Ming Ouyang
Enhancing Depth Completion with Multi-View Monitored Distillation
Mar 29, 2023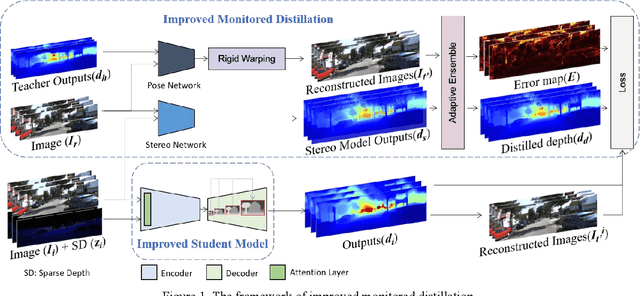
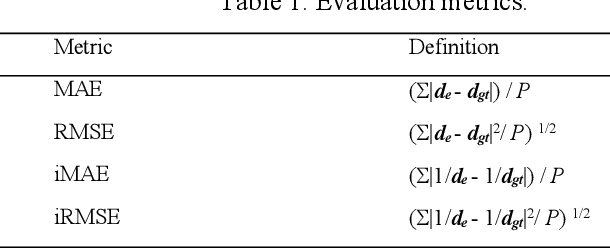
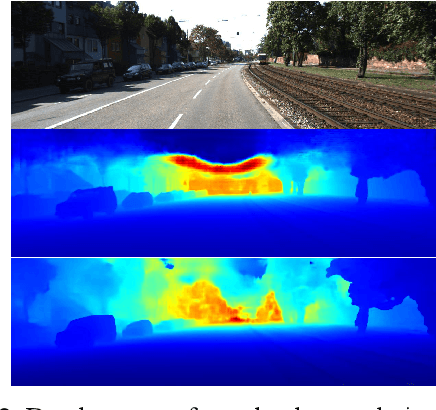
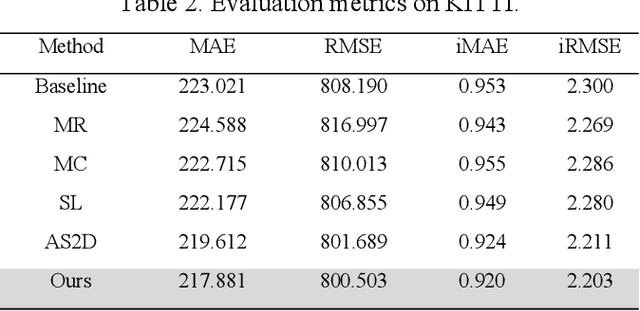
Abstract:This paper presents a novel method for depth completion, which leverages multi-view improved monitored distillation to generate more precise depth maps. Our approach builds upon the state-of-the-art ensemble distillation method, in which we introduce a stereo-based model as a teacher model to improve the accuracy of the student model for depth completion. By minimizing the reconstruction error for a given image during ensemble distillation, we can avoid learning inherent error modes of completion-based teachers. To provide self-supervised information, we also employ multi-view depth consistency and multi-scale minimum reprojection. These techniques utilize existing structural constraints to yield supervised signals for student model training, without requiring costly ground truth depth information. Our extensive experimental evaluation demonstrates that our proposed method significantly improves the accuracy of the baseline monitored distillation method.
Computer Vision-Aided Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Based Beam Tracking: Prototyping and Experimental Results
Jul 11, 2022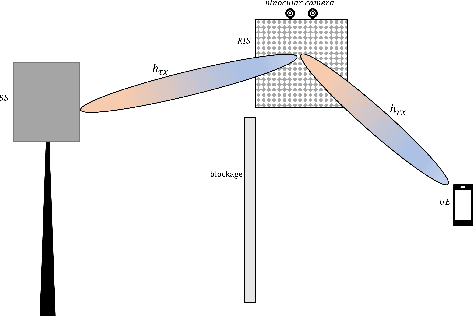
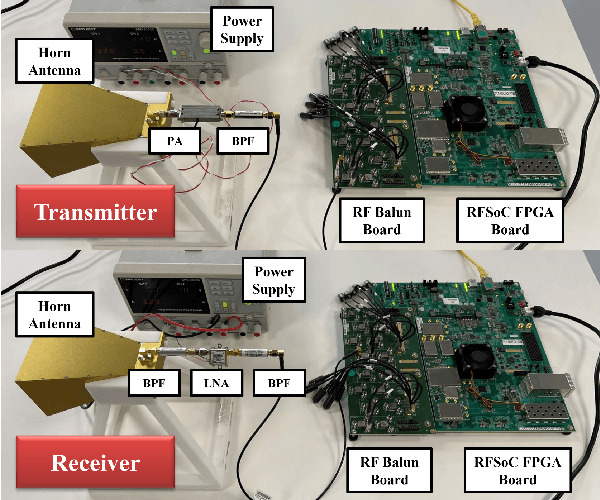
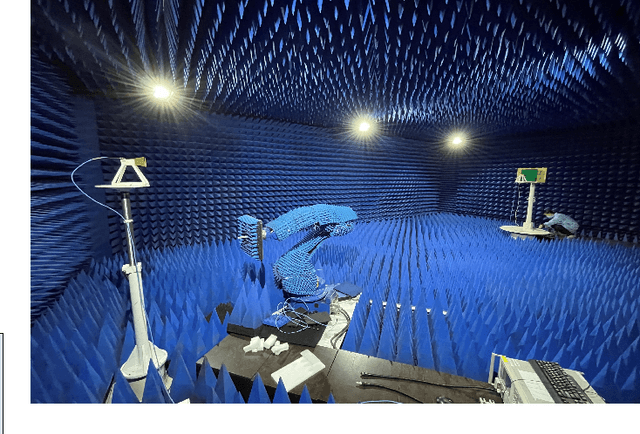
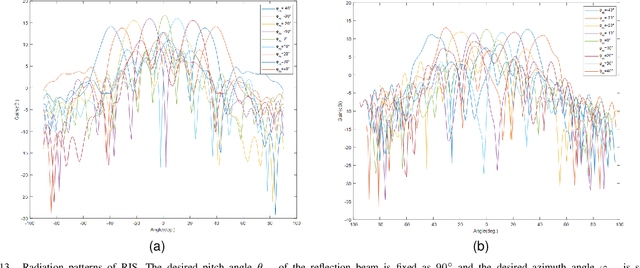
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel computer vision-based approach to aid Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) for dynamic beam tracking and then implement the corresponding prototype verification system. A camera is attached at the RIS to obtain the visual information about the surrounding environment, with which RIS identifies the desired reflected beam direction and then adjusts the reflection coefficients according to the pre-designed codebook. Compared to the conventional approaches that utilize channel estimation or beam sweeping to obtain the reflection coefficients, the proposed one not only saves beam training overhead but also eliminates the requirement for extra feedback links. We build a 20-by-20 RIS running at 5.4 GHz and develop a high-speed control board to ensure the real-time refresh of the reflection coefficients. Meanwhile we implement an independent peer-to-peer communication system to simulate the communication between the base station and the user equipment. The vision-aided RIS prototype system is tested in two mobile scenarios: RIS works in near-field conditions as a passive array antenna of the base station; RIS works in far-field conditions to assist the communication between the base station and the user equipment. The experimental results show that RIS can quickly adjust the reflection coefficients for dynamic beam tracking with the help of visual information.
Hierarchical Segment-based Optimization for SLAM
Nov 07, 2021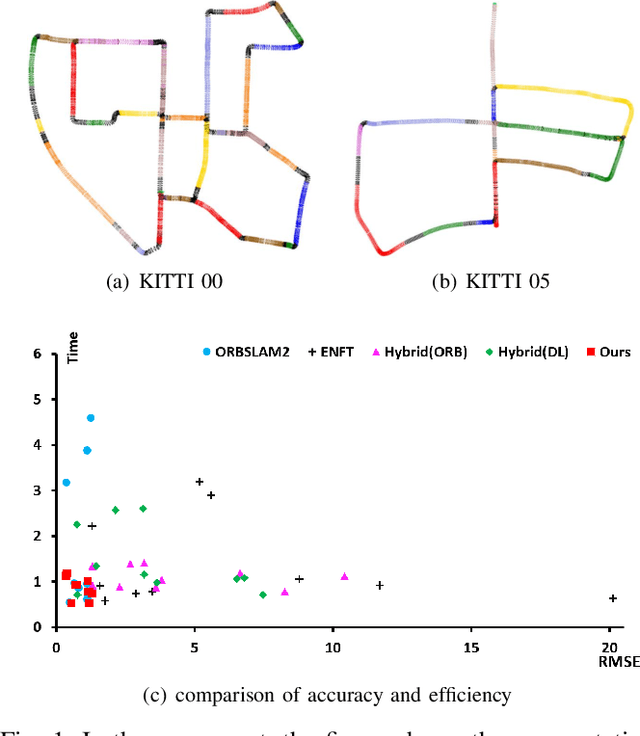
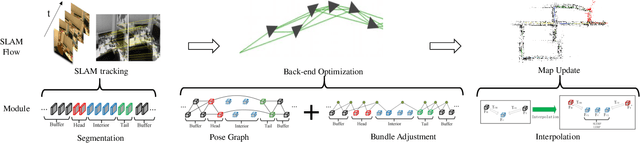
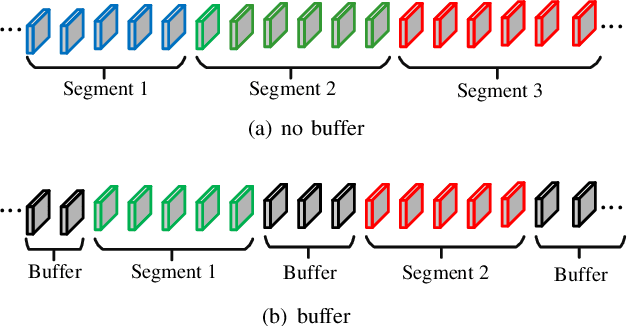
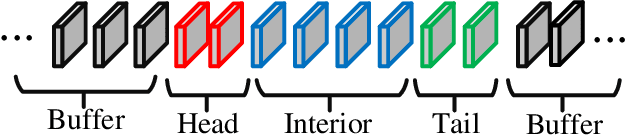
Abstract:This paper presents a hierarchical segment-based optimization method for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) system. First we propose a reliable trajectory segmentation method that can be used to increase efficiency in the back-end optimization. Then we propose a buffer mechanism for the first time to improve the robustness of the segmentation. During the optimization, we use global information to optimize the frames with large error, and interpolation instead of optimization to update well-estimated frames to hierarchically allocate the amount of computation according to error of each frame. Comparative experiments on the benchmark show that our method greatly improves the efficiency of optimization with almost no drop in accuracy, and outperforms existing high-efficiency optimization method by a large margin.
A Collaborative Visual SLAM Framework for Service Robots
Feb 05, 2021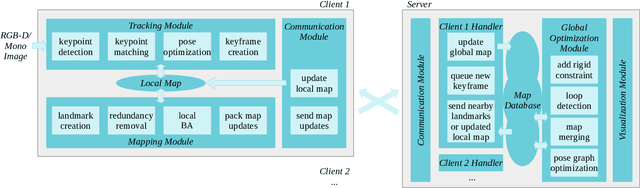
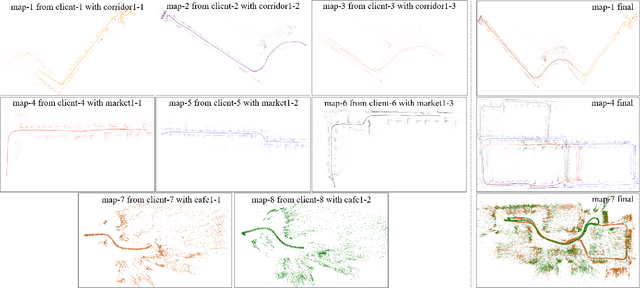
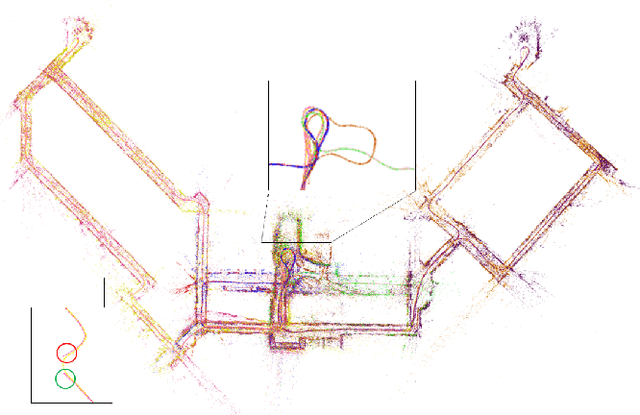
Abstract:With the rapid deployment of service robots, a method should be established to allow multiple robots to work in the same place to collaborate and share the spatial information. To this end, we present a collaborative visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) framework particularly designed for service robot scenarios. With an edge server maintaining a map database and performing global optimization, each robot can register to an existing map, update the map, or build new maps, all with a unified interface and low computation and memory cost. To enable real-time information sharing, an efficient landmark retrieval method is proposed to allow each robot to get nearby landmarks observed by others. The framework is general enough to support both RGB-D and monocular cameras, as well as robots with multiple cameras, taking the rigid constraints between cameras into consideration. The proposed framework has been fully implemented and verified with public datasets and live experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge