Yujun Zhang
OPAL: Operator-Programmed Algorithms for Landscape-Aware Black-Box Optimization
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Black-box optimization often relies on evolutionary and swarm algorithms whose performance is highly problem dependent. We view an optimizer as a short program over a small vocabulary of search operators and learn this operator program separately for each problem instance. We instantiate this idea in Operator-Programmed Algorithms (OPAL), a landscape-aware framework for continuous black-box optimization that uses a small design budget with a standard differential evolution baseline to probe the landscape, builds a $k$-nearest neighbor graph over sampled points, and encodes this trajectory with a graph neural network. A meta-learner then maps the resulting representation to a phase-wise schedule of exploration, restart, and local search operators. On the CEC~2017 test suite, a single meta-trained OPAL policy is statistically competitive with state-of-the-art adaptive differential evolution variants and achieves significant improvements over simpler baselines under nonparametric tests. Ablation studies on CEC~2017 justify the choices for the design phase, the trajectory graph, and the operator-program representation, while the meta-components add only modest wall-clock overhead. Overall, the results indicate that operator-programmed, landscape-aware per-instance design is a practical way forward beyond ad hoc metaphor-based algorithms in black-box optimization.
Enhance Graph Alignment for Large Language Models
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Graph-structured data is prevalent in the real world. Recently, due to the powerful emergent capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promising performance in modeling graphs. The key to effectively applying LLMs on graphs is converting graph data into a format LLMs can comprehend. Graph-to-token approaches are popular in enabling LLMs to process graph information. They transform graphs into sequences of tokens and align them with text tokens through instruction tuning, where self-supervised instruction tuning helps LLMs acquire general knowledge about graphs, and supervised fine-tuning specializes LLMs for the downstream tasks on graphs. Despite their initial success, we find that existing methods have a misalignment between self-supervised tasks and supervised downstream tasks, resulting in negative transfer from self-supervised fine-tuning to downstream tasks. To address these issues, we propose Graph Alignment Large Language Models (GALLM) to benefit from aligned task templates. In the self-supervised tuning stage, we introduce a novel text matching task using templates aligned with downstream tasks. In the task-specific tuning stage, we propose two category prompt methods that learn supervision information from additional explanation with further aligned templates. Experimental evaluations on four datasets demonstrate substantial improvements in supervised learning, multi-dataset generalizability, and particularly in zero-shot capability, highlighting the model's potential as a graph foundation model.
Spectral-based Graph Neural Networks for Complementary Item Recommendation
Jan 11, 2024



Abstract:Modeling complementary relationships greatly helps recommender systems to accurately and promptly recommend the subsequent items when one item is purchased. Unlike traditional similar relationships, items with complementary relationships may be purchased successively (such as iPhone and Airpods Pro), and they not only share relevance but also exhibit dissimilarity. Since the two attributes are opposites, modeling complementary relationships is challenging. Previous attempts to exploit these relationships have either ignored or oversimplified the dissimilarity attribute, resulting in ineffective modeling and an inability to balance the two attributes. Since Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) can capture the relevance and dissimilarity between nodes in the spectral domain, we can leverage spectral-based GNNs to effectively understand and model complementary relationships. In this study, we present a novel approach called Spectral-based Complementary Graph Neural Networks (SComGNN) that utilizes the spectral properties of complementary item graphs. We make the first observation that complementary relationships consist of low-frequency and mid-frequency components, corresponding to the relevance and dissimilarity attributes, respectively. Based on this spectral observation, we design spectral graph convolutional networks with low-pass and mid-pass filters to capture the low-frequency and mid-frequency components. Additionally, we propose a two-stage attention mechanism to adaptively integrate and balance the two attributes. Experimental results on four e-commerce datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, with SComGNN significantly outperforming existing baseline models.
NetGPT: Generative Pretrained Transformer for Network Traffic
Apr 19, 2023



Abstract:Pretrained models for network traffic can utilize large-scale raw data to learn the essential characteristics of network traffic, and generate distinguishable results for input traffic without considering specific downstream tasks. Effective pretrained models can significantly optimize the training efficiency and effectiveness of downstream tasks, such as traffic classification, attack detection, resource scheduling, protocol analysis, and traffic generation. Despite the great success of pretraining in natural language processing, there is no work in the network field. Considering the diverse demands and characteristics of network traffic and network tasks, it is non-trivial to build a pretrained model for network traffic and we face various challenges, especially the heterogeneous headers and payloads in the multi-pattern network traffic and the different dependencies for contexts of diverse downstream network tasks. To tackle these challenges, in this paper, we make the first attempt to provide a generative pretrained model for both traffic understanding and generation tasks. We propose the multi-pattern network traffic modeling to construct unified text inputs and support both traffic understanding and generation tasks. We further optimize the adaptation effect of the pretrained model to diversified tasks by shuffling header fields, segmenting packets in flows, and incorporating diverse task labels with prompts. Expensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our NetGPT in a range of traffic understanding and generation tasks, and outperform state-of-the-art baselines by a wide margin.
VIL-100: A New Dataset and A Baseline Model for Video Instance Lane Detection
Aug 19, 2021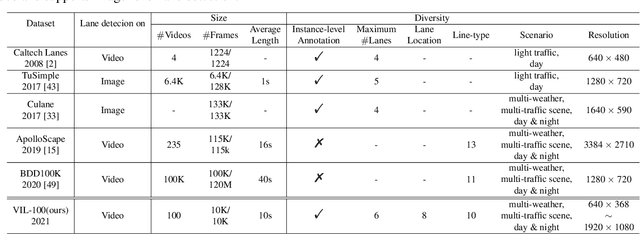

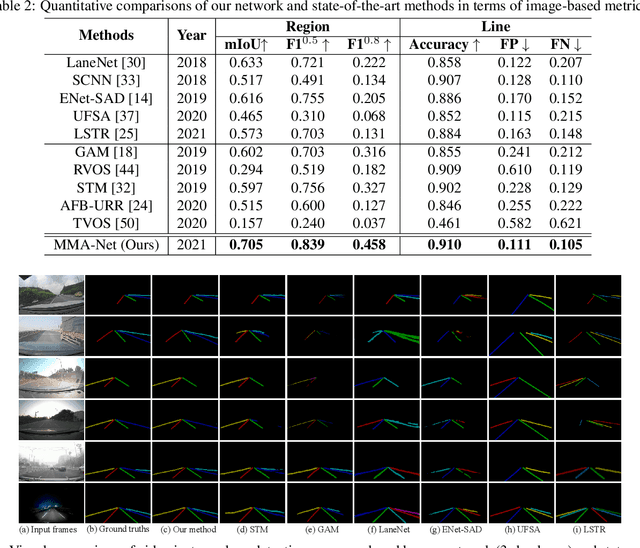
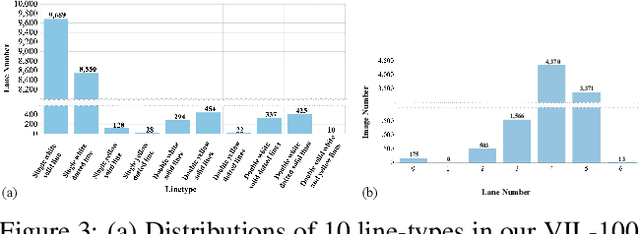
Abstract:Lane detection plays a key role in autonomous driving. While car cameras always take streaming videos on the way, current lane detection works mainly focus on individual images (frames) by ignoring dynamics along the video. In this work, we collect a new video instance lane detection (VIL-100) dataset, which contains 100 videos with in total 10,000 frames, acquired from different real traffic scenarios. All the frames in each video are manually annotated to a high-quality instance-level lane annotation, and a set of frame-level and video-level metrics are included for quantitative performance evaluation. Moreover, we propose a new baseline model, named multi-level memory aggregation network (MMA-Net), for video instance lane detection. In our approach, the representation of current frame is enhanced by attentively aggregating both local and global memory features from other frames. Experiments on the new collected dataset show that the proposed MMA-Net outperforms state-of-the-art lane detection methods and video object segmentation methods. We release our dataset and code at https://github.com/yujun0-0/MMA-Net.
Multiple Human Association between Top and Horizontal Views by Matching Subjects' Spatial Distributions
Jul 26, 2019

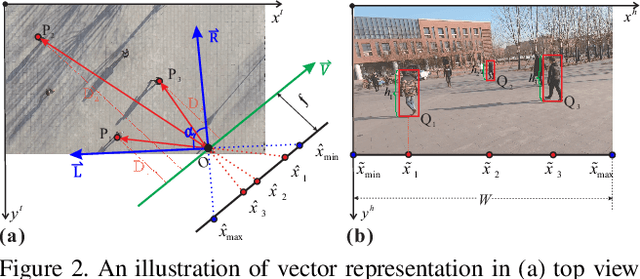
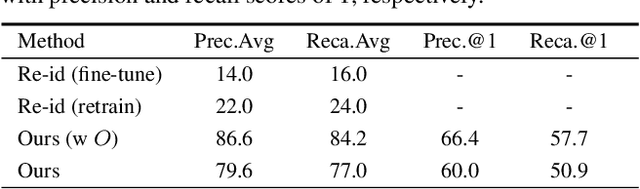
Abstract:Video surveillance can be significantly enhanced by using both top-view data, e.g., those from drone-mounted cameras in the air, and horizontal-view data, e.g., those from wearable cameras on the ground. Collaborative analysis of different-view data can facilitate various kinds of applications, such as human tracking, person identification, and human activity recognition. However, for such collaborative analysis, the first step is to associate people, referred to as subjects in this paper, across these two views. This is a very challenging problem due to large human-appearance difference between top and horizontal views. In this paper, we present a new approach to address this problem by exploring and matching the subjects' spatial distributions between the two views. More specifically, on the top-view image, we model and match subjects' relative positions to the horizontal-view camera in both views and define a matching cost to decide the actual location of horizontal-view camera and its view angle in the top-view image. We collect a new dataset consisting of top-view and horizontal-view image pairs for performance evaluation and the experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge