Drew Patel
Inference with Hybrid Bio-hardware Neural Networks
May 28, 2019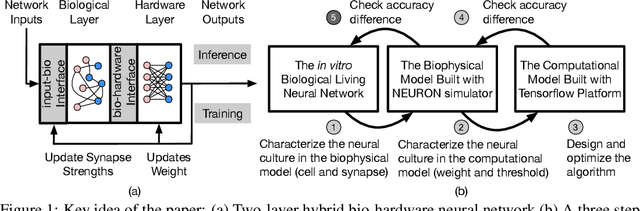
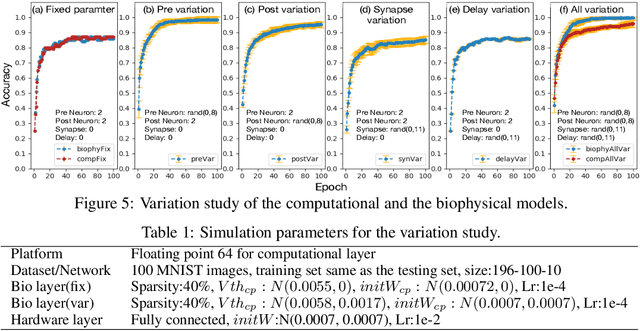
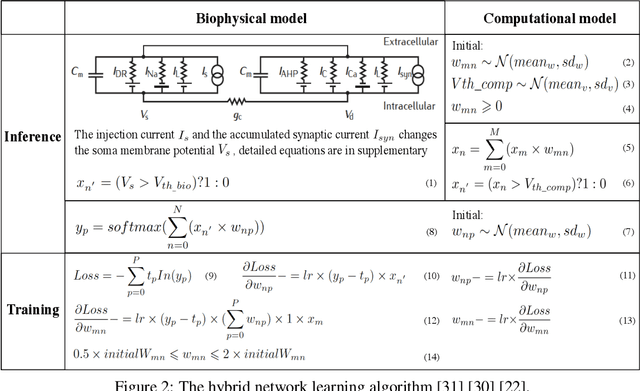
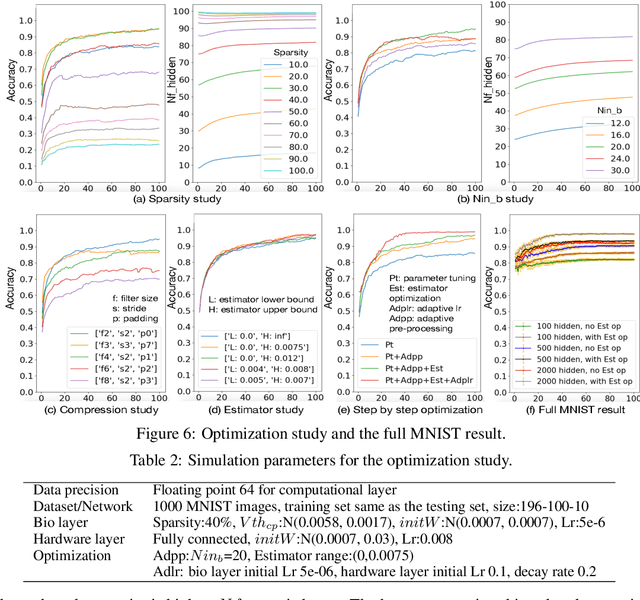
Abstract:To understand the learning process in brains, biologically plausible algorithms have been explored by modeling the detailed neuron properties and dynamics. On the other hand, simplified multi-layer models of neural networks have shown great success on computational tasks such as image classification and speech recognition. However, the computational models that can achieve good accuracy for these learning applications are very different from the bio-plausible models. This paper studies whether a bio-plausible model of a in vitro living neural network can be used to perform machine learning tasks and achieve good inference accuracy. A novel two-layer bio-hardware hybrid neural network is proposed. The biological layer faithfully models variations of synapses, neurons, and network sparsity in in vitro living neural networks. The hardware layer is a computational fully-connected layer that tunes parameters to optimize for accuracy. Several techniques are proposed to improve the inference accuracy of the proposed hybrid neural network. For instance, an adaptive pre-processing technique helps the proposed neural network to achieve good learning accuracy for different living neural network sparsity. The proposed hybrid neural network with realistic neuron parameters and variations achieves a 98.3% testing accuracy for the handwritten digit recognition task on the full MNIST dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge