Yusuke Kurose
RealX3D: A Physically-Degraded 3D Benchmark for Multi-view Visual Restoration and Reconstruction
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce RealX3D, a real-capture benchmark for multi-view visual restoration and 3D reconstruction under diverse physical degradations. RealX3D groups corruptions into four families, including illumination, scattering, occlusion, and blurring, and captures each at multiple severity levels using a unified acquisition protocol that yields pixel-aligned LQ/GT views. Each scene includes high-resolution capture, RAW images, and dense laser scans, from which we derive world-scale meshes and metric depth. Benchmarking a broad range of optimization-based and feed-forward methods shows substantial degradation in reconstruction quality under physical corruptions, underscoring the fragility of current multi-view pipelines in real-world challenging environments.
Domain Adaptive Multiple Instance Learning for Instance-level Prediction of Pathological Images
Apr 07, 2023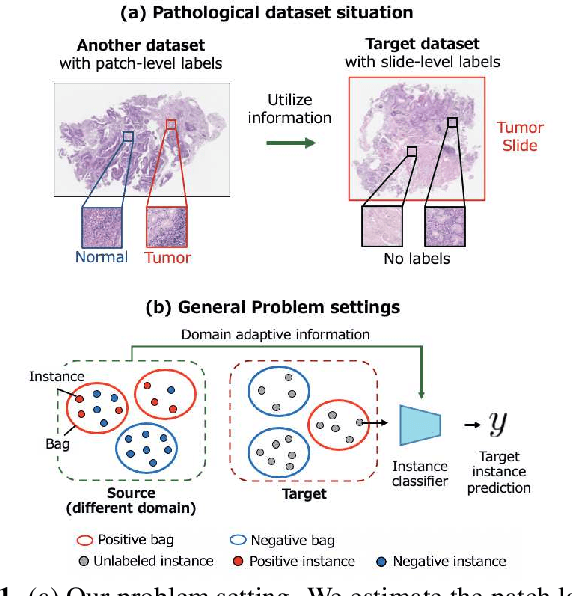
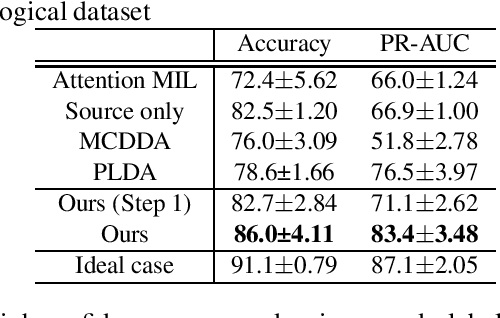
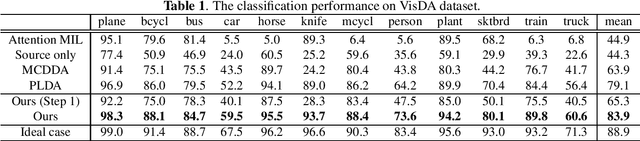
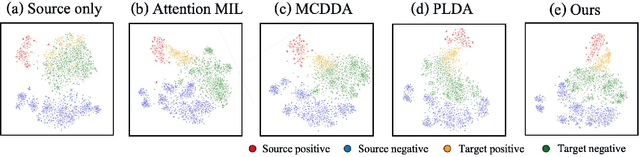
Abstract:Pathological image analysis is an important process for detecting abnormalities such as cancer from cell images. However, since the image size is generally very large, the cost of providing detailed annotations is high, which makes it difficult to apply machine learning techniques. One way to improve the performance of identifying abnormalities while keeping the annotation cost low is to use only labels for each slide, or to use information from another dataset that has already been labeled. However, such weak supervisory information often does not provide sufficient performance. In this paper, we proposed a new task setting to improve the classification performance of the target dataset without increasing annotation costs. And to solve this problem, we propose a pipeline that uses multiple instance learning (MIL) and domain adaptation (DA) methods. Furthermore, in order to combine the supervisory information of both methods effectively, we propose a method to create pseudo-labels with high confidence. We conducted experiments on the pathological image dataset we created for this study and showed that the proposed method significantly improves the classification performance compared to existing methods.
Sketch-based Medical Image Retrieval
Mar 07, 2023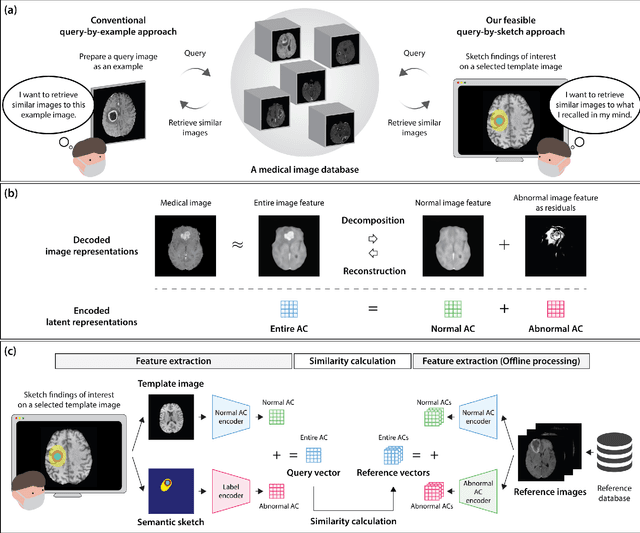
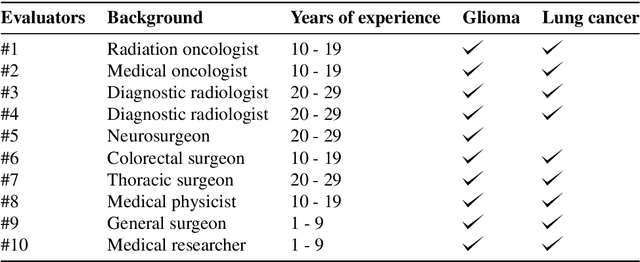
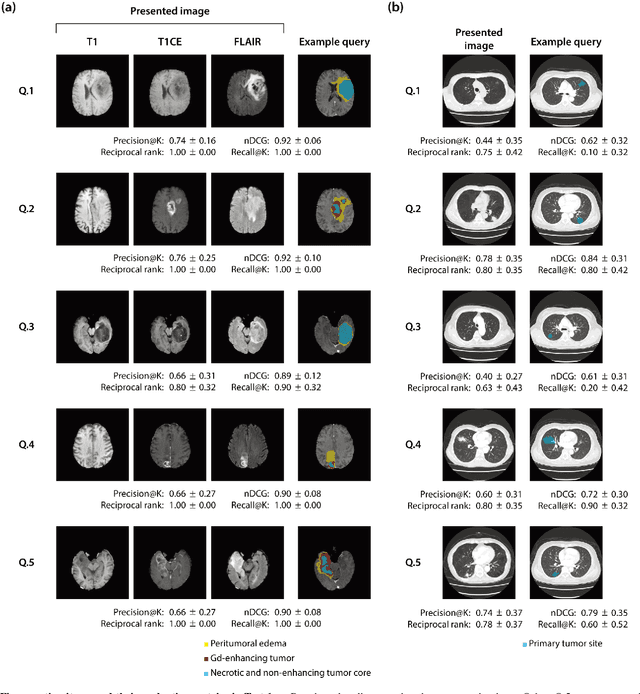
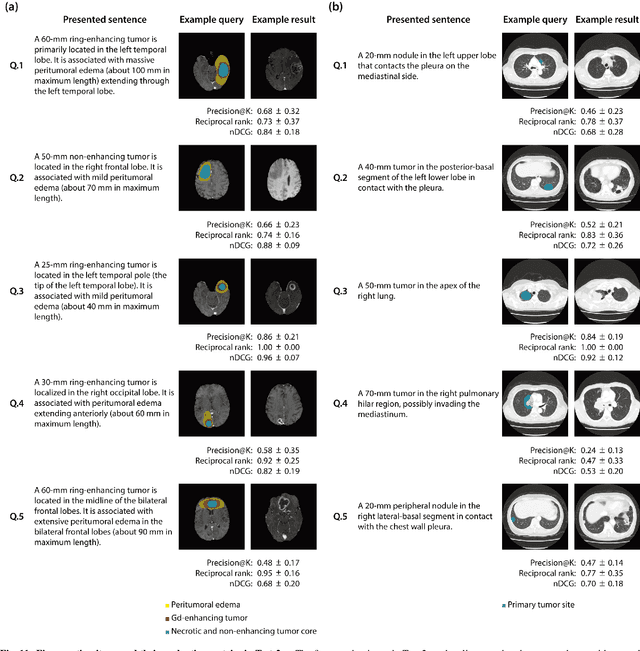
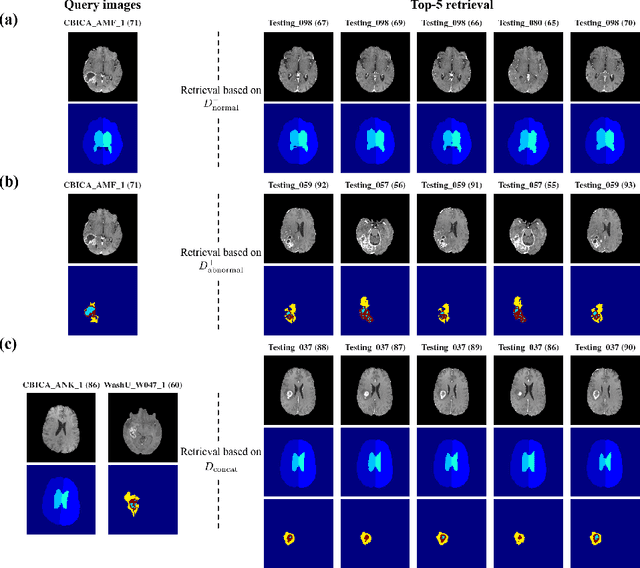
Abstract:The amount of medical images stored in hospitals is increasing faster than ever; however, utilizing the accumulated medical images has been limited. This is because existing content-based medical image retrieval (CBMIR) systems usually require example images to construct query vectors; nevertheless, example images cannot always be prepared. Besides, there can be images with rare characteristics that make it difficult to find similar example images, which we call isolated samples. Here, we introduce a novel sketch-based medical image retrieval (SBMIR) system that enables users to find images of interest without example images. The key idea lies in feature decomposition of medical images, whereby the entire feature of a medical image can be decomposed into and reconstructed from normal and abnormal features. By extending this idea, our SBMIR system provides an easy-to-use two-step graphical user interface: users first select a template image to specify a normal feature and then draw a semantic sketch of the disease on the template image to represent an abnormal feature. Subsequently, it integrates the two kinds of input to construct a query vector and retrieves reference images with the closest reference vectors. Using two datasets, ten healthcare professionals with various clinical backgrounds participated in the user test for evaluation. As a result, our SBMIR system enabled users to overcome previous challenges, including image retrieval based on fine-grained image characteristics, image retrieval without example images, and image retrieval for isolated samples. Our SBMIR system achieves flexible medical image retrieval on demand, thereby expanding the utility of medical image databases.
Plaque segmentation via masking of the artery wall
Jan 26, 2022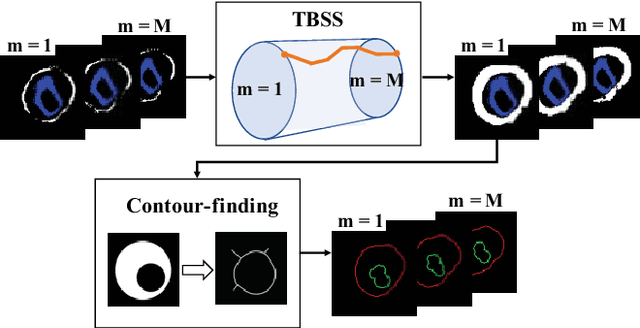
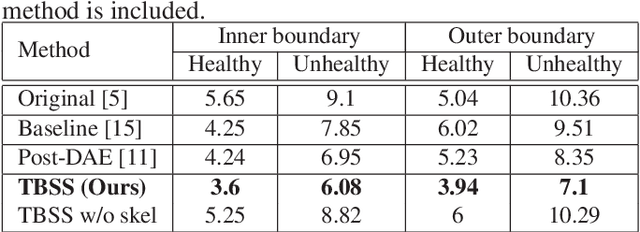
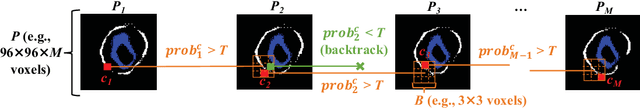
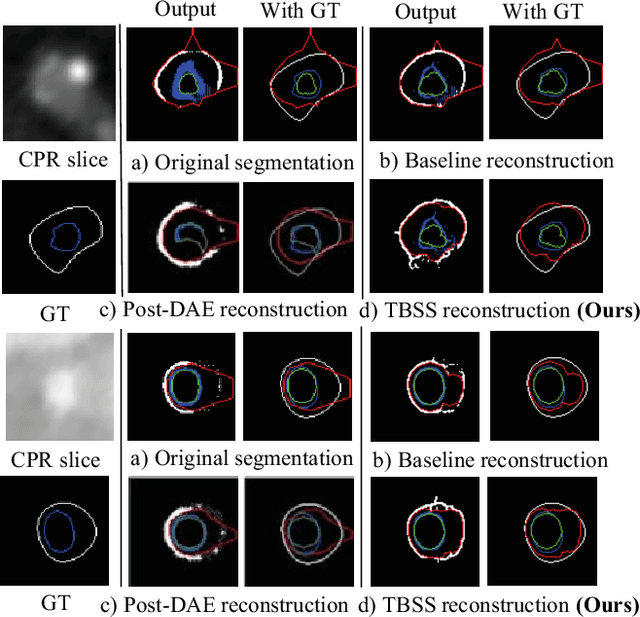
Abstract:The presence of plaques in the coronary arteries are a major risk to the patients' life. In particular, non-calcified plaques pose a great challenge, as they are harder to detect and more likely to rupture than calcified plaques. While current deep learning techniques allow precise segmentation of regular images, the performance in medical images is still low, caused mostly by blurriness and ambiguous voxel intensities of unrelated parts that fall on the same range. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology for segmenting calcified and non-calcified plaques in CCTA-CPR scans of coronary arteries. The input slices are masked so only the voxels within the wall vessel are considered for segmentation. We also provide an exhaustive evaluation by applying different types of masks, in order to validate the potential of vessel masking for plaque segmentation. Our methodology results in a prominent boost in segmentation performance, in both quantitative and qualitative evaluation, achieving accurate plaque shapes even for the challenging non-calcified plaques. We believe our findings can lead the future research for high-performance plaque segmentation.
Decomposing Normal and Abnormal Features of Medical Images into Discrete Latent Codes for Content-Based Image Retrieval
Mar 23, 2021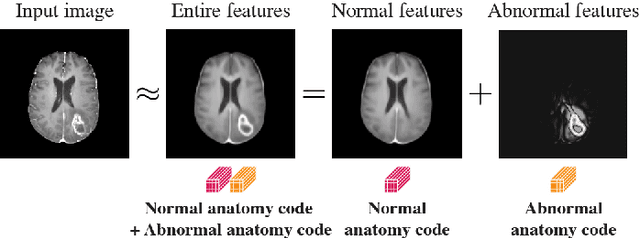
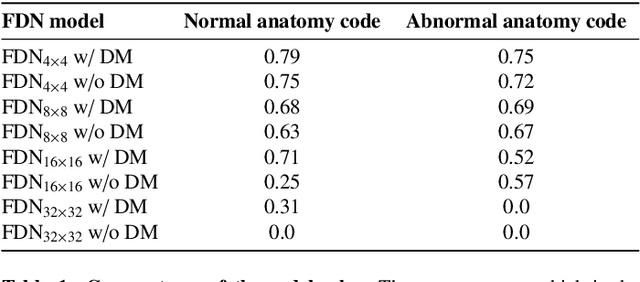
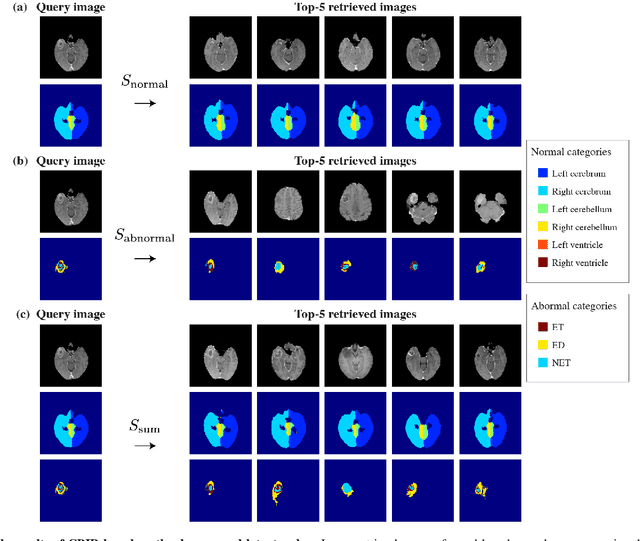
Abstract:In medical imaging, the characteristics purely derived from a disease should reflect the extent to which abnormal findings deviate from the normal features. Indeed, physicians often need corresponding images without abnormal findings of interest or, conversely, images that contain similar abnormal findings regardless of normal anatomical context. This is called comparative diagnostic reading of medical images, which is essential for a correct diagnosis. To support comparative diagnostic reading, content-based image retrieval (CBIR), which can selectively utilize normal and abnormal features in medical images as two separable semantic components, will be useful. Therefore, we propose a neural network architecture to decompose the semantic components of medical images into two latent codes: normal anatomy code and abnormal anatomy code. The normal anatomy code represents normal anatomies that should have existed if the sample is healthy, whereas the abnormal anatomy code attributes to abnormal changes that reflect deviation from the normal baseline. These latent codes are discretized through vector quantization to enable binary hashing, which can reduce the computational burden at the time of similarity search. By calculating the similarity based on either normal or abnormal anatomy codes or the combination of the two codes, our algorithm can retrieve images according to the selected semantic component from a dataset consisting of brain magnetic resonance images of gliomas. Our CBIR system qualitatively and quantitatively achieves remarkable results.
Decomposing Normal and Abnormal Features of Medical Images for Content-based Image Retrieval
Nov 12, 2020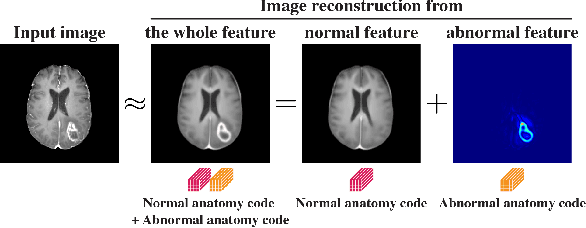
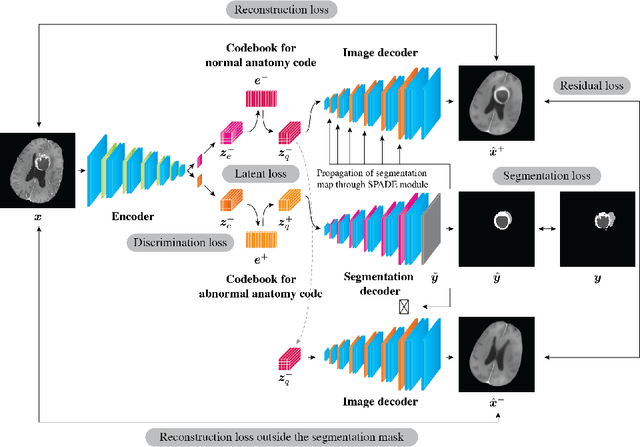
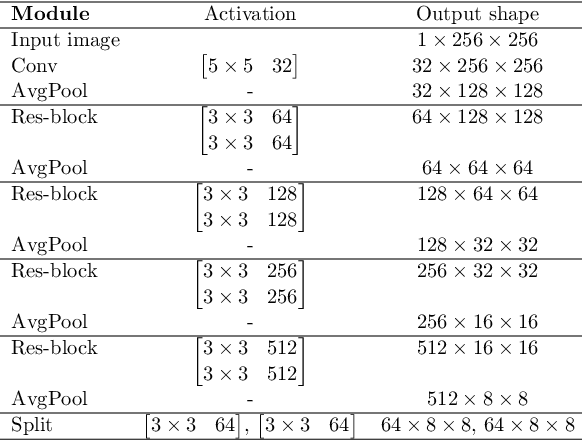
Abstract:Medical images can be decomposed into normal and abnormal features, which is considered as the compositionality. Based on this idea, we propose an encoder-decoder network to decompose a medical image into two discrete latent codes: a normal anatomy code and an abnormal anatomy code. Using these latent codes, we demonstrate a similarity retrieval by focusing on either normal or abnormal features of medical images.
Unsupervised Brain Abnormality Detection Using High Fidelity Image Reconstruction Networks
Jun 02, 2020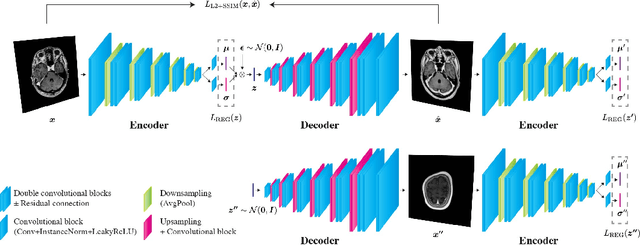
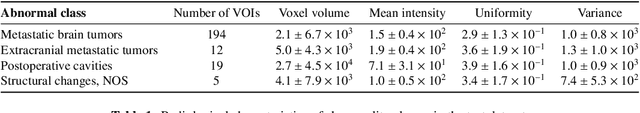
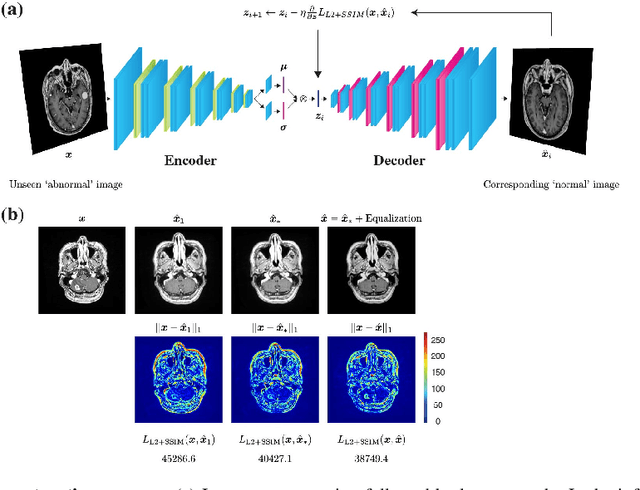
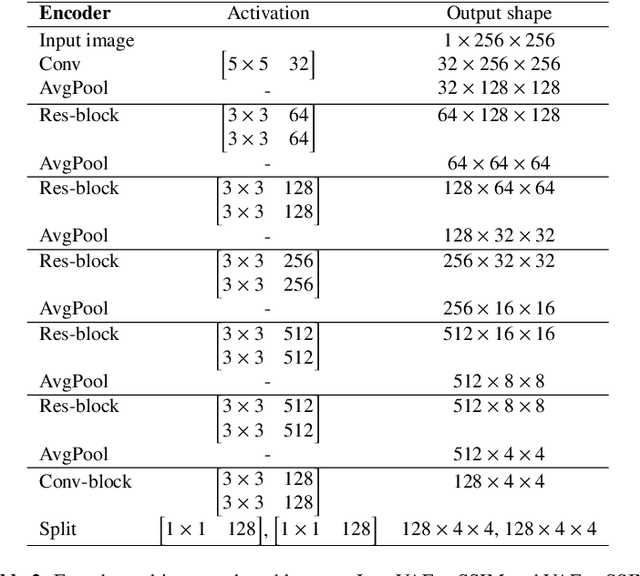
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have facilitated near-expert medical image analysis. Supervised learning is the mainstay of current approaches, though its success requires the use of large, fully labeled datasets. However, in real-world medical practice, previously unseen disease phenotypes are encountered that have not been defined a priori in finite-size datasets. Unsupervised learning, a hypothesis-free learning framework, may play a complementary role to supervised learning. Here, we demonstrate a novel framework for voxel-wise abnormality detection in brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which exploits an image reconstruction network based on an introspective variational autoencoder trained with a structural similarity constraint. The proposed network learns a latent representation for "normal" anatomical variation using a series of images that do not include annotated abnormalities. After training, the network can map unseen query images to positions in the latent space, and latent variables sampled from those positions can be mapped back to the image space to yield normal-looking replicas of the input images. Finally, the network considers abnormality scores, which are designed to reflect differences at several image feature levels, in order to locate image regions that may contain abnormalities. The proposed method is evaluated on a comprehensively annotated dataset spanning clinically significant structural abnormalities of the brain parenchyma in a population having undergone radiotherapy for brain metastasis, demonstrating that it is particularly effective for contrast-enhanced lesions, i.e., metastatic brain tumors and extracranial metastatic tumors.
Coronary Wall Segmentation in CCTA Scans via a Hybrid Net with Contours Regularization
Feb 27, 2020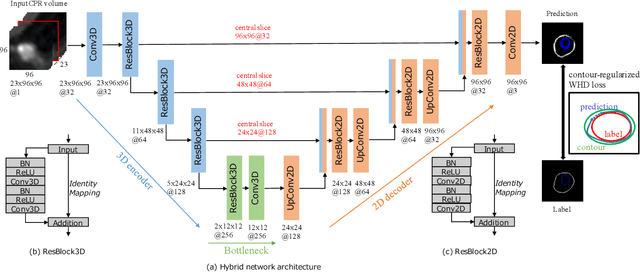
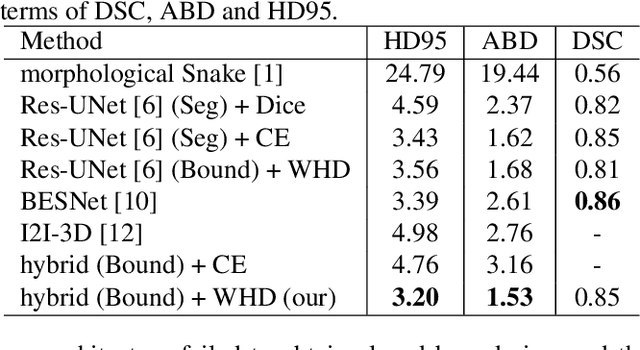
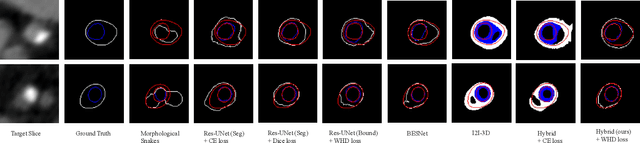
Abstract:Providing closed and well-connected boundaries of coronary artery is essential to assist cardiologists in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). Recently, several deep learning-based methods have been proposed for boundary detection and segmentation in a medical image. However, when applied to coronary wall detection, they tend to produce disconnected and inaccurate boundaries. In this paper, we propose a novel boundary detection method for coronary arteries that focuses on the continuity and connectivity of the boundaries. In order to model the spatial continuity of consecutive images, our hybrid architecture takes a volume (i.e., a segment of the coronary artery) as input and detects the boundary of the target slice (i.e., the central slice of the segment). Then, to ensure closed boundaries, we propose a contour-constrained weighted Hausdorff distance loss. We evaluate our method on a dataset of 34 patients of coronary CT angiography scans with curved planar reconstruction (CCTA-CPR) of the arteries (i.e., cross-sections). Experiment results show that our method can produce smooth closed boundaries outperforming the state-of-the-art accuracy.
Multi-Stage Pathological Image Classification using Semantic Segmentation
Oct 10, 2019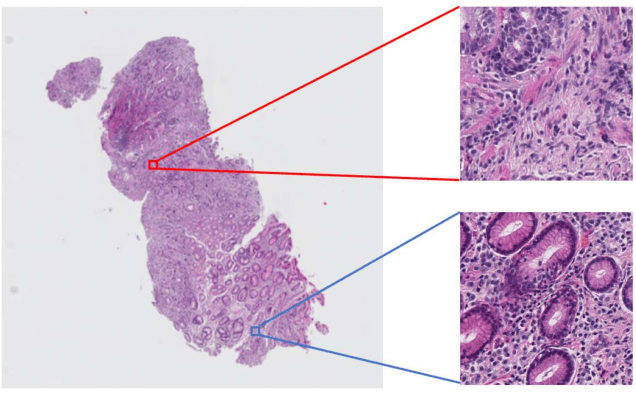
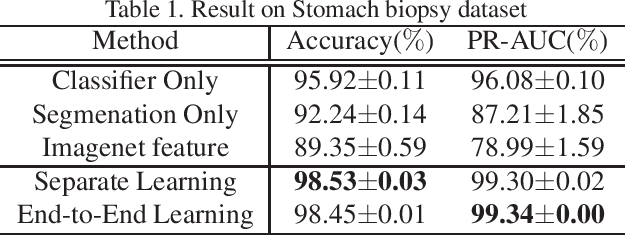
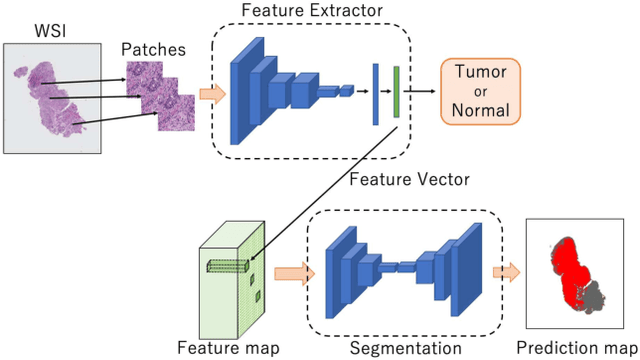
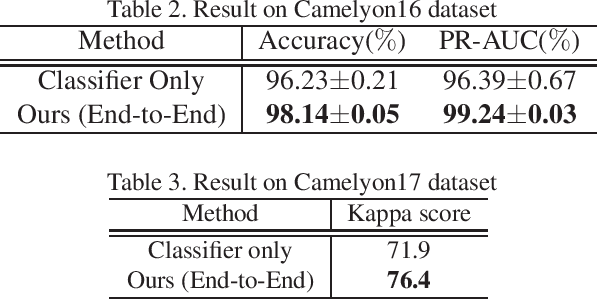
Abstract:Histopathological image analysis is an essential process for the discovery of diseases such as cancer. However, it is challenging to train CNN on whole slide images (WSIs) of gigapixel resolution considering the available memory capacity. Most of the previous works divide high resolution WSIs into small image patches and separately input them into the model to classify it as a tumor or a normal tissue. However, patch-based classification uses only patch-scale local information but ignores the relationship between neighboring patches. If we consider the relationship of neighboring patches and global features, we can improve the classification performance. In this paper, we propose a new model structure combining the patch-based classification model and whole slide-scale segmentation model in order to improve the prediction performance of automatic pathological diagnosis. We extract patch features from the classification model and input them into the segmentation model to obtain a whole slide tumor probability heatmap. The classification model considers patch-scale local features, and the segmentation model can take global information into account. We also propose a new optimization method that retains gradient information and trains the model partially for end-to-end learning with limited GPU memory capacity. We apply our method to the tumor/normal prediction on WSIs and the classification performance is improved compared with the conventional patch-based method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge