Yucong Wang
Integrated Sensing and Communications Framework for 6G Networks
May 30, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) framework for the sixth generation (6G) mobile networks, in which we decompose the real physical world into static environment, dynamic targets, and various object materials. The ubiquitous static environment occupies the vast majority of the physical world, for which we design static environment reconstruction (SER) scheme to obtain the layout and point cloud information of static buildings. The dynamic targets floating in static environments create the spatiotemporal transition of the physical world, for which we design comprehensive dynamic target sensing (DTS) scheme to detect, estimate, track, image and recognize the dynamic targets in real-time. The object materials enrich the electromagnetic laws of the physical world, for which we develop object material recognition (OMR) scheme to estimate the electromagnetic coefficient of the objects. Besides, to integrate these sensing functions into existing communications systems, we discuss the interference issues and corresponding solutions for ISAC cellular networks. Furthermore, we develop an ISAC hardware prototype platform that can reconstruct the environmental maps and sense the dynamic targets while maintaining communications services. With all these designs, the proposed ISAC framework can support multifarious emerging applications, such as digital twins, low altitude economy, internet of vehicles, marine management, deformation monitoring, etc.
Integrated Sensing and Communications in Clutter Environment
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a practical integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) framework to sense dynamic targets from clutter environment while ensuring users communications quality. To implement communications function and sensing function simultaneously, we design multiple communications beams that can communicate with the users as well as one sensing beam that can rotate and scan the entire space. To minimize the interference of sensing beam on existing communications systems, we divide the service area into sensing beam for sensing (S4S) sector and communications beam for sensing (C4S) sector, and provide beamforming design and power allocation optimization strategies for each type sector. Unlike most existing ISAC studies that ignore the interference of static environmental clutter on target sensing, we construct a mixed sensing channel model that includes both static environment and dynamic targets. When base station receives the echo signals, the mean phasor cancellation (MPC) method is employed to filter out the interference from static environmental clutter and to extract the effective dynamic target echoes. Then a complete and practical dynamic target sensing scheme is designed to detect the presence of dynamic targets and to estimate their angles, distances, and velocities. In particular, dynamic target detection and angle estimation are realized through angle-Doppler spectrum estimation (ADSE) and joint detection over multiple subcarriers (MSJD), while distance and velocity estimation are realized through the extended subspace algorithm. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and its superiority over the existing methods that ignore environmental clutter.
Computer Vision-Aided Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Based Beam Tracking: Prototyping and Experimental Results
Jul 11, 2022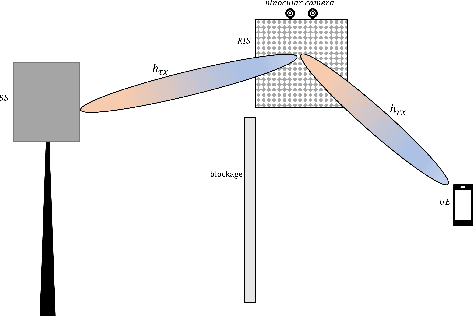
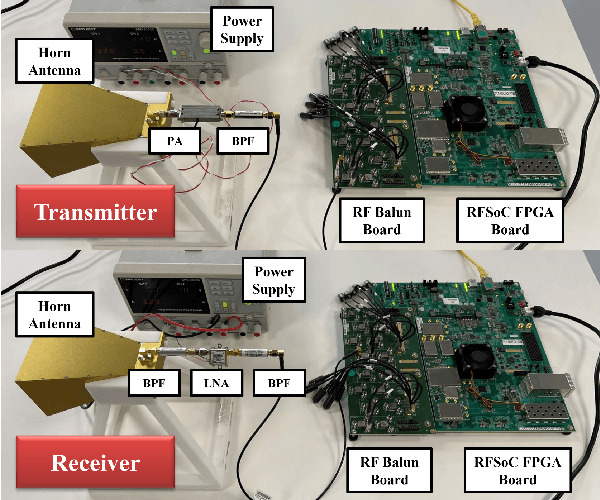
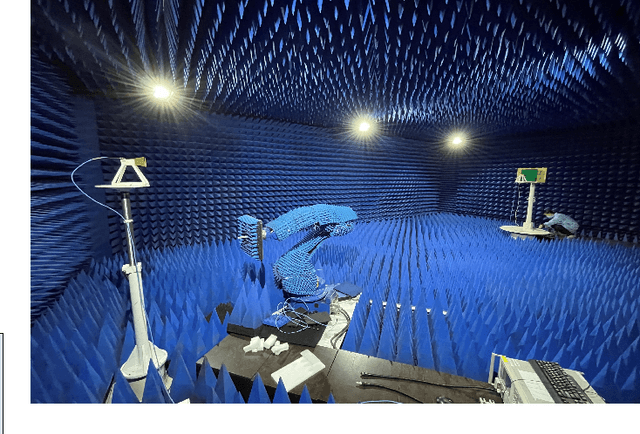
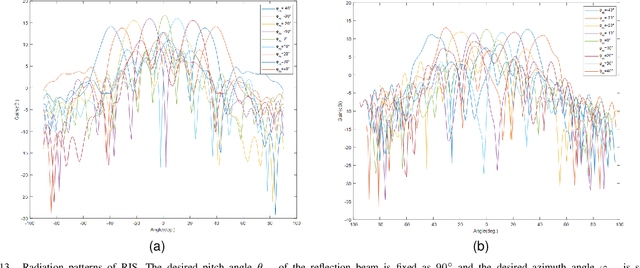
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel computer vision-based approach to aid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) for dynamic beam tracking and then implement the corresponding prototype verification system. A camera is attached at the RIS to obtain the visual information about the surrounding environment, with which RIS identifies the desired reflected beam direction and then adjusts the reflection coefficients according to the pre-designed codebook. Compared to the conventional approaches that utilize channel estimation or beam sweeping to obtain the reflection coefficients, the proposed one not only saves beam training overhead but also eliminates the requirement for extra feedback links. We build a 20-by-20 RIS running at 5.4 GHz and develop a high-speed control board to ensure the real-time refresh of the reflection coefficients. Meanwhile we implement an independent peer-to-peer communication system to simulate the communication between the base station and the user equipment. The vision-aided RIS prototype system is tested in two mobile scenarios: RIS works in near-field conditions as a passive array antenna of the base station; RIS works in far-field conditions to assist the communication between the base station and the user equipment. The experimental results show that RIS can quickly adjust the reflection coefficients for dynamic beam tracking with the help of visual information.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Efficient Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
May 11, 2022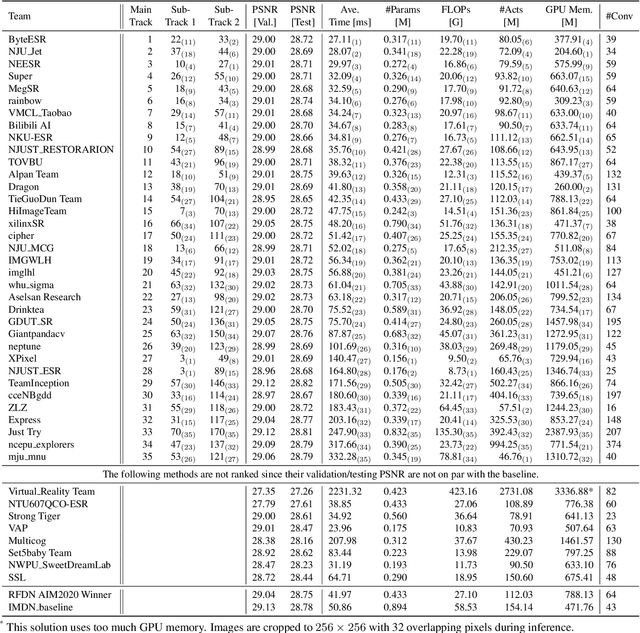
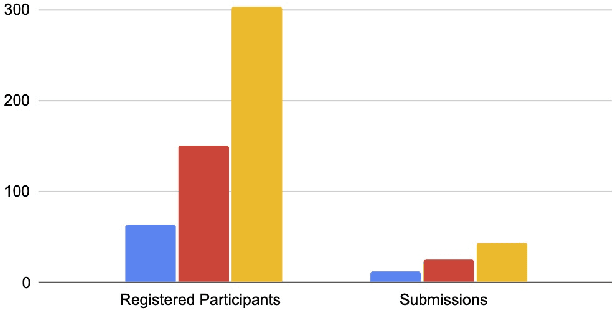
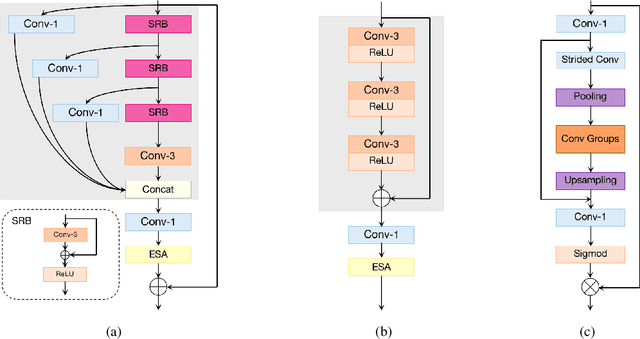
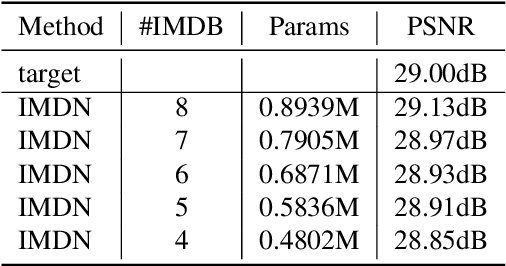
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 challenge on efficient single image super-resolution with focus on the proposed solutions and results. The task of the challenge was to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor of $\times$4 based on pairs of low and corresponding high resolution images. The aim was to design a network for single image super-resolution that achieved improvement of efficiency measured according to several metrics including runtime, parameters, FLOPs, activations, and memory consumption while at least maintaining the PSNR of 29.00dB on DIV2K validation set. IMDN is set as the baseline for efficiency measurement. The challenge had 3 tracks including the main track (runtime), sub-track one (model complexity), and sub-track two (overall performance). In the main track, the practical runtime performance of the submissions was evaluated. The rank of the teams were determined directly by the absolute value of the average runtime on the validation set and test set. In sub-track one, the number of parameters and FLOPs were considered. And the individual rankings of the two metrics were summed up to determine a final ranking in this track. In sub-track two, all of the five metrics mentioned in the description of the challenge including runtime, parameter count, FLOPs, activations, and memory consumption were considered. Similar to sub-track one, the rankings of five metrics were summed up to determine a final ranking. The challenge had 303 registered participants, and 43 teams made valid submissions. They gauge the state-of-the-art in efficient single image super-resolution.
NTIRE 2021 Challenge on Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Methods and Results
May 02, 2021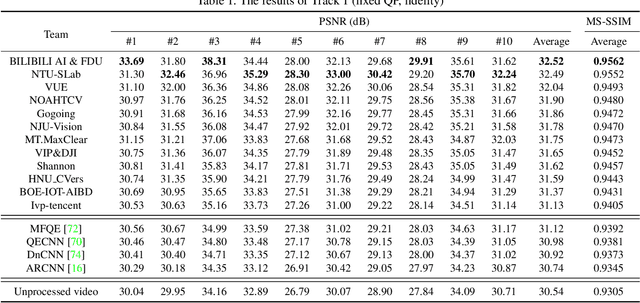
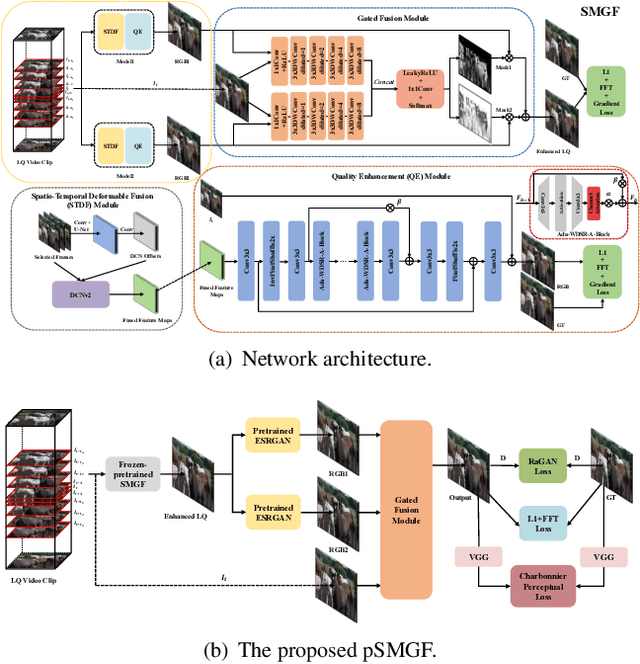
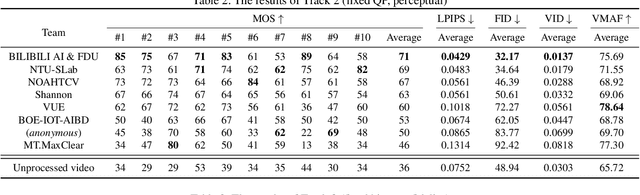
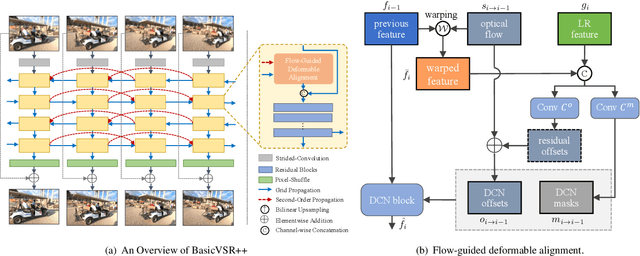
Abstract:This paper reviews the first NTIRE challenge on quality enhancement of compressed video, with a focus on the proposed methods and results. In this challenge, the new Large-scale Diverse Video (LDV) dataset is employed. The challenge has three tracks. Tracks 1 and 2 aim at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP, while Track 3 is designed for enhancing the videos compressed by x265 at a fixed bit-rate. Besides, the quality enhancement of Tracks 1 and 3 targets at improving the fidelity (PSNR), and Track 2 targets at enhancing the perceptual quality. The three tracks totally attract 482 registrations. In the test phase, 12 teams, 8 teams and 11 teams submitted the final results of Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of video quality enhancement. The homepage of the challenge: https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE21_VEnh
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge