Zeyu Yan
Cybernetic Marionette: Channeling Collective Agency Through a Wearable Robot in a Live Dancer-Robot Duet
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:We describe DANCE^2, an interactive dance performance in which audience members channel their collective agency into a dancer-robot duet by voting on the behavior of a wearable robot affixed to the dancer's body. At key moments during the performance, the audience is invited to either continue the choreography or override it, shaping the unfolding interaction through real-time collective input. While post-performance surveys revealed that participants felt their choices meaningfully influenced the performance, voting data across four public performances exhibited strikingly consistent patterns. This tension between what audience members do, what they feel, and what actually changes highlights a complex interplay between agentive behavior, the experience of agency, and power. We reflect on how choreography, interaction design, and the structure of the performance mediate this relationship, offering a live analogy for algorithmically curated digital systems where agency is felt, but not exercised.
PCB Renewal: Iterative Reuse of PCB Substrates for Sustainable Electronic Making
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:PCB (printed circuit board) substrates are often single-use, leading to material waste in electronics making. We introduce PCB Renewal, a novel technique that "erases" and "reconfigures" PCB traces by selectively depositing conductive epoxy onto outdated areas, transforming isolated paths into conductive planes that support new traces. We present the PCB Renewal workflow, evaluate its electrical performance and mechanical durability, and model its sustainability impact, including material usage, cost, energy consumption, and time savings. We develop a software plug-in that guides epoxy deposition, generates updated PCB profiles, and calculates resource usage. To demonstrate PCB Renewal's effectiveness and versatility, we repurpose a single PCB across four design iterations spanning three projects: a camera roller, a WiFi radio, and an ESPboy game console. We also show how an outsourced double-layer PCB can be reconfigured, transforming it from an LED watch to an interactive cat toy. The paper concludes with limitations and future directions.
A Two-Stage Training Framework for Joint Speech Compression and Enhancement
Sep 08, 2023
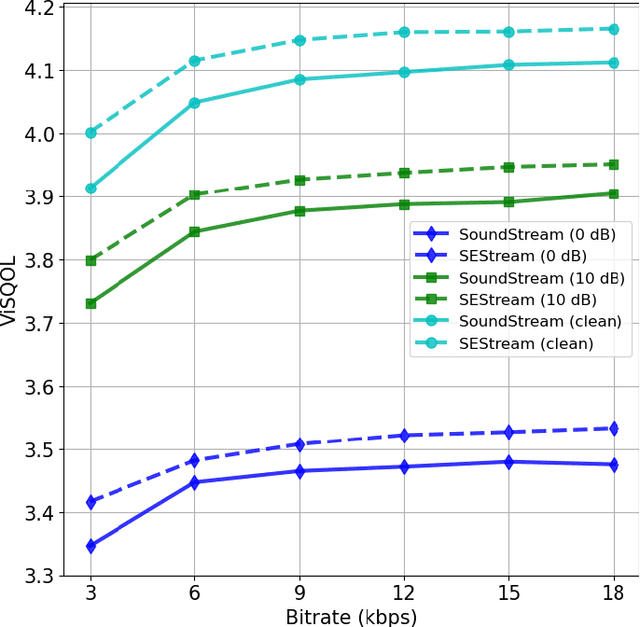
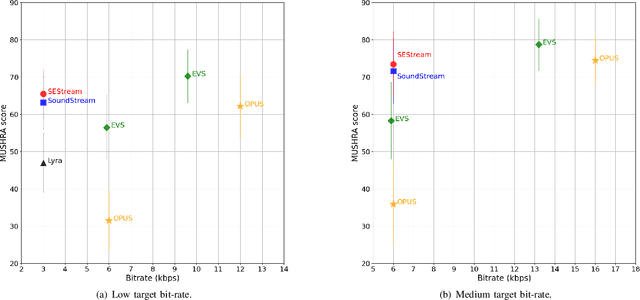
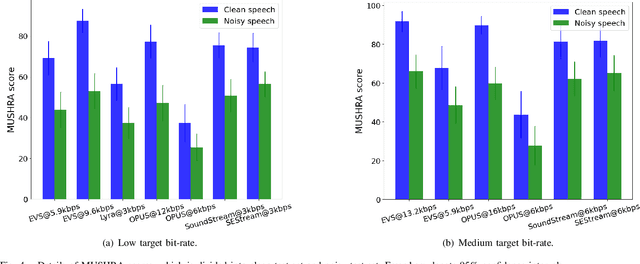
Abstract:This paper considers the joint compression and enhancement problem for speech signal in the presence of noise. Recently, the SoundStream codec, which relies on end-to-end joint training of an encoder-decoder pair and a residual vector quantizer by a combination of adversarial and reconstruction losses,has shown very promising performance, especially in subjective perception quality. In this work, we provide a theoretical result to show that, to simultaneously achieve low distortion and high perception in the presence of noise, there exist an optimal two-stage optimization procedure for the joint compression and enhancement problem. This procedure firstly optimizes an encoder-decoder pair using only distortion loss and then fixes the encoder to optimize a perceptual decoder using perception loss. Based on this result, we construct a two-stage training framework for joint compression and enhancement of noisy speech signal. Unlike existing training methods which are heuristic, the proposed two-stage training method has a theoretical foundation. Finally, experimental results for various noise and bit-rate conditions are provided. The results demonstrate that a codec trained by the proposed framework can outperform SoundStream and other representative codecs in terms of both objective and subjective evaluation metrics. Code is available at \textit{https://github.com/jscscloris/SEStream}.
Toucha11y: Making Inaccessible Public Touchscreens Accessible
May 06, 2023
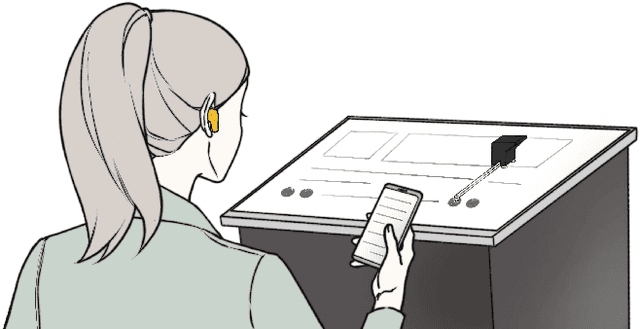

Abstract:Despite their growing popularity, many public kiosks with touchscreens are inaccessible to blind people. Toucha11y is a working prototype that allows blind users to use existing inaccessible touchscreen kiosks independently and with little effort. Toucha11y consists of a mechanical bot that can be instrumented to an arbitrary touchscreen kiosk by a blind user and a companion app on their smartphone. The bot, once attached to a touchscreen, will recognize its content, retrieve the corresponding information from a database, and render it on the user's smartphone. As a result, a blind person can use the smartphone's built-in accessibility features to access content and make selections. The mechanical bot will detect and activate the corresponding touchscreen interface. We present the system design of Toucha11y along with a series of technical evaluations. Through a user study, we found out that Toucha11y could help blind users operate inaccessible touchscreen devices.
Optimally Controllable Perceptual Lossy Compression
Jun 21, 2022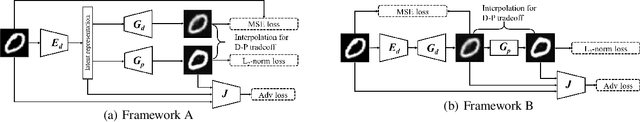
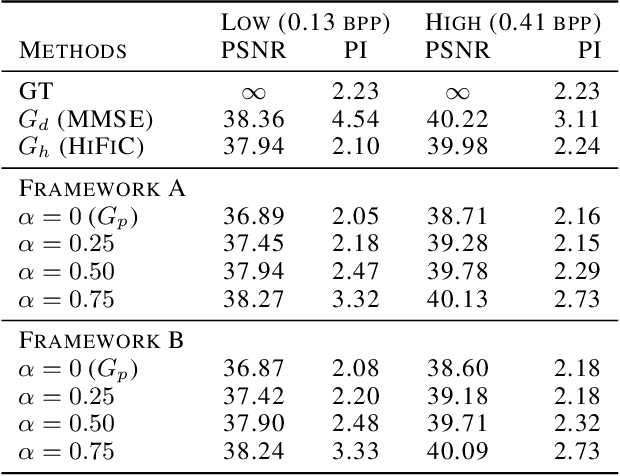
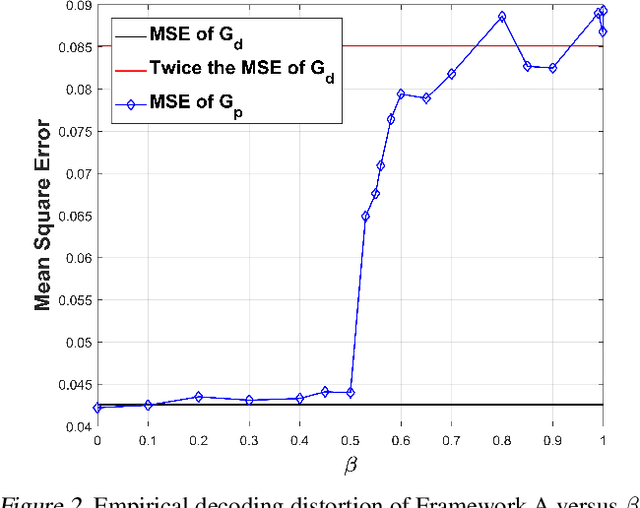
Abstract:Recent studies in lossy compression show that distortion and perceptual quality are at odds with each other, which put forward the tradeoff between distortion and perception (D-P). Intuitively, to attain different perceptual quality, different decoders have to be trained. In this paper, we present a nontrivial finding that only two decoders are sufficient for optimally achieving arbitrary (an infinite number of different) D-P tradeoff. We prove that arbitrary points of the D-P tradeoff bound can be achieved by a simple linear interpolation between the outputs of a minimum MSE decoder and a specifically constructed perfect perceptual decoder. Meanwhile, the perceptual quality (in terms of the squared Wasserstein-2 distance metric) can be quantitatively controlled by the interpolation factor. Furthermore, to construct a perfect perceptual decoder, we propose two theoretically optimal training frameworks. The new frameworks are different from the distortion-plus-adversarial loss based heuristic framework widely used in existing methods, which are not only theoretically optimal but also can yield state-of-the-art performance in practical perceptual decoding. Finally, we validate our theoretical finding and demonstrate the superiority of our frameworks via experiments. Code is available at: https://github.com/ZeyuYan/Controllable-Perceptual-Compression
Optimal Transport for Unsupervised Restoration Learning
Aug 07, 2021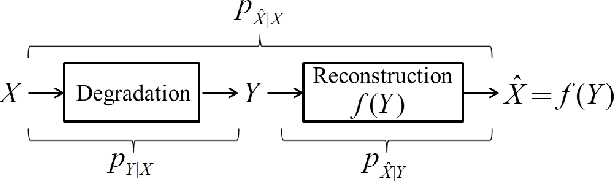
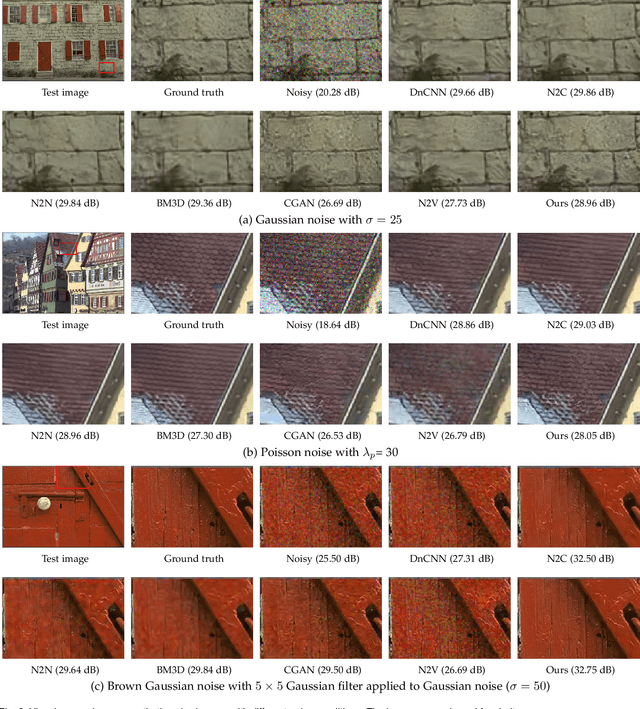
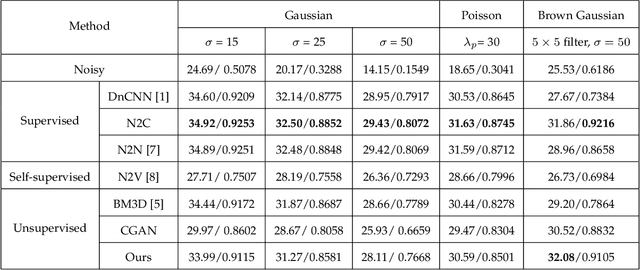
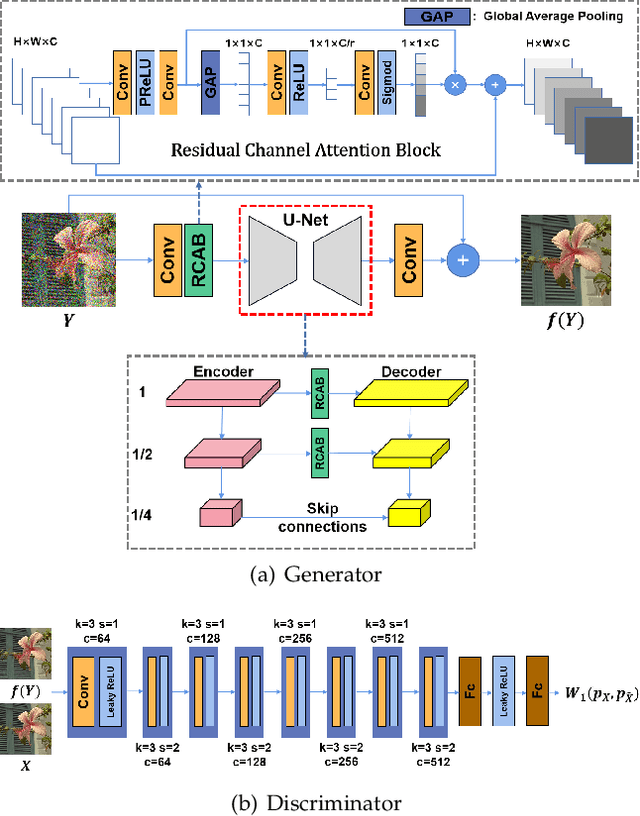

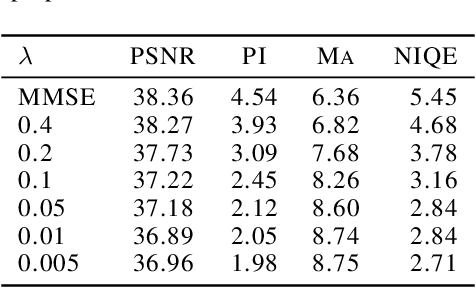
Abstract:Recently, much progress has been made in unsupervised restoration learning. However, existing methods more or less rely on some assumptions on the signal and/or degradation model, which limits their practical performance. How to construct an optimal criterion for unsupervised restoration learning without any prior knowledge on the degradation model is still an open question. Toward answering this question, this work proposes a criterion for unsupervised restoration learning based on the optimal transport theory. This criterion has favorable properties, e.g., approximately maximal preservation of the information of the signal, whilst achieving perceptual reconstruction. Furthermore, though a relaxed unconstrained formulation is used in practical implementation, we show that the relaxed formulation in theory has the same solution as the original constrained formulation. Experiments on synthetic and real-world data, including realistic photographic, microscopy, depth, and raw depth images, demonstrate that the proposed method even compares favorably with supervised methods, e.g., approaching the PSNR of supervised methods while having better perceptual quality. Particularly, for spatially correlated noise and realistic microscopy images, the proposed method not only achieves better perceptual quality but also has higher PSNR than supervised methods. Besides, it shows remarkable superiority in harsh practical conditions with complex noise, e.g., raw depth images.
On Perceptual Lossy Compression: The Cost of Perceptual Reconstruction and An Optimal Training Framework
Jun 05, 2021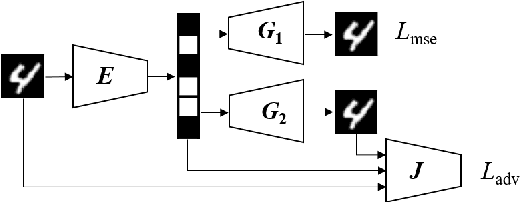
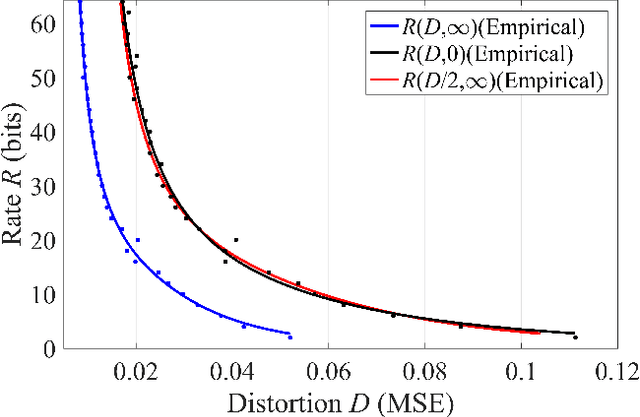
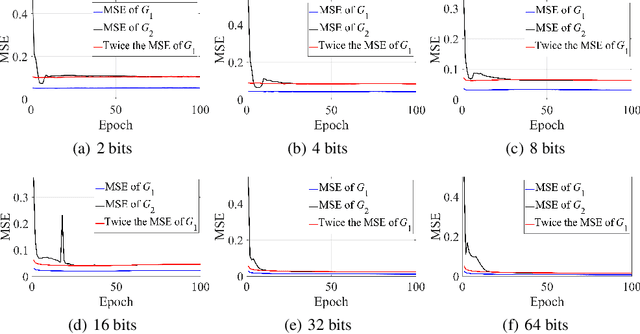
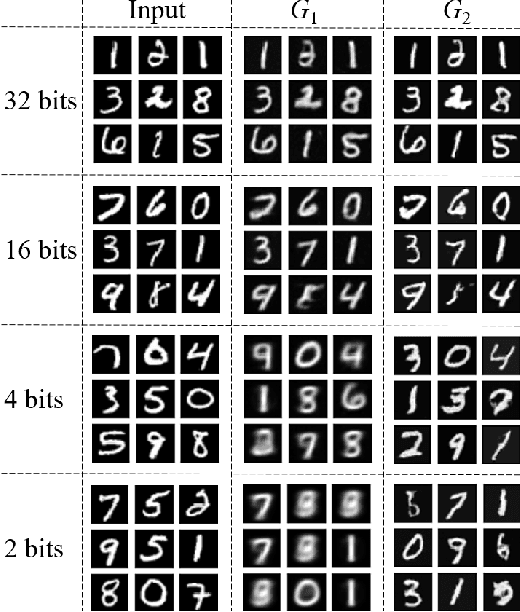
Abstract:Lossy compression algorithms are typically designed to achieve the lowest possible distortion at a given bit rate. However, recent studies show that pursuing high perceptual quality would lead to increase of the lowest achievable distortion (e.g., MSE). This paper provides nontrivial results theoretically revealing that, \textit{1}) the cost of achieving perfect perception quality is exactly a doubling of the lowest achievable MSE distortion, \textit{2}) an optimal encoder for the "classic" rate-distortion problem is also optimal for the perceptual compression problem, \textit{3}) distortion loss is unnecessary for training a perceptual decoder. Further, we propose a novel training framework to achieve the lowest MSE distortion under perfect perception constraint at a given bit rate. This framework uses a GAN with discriminator conditioned on an MSE-optimized encoder, which is superior over the traditional framework using distortion plus adversarial loss. Experiments are provided to verify the theoretical finding and demonstrate the superiority of the proposed training framework.
Mention Extraction and Linking for SQL Query Generation
Dec 18, 2020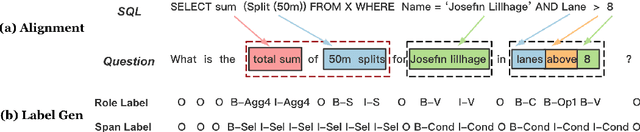



Abstract:On the WikiSQL benchmark, state-of-the-art text-to-SQL systems typically take a slot-filling approach by building several dedicated models for each type of slots. Such modularized systems are not only complex butalso of limited capacity for capturing inter-dependencies among SQL clauses. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a novel extraction-linking approach, where a unified extractor recognizes all types of slot mentions appearing in the question sentence before a linker maps the recognized columns to the table schema to generate executable SQL queries. Trained with automatically generated annotations, the proposed method achieves the first place on the WikiSQL benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge