Yuan Zeng
Hyb-NeRF: A Multiresolution Hybrid Encoding for Neural Radiance Fields
Nov 21, 2023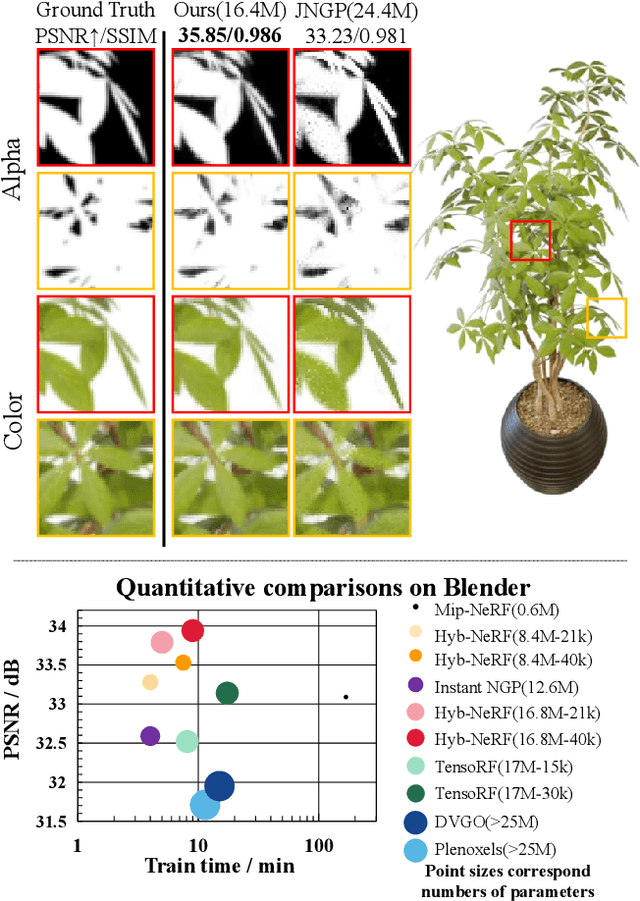

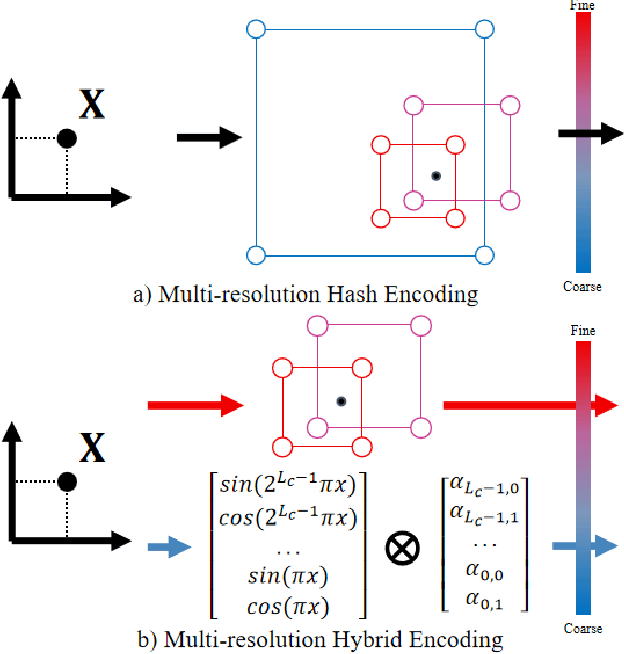

Abstract:Recent advances in Neural radiance fields (NeRF) have enabled high-fidelity scene reconstruction for novel view synthesis. However, NeRF requires hundreds of network evaluations per pixel to approximate a volume rendering integral, making it slow to train. Caching NeRFs into explicit data structures can effectively enhance rendering speed but at the cost of higher memory usage. To address these issues, we present Hyb-NeRF, a novel neural radiance field with a multi-resolution hybrid encoding that achieves efficient neural modeling and fast rendering, which also allows for high-quality novel view synthesis. The key idea of Hyb-NeRF is to represent the scene using different encoding strategies from coarse-to-fine resolution levels. Hyb-NeRF exploits memory-efficiency learnable positional features at coarse resolutions and the fast optimization speed and local details of hash-based feature grids at fine resolutions. In addition, to further boost performance, we embed cone tracing-based features in our learnable positional encoding that eliminates encoding ambiguity and reduces aliasing artifacts. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that Hyb-NeRF achieves faster rendering speed with better rending quality and even a lower memory footprint in comparison to previous state-of-the-art methods.
Multi-Channel Attentive Feature Fusion for Radio Frequency Fingerprinting
Mar 19, 2023



Abstract:Radio frequency fingerprinting (RFF) is a promising device authentication technique for securing the Internet of things. It exploits the intrinsic and unique hardware impairments of the transmitters for RF device identification. In real-world communication systems, hardware impairments across transmitters are subtle, which are difficult to model explicitly. Recently, due to the superior performance of deep learning (DL)-based classification models on real-world datasets, DL networks have been explored for RFF. Most existing DL-based RFF models use a single representation of radio signals as the input. Multi-channel input model can leverage information from different representations of radio signals and improve the identification accuracy of the RF fingerprint. In this work, we propose a novel multi-channel attentive feature fusion (McAFF) method for RFF. It utilizes multi-channel neural features extracted from multiple representations of radio signals, including IQ samples, carrier frequency offset, fast Fourier transform coefficients and short-time Fourier transform coefficients, for better RF fingerprint identification. The features extracted from different channels are fused adaptively using a shared attention module, where the weights of neural features from multiple channels are learned during training the McAFF model. In addition, we design a signal identification module using a convolution-based ResNeXt block to map the fused features to device identities. To evaluate the identification performance of the proposed method, we construct a WiFi dataset, named WFDI, using commercial WiFi end-devices as the transmitters and a Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP) as the receiver. ...
Learning to Scale Temperature in Masked Self-Attention for Image Inpainting
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in deep generative adversarial networks (GAN) and self-attention mechanism have led to significant improvements in the challenging task of inpainting large missing regions in an image. These methods integrate self-attention mechanism in neural networks to utilize surrounding neural elements based on their correlation and help the networks capture long-range dependencies. Temperature is a parameter in the Softmax function used in the self-attention, and it enables biasing the distribution of attention scores towards a handful of similar patches. Most existing self-attention mechanisms in image inpainting are convolution-based and set the temperature as a constant, performing patch matching in a limited feature space. In this work, we analyze the artifacts and training problems in previous self-attention mechanisms, and redesign the temperature learning network as well as the self-attention mechanism to address them. We present an image inpainting framework with a multi-head temperature masked self-attention mechanism, which provides stable and efficient temperature learning and uses multiple distant contextual information for high quality image inpainting. In addition to improving image quality of inpainting results, we generalize the proposed model to user-guided image editing by introducing a new sketch generation method. Extensive experiments on various datasets such as Paris StreetView, CelebA-HQ and Places2 clearly demonstrate that our method not only generates more natural inpainting results than previous works both in terms of perception image quality and quantitative metrics, but also enables to help users to generate more flexible results that are related to their sketch guidance.
Collaborative 3D Object Detection for Automatic Vehicle Systems via Learnable Communications
May 24, 2022



Abstract:Accurate detection of objects in 3D point clouds is a key problem in autonomous driving systems. Collaborative perception can incorporate information from spatially diverse sensors and provide significant benefits for improving the perception accuracy of autonomous driving systems. In this work, we consider that the autonomous vehicle uses local point cloud data and combines information from neighboring infrastructures through wireless links for cooperative 3D object detection. However, information sharing among vehicle and infrastructures in predefined communication schemes may result in communication congestion and/or bring limited performance improvement. To this end, we propose a novel collaborative 3D object detection framework that consists of three components: feature learning networks that map point clouds into feature maps; an efficient communication block that propagates compact and fine-grained query feature maps from vehicle to support infrastructures and optimizes attention weights between query and key to refine support feature maps; a region proposal network that fuses local feature maps and weighted support feature maps for 3D object detection. We evaluate the performance of the proposed framework using a synthetic cooperative dataset created in two complex driving scenarios: a roundabout and a T-junction. Experiment results and bandwidth usage analysis demonstrate that our approach can save communication and computation costs and significantly improve detection performance under different detection difficulties in all scenarios.
Learning of Frequency-Time Attention Mechanism for Automatic Modulation Recognition
Nov 05, 2021
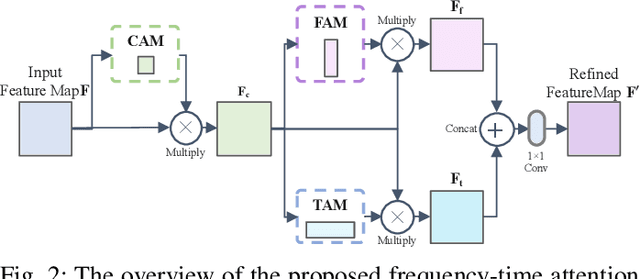
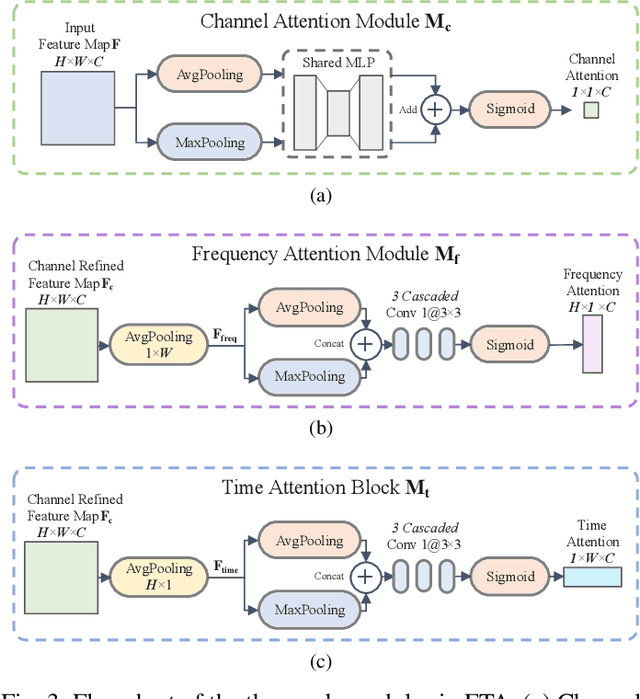
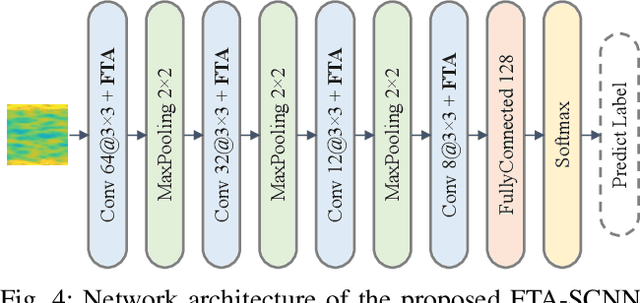
Abstract:Recent learning-based image classification and speech recognition approaches make extensive use of attention mechanisms to achieve state-of-the-art recognition power, which demonstrates the effectiveness of attention mechanisms. Motivated by the fact that the frequency and time information of modulated radio signals are crucial for modulation mode recognition, this paper proposes a frequency-time attention mechanism for a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based modulation recognition framework. The proposed frequency-time attention module is designed to learn which channel, frequency and time information is more meaningful in CNN for modulation recognition. We analyze the effectiveness of the proposed frequency-time attention mechanism and compare the proposed method with two existing learning-based methods. Experiments on an open-source modulation recognition dataset show that the recognition performance of the proposed framework is better than those of the framework without frequency-time attention and existing learning-based methods.
Inference with Hybrid Bio-hardware Neural Networks
May 28, 2019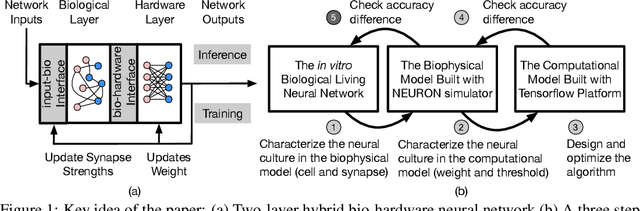
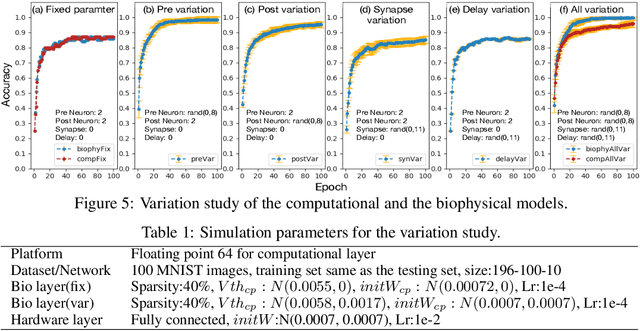
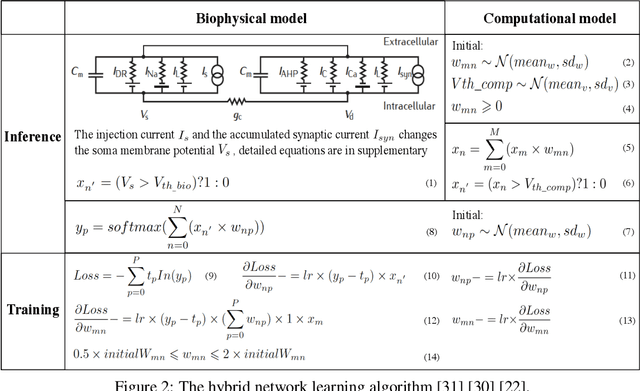
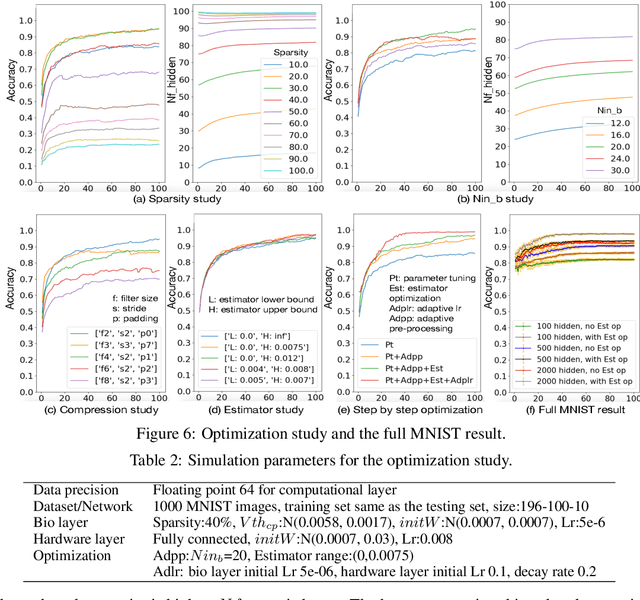
Abstract:To understand the learning process in brains, biologically plausible algorithms have been explored by modeling the detailed neuron properties and dynamics. On the other hand, simplified multi-layer models of neural networks have shown great success on computational tasks such as image classification and speech recognition. However, the computational models that can achieve good accuracy for these learning applications are very different from the bio-plausible models. This paper studies whether a bio-plausible model of a in vitro living neural network can be used to perform machine learning tasks and achieve good inference accuracy. A novel two-layer bio-hardware hybrid neural network is proposed. The biological layer faithfully models variations of synapses, neurons, and network sparsity in in vitro living neural networks. The hardware layer is a computational fully-connected layer that tunes parameters to optimize for accuracy. Several techniques are proposed to improve the inference accuracy of the proposed hybrid neural network. For instance, an adaptive pre-processing technique helps the proposed neural network to achieve good learning accuracy for different living neural network sparsity. The proposed hybrid neural network with realistic neuron parameters and variations achieves a 98.3% testing accuracy for the handwritten digit recognition task on the full MNIST dataset.
A context-based geoprocessing framework for optimizing meetup location of multiple moving objects along road networks
Dec 10, 2018

Abstract:Given different types of constraints on human life, people must make decisions that satisfy social activity needs. Minimizing costs (i.e., distance, time, or money) associated with travel plays an important role in perceived and realized social quality of life. Identifying optimal interaction locations on road networks when there are multiple moving objects (MMO) with space-time constraints remains a challenge. In this research, we formalize the problem of finding dynamic ideal interaction locations for MMO as a spatial optimization model and introduce a context-based geoprocessing heuristic framework to address this problem. As a proof of concept, a case study involving identification of a meetup location for multiple people under traffic conditions is used to validate the proposed geoprocessing framework. Five heuristic methods with regard to efficient shortest-path search space have been tested. We find that the R* tree-based algorithm performs the best with high quality solutions and low computation time. This framework is implemented in a GIS environment to facilitate integration with external geographic contextual information, e.g., temporary road barriers, points of interest (POI), and real-time traffic information, when dynamically searching for ideal meetup sites. The proposed method can be applied in trip planning, carpooling services, collaborative interaction, and logistics management.
* 34 pages, 8 figures
A Supervised STDP-based Training Algorithm for Living Neural Networks
Mar 21, 2018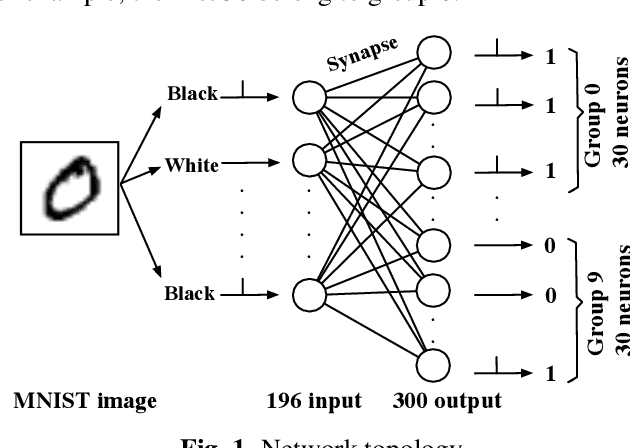
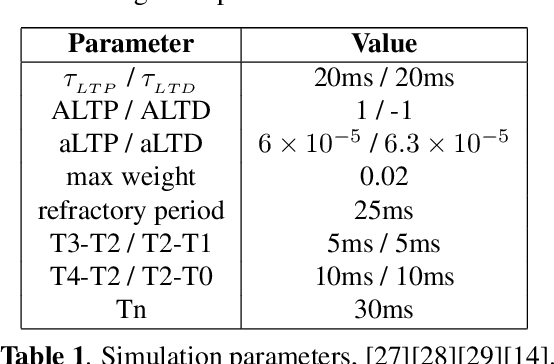
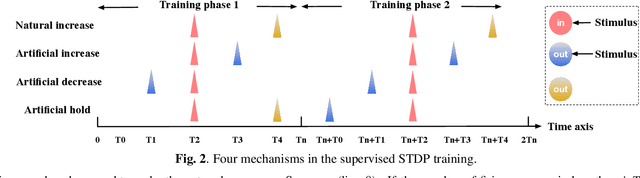
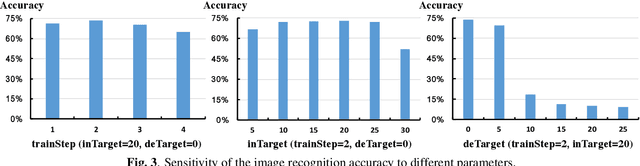
Abstract:Neural networks have shown great potential in many applications like speech recognition, drug discovery, image classification, and object detection. Neural network models are inspired by biological neural networks, but they are optimized to perform machine learning tasks on digital computers. The proposed work explores the possibilities of using living neural networks in vitro as basic computational elements for machine learning applications. A new supervised STDP-based learning algorithm is proposed in this work, which considers neuron engineering constrains. A 74.7% accuracy is achieved on the MNIST benchmark for handwritten digit recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge