Yongkang Zhang
Learning with Challenges: Adaptive Difficulty-Aware Data Generation for Mobile GUI Agent Training
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large-scale, high-quality interaction trajectories are essential for advancing mobile Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents. While existing methods typically rely on labor-intensive human demonstrations or automated model exploration to generate GUI trajectories, they lack fine-grained control over task difficulty. This fundamentally restricts learning effectiveness due to the mismatch between the training difficulty and the agent's capabilities. Inspired by how humans acquire skills through progressively challenging tasks, we propose MobileGen, a novel data generation framework that adaptively aligns training difficulty with the GUI agent's capability frontier. Specifically, MobileGen explicitly decouples task difficulty into structural (e.g., trajectory length) and semantic (e.g., task goal) dimensions. It then iteratively evaluates the agent on a curated prior dataset to construct a systematic profile of its capability frontier across these two dimensions. With this profile, the probability distribution of task difficulty is adaptively computed, from which the target difficulty for the next round of training can be sampled. Guided by the sampled difficulty, a multi-agent controllable generator is finally used to synthesize high-quality interaction trajectories along with corresponding task instructions. Extensive experiments show that MobileGen consistently outperforms existing data generation methods by improving the average performance of GUI agents by 1.57 times across multiple challenging benchmarks. This highlights the importance of capability-aligned data generation for effective mobile GUI agent training.
MVSS: A Unified Framework for Multi-View Structured Survey Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Scientific surveys require not only summarizing large bodies of literature, but also organizing them into clear and coherent conceptual structures. Existing automatic survey generation methods typically focus on linear text generation and struggle to explicitly model hierarchical relations among research topics and structured methodological comparisons, resulting in gaps in structural organization compared to expert-written surveys. We propose MVSS, a multi-view structured survey generation framework that jointly generates and aligns citation-grounded hierarchical trees, structured comparison tables, and survey text. MVSS follows a structure-first paradigm: it first constructs a conceptual tree of the research domain, then generates comparison tables constrained by the tree, and finally uses both as structural constraints for text generation. This enables complementary multi-view representations across structure, comparison, and narrative. We introduce an evaluation framework assessing structural quality, comparative completeness, and citation fidelity. Experiments on 76 computer science topics show MVSS outperforms existing methods in organization and evidence grounding, achieving performance comparable to expert surveys.
Temporal Transformer Networks with Self-Supervision for Action Recognition
Dec 17, 2021
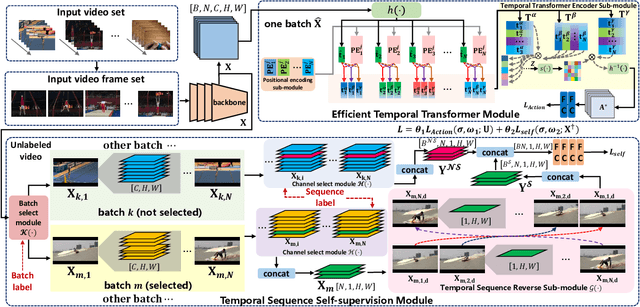
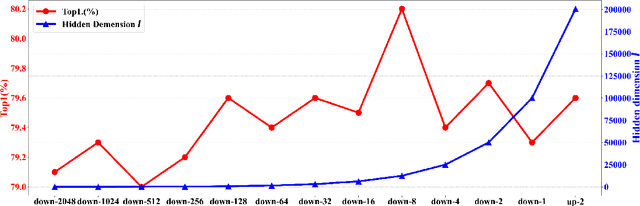
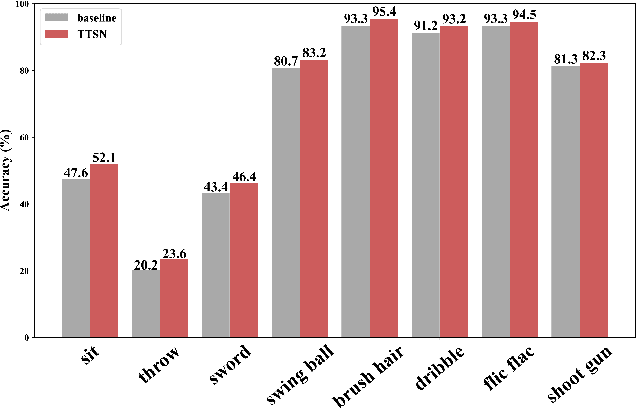
Abstract:In recent years, 2D Convolutional Networks-based video action recognition has encouragingly gained wide popularity; However, constrained by the lack of long-range non-linear temporal relation modeling and reverse motion information modeling, the performance of existing models is, therefore, undercut seriously. To address this urgent problem, we introduce a startling Temporal Transformer Network with Self-supervision (TTSN). Our high-performance TTSN mainly consists of a temporal transformer module and a temporal sequence self-supervision module. Concisely speaking, we utilize the efficient temporal transformer module to model the non-linear temporal dependencies among non-local frames, which significantly enhances complex motion feature representations. The temporal sequence self-supervision module we employ unprecedentedly adopts the streamlined strategy of "random batch random channel" to reverse the sequence of video frames, allowing robust extractions of motion information representation from inversed temporal dimensions and improving the generalization capability of the model. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets (HMDB51, UCF101, and Something-something V1) have conclusively demonstrated that our proposed TTSN is promising as it successfully achieves state-of-the-art performance for action recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge