior-Guided Personalized Portrait Generation
Dec 05, 2023Abstract:Generating realistic talking faces is an interesting and long-standing topic in the field of computer vision. Although significant progress has been made, it is still challenging to generate high-quality dynamic faces with personalized details. This is mainly due to the inability of the general model to represent personalized details and the generalization problem to unseen controllable parameters. In this work, we propose Myportrait, a simple, general, and flexible framework for neural portrait generation. We incorporate personalized prior in a monocular video and morphable prior in 3D face morphable space for generating personalized details under novel controllable parameters. Our proposed framework supports both video-driven and audio-driven face animation given a monocular video of a single person. Distinguished by whether the test data is sent to training or not, our method provides a real-time online version and a high-quality offline version. Comprehensive experiments in various metrics demonstrate the superior performance of our method over the state-of-the-art methods. The code will be publicly available.
Unpaired Multi-domain Attribute Translation of 3D Facial Shapes with a Square and Symmetric Geometric Map
Aug 25, 2023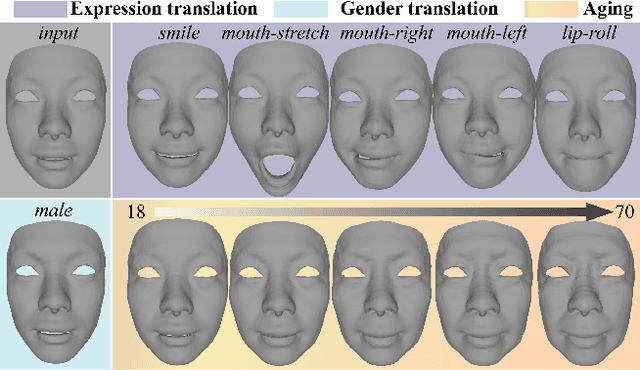
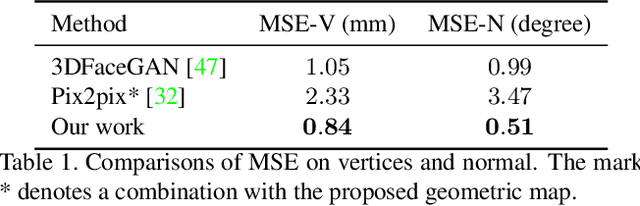
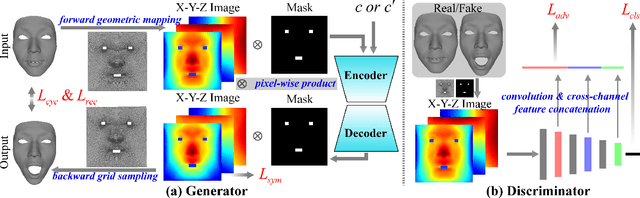
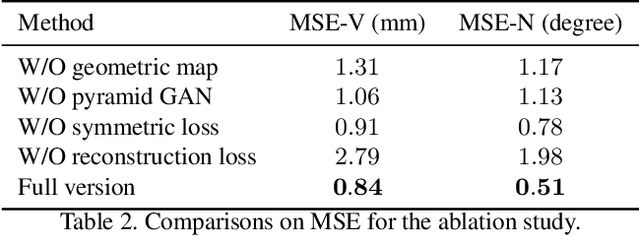
Abstract:While impressive progress has recently been made in image-oriented facial attribute translation, shape-oriented 3D facial attribute translation remains an unsolved issue. This is primarily limited by the lack of 3D generative models and ineffective usage of 3D facial data. We propose a learning framework for 3D facial attribute translation to relieve these limitations. Firstly, we customize a novel geometric map for 3D shape representation and embed it in an end-to-end generative adversarial network. The geometric map represents 3D shapes symmetrically on a square image grid, while preserving the neighboring relationship of 3D vertices in a local least-square sense. This enables effective learning for the latent representation of data with different attributes. Secondly, we employ a unified and unpaired learning framework for multi-domain attribute translation. It not only makes effective usage of data correlation from multiple domains, but also mitigates the constraint for hardly accessible paired data. Finally, we propose a hierarchical architecture for the discriminator to guarantee robust results against both global and local artifacts. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the advantage of the proposed framework over the state-of-the-art in generating high-fidelity facial shapes. Given an input 3D facial shape, the proposed framework is able to synthesize novel shapes of different attributes, which covers some downstream applications, such as expression transfer, gender translation, and aging. Code at https://github.com/NaughtyZZ/3D_facial_shape_attribute_translation_ssgmap.
RaSa: Relation and Sensitivity Aware Representation Learning for Text-based Person Search
May 23, 2023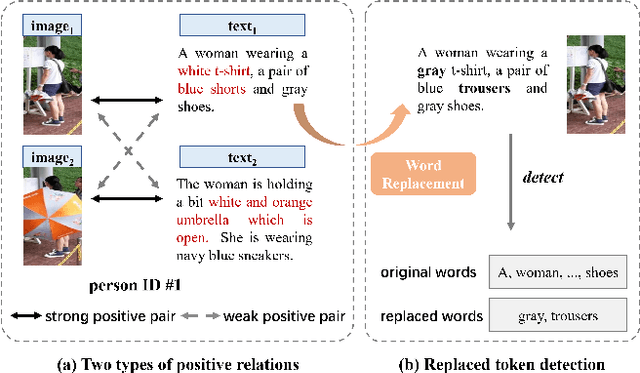
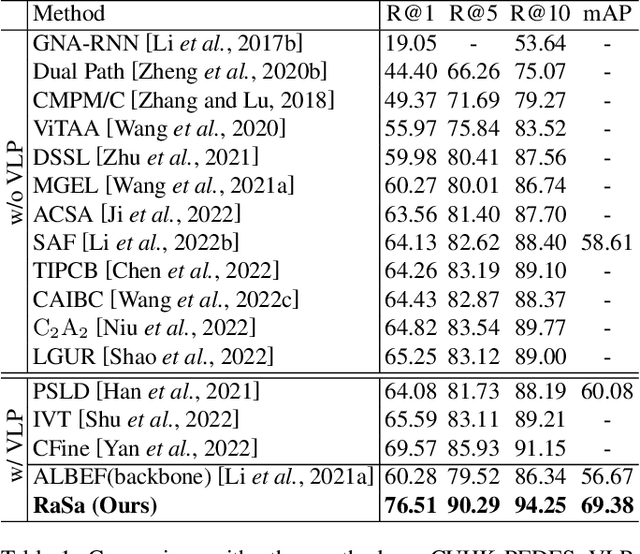
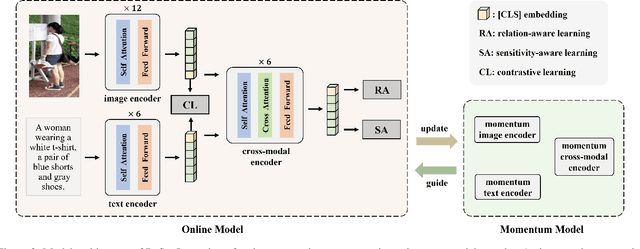
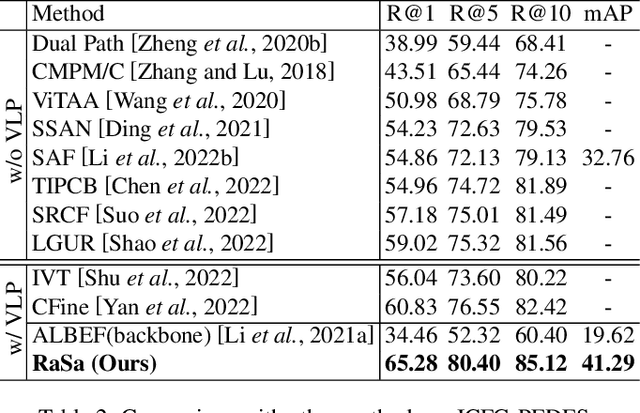
Abstract:Text-based person search aims to retrieve the specified person images given a textual description. The key to tackling such a challenging task is to learn powerful multi-modal representations. Towards this, we propose a Relation and Sensitivity aware representation learning method (RaSa), including two novel tasks: Relation-Aware learning (RA) and Sensitivity-Aware learning (SA). For one thing, existing methods cluster representations of all positive pairs without distinction and overlook the noise problem caused by the weak positive pairs where the text and the paired image have noise correspondences, thus leading to overfitting learning. RA offsets the overfitting risk by introducing a novel positive relation detection task (i.e., learning to distinguish strong and weak positive pairs). For another thing, learning invariant representation under data augmentation (i.e., being insensitive to some transformations) is a general practice for improving representation's robustness in existing methods. Beyond that, we encourage the representation to perceive the sensitive transformation by SA (i.e., learning to detect the replaced words), thus promoting the representation's robustness. Experiments demonstrate that RaSa outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by 6.94%, 4.45% and 15.35% in terms of Rank@1 on CUHK-PEDES, ICFG-PEDES and RSTPReid datasets, respectively. Code is available at: https://github.com/Flame-Chasers/RaSa.
Towards Fine-grained 3D Face Dense Registration: An Optimal Dividing and Diffusing Method
Sep 23, 2021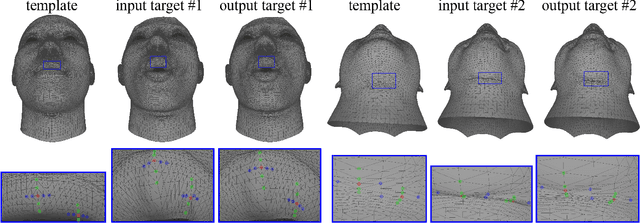
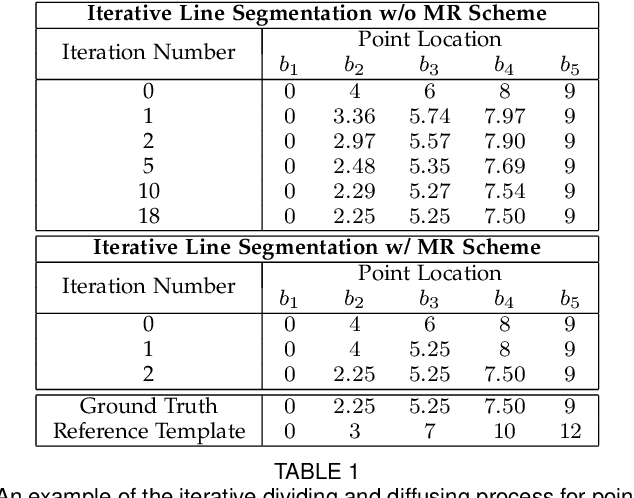
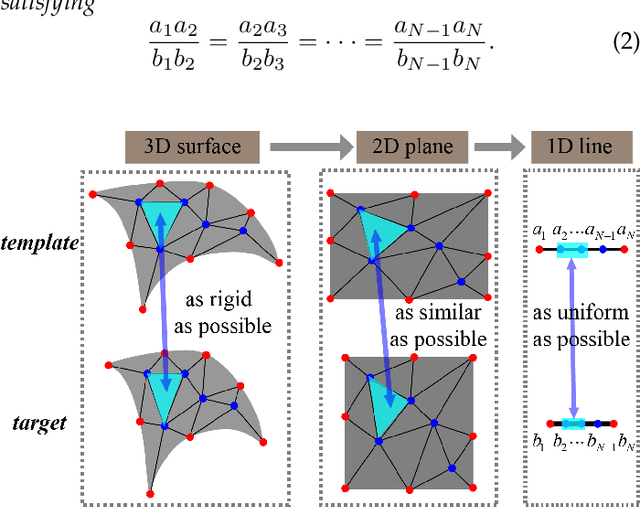
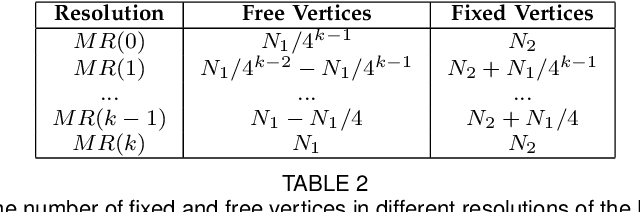
Abstract:Dense vertex-to-vertex correspondence between 3D faces is a fundamental and challenging issue for 3D&2D face analysis. While the sparse landmarks have anatomically ground-truth correspondence, the dense vertex correspondences on most facial regions are unknown. In this view, the current literatures commonly result in reasonable but diverse solutions, which deviate from the optimum to the 3D face dense registration problem. In this paper, we revisit dense registration by a dimension-degraded problem, i.e. proportional segmentation of a line, and employ an iterative dividing and diffusing method to reach the final solution uniquely. This method is then extended to 3D surface by formulating a local registration problem for dividing and a linear least-square problem for diffusing, with constraints on fixed features. On this basis, we further propose a multi-resolution algorithm to accelerate the computational process. The proposed method is linked to a novel local scaling metric, where we illustrate the physical meaning as smooth rearrangement for local cells of 3D facial shapes. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in various aspects. Generally, the proposed method leads to coherent local registrations and elegant mesh grid routines for fine-grained 3D face dense registrations, which benefits many downstream applications significantly. It can also be applied to dense correspondence for other format of data which are not limited to face. The core code will be publicly available at https://github.com/NaughtyZZ/3D_face_dense_registration.
3D-TalkEmo: Learning to Synthesize 3D Emotional Talking Head
Apr 25, 2021
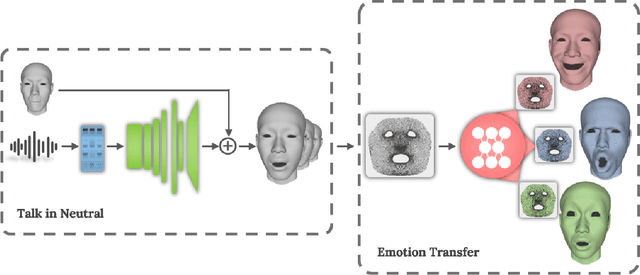


Abstract:Impressive progress has been made in audio-driven 3D facial animation recently, but synthesizing 3D talking-head with rich emotion is still unsolved. This is due to the lack of 3D generative models and available 3D emotional dataset with synchronized audios. To address this, we introduce 3D-TalkEmo, a deep neural network that generates 3D talking head animation with various emotions. We also create a large 3D dataset with synchronized audios and videos, rich corpus, as well as various emotion states of different persons with the sophisticated 3D face reconstruction methods. In the emotion generation network, we propose a novel 3D face representation structure - geometry map by classical multi-dimensional scaling analysis. It maps the coordinates of vertices on a 3D face to a canonical image plane, while preserving the vertex-to-vertex geodesic distance metric in a least-square sense. This maintains the adjacency relationship of each vertex and holds the effective convolutional structure for the 3D facial surface. Taking a neutral 3D mesh and a speech signal as inputs, the 3D-TalkEmo is able to generate vivid facial animations. Moreover, it provides access to change the emotion state of the animated speaker. We present extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluation of our method, in addition to user studies, demonstrating the generated talking-heads of significantly higher quality compared to previous state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge