Duo Wu
Learning with Challenges: Adaptive Difficulty-Aware Data Generation for Mobile GUI Agent Training
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large-scale, high-quality interaction trajectories are essential for advancing mobile Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents. While existing methods typically rely on labor-intensive human demonstrations or automated model exploration to generate GUI trajectories, they lack fine-grained control over task difficulty. This fundamentally restricts learning effectiveness due to the mismatch between the training difficulty and the agent's capabilities. Inspired by how humans acquire skills through progressively challenging tasks, we propose MobileGen, a novel data generation framework that adaptively aligns training difficulty with the GUI agent's capability frontier. Specifically, MobileGen explicitly decouples task difficulty into structural (e.g., trajectory length) and semantic (e.g., task goal) dimensions. It then iteratively evaluates the agent on a curated prior dataset to construct a systematic profile of its capability frontier across these two dimensions. With this profile, the probability distribution of task difficulty is adaptively computed, from which the target difficulty for the next round of training can be sampled. Guided by the sampled difficulty, a multi-agent controllable generator is finally used to synthesize high-quality interaction trajectories along with corresponding task instructions. Extensive experiments show that MobileGen consistently outperforms existing data generation methods by improving the average performance of GUI agents by 1.57 times across multiple challenging benchmarks. This highlights the importance of capability-aligned data generation for effective mobile GUI agent training.
CoBel-World: Harnessing LLM Reasoning to Build a Collaborative Belief World for Optimizing Embodied Multi-Agent Collaboration
Sep 26, 2025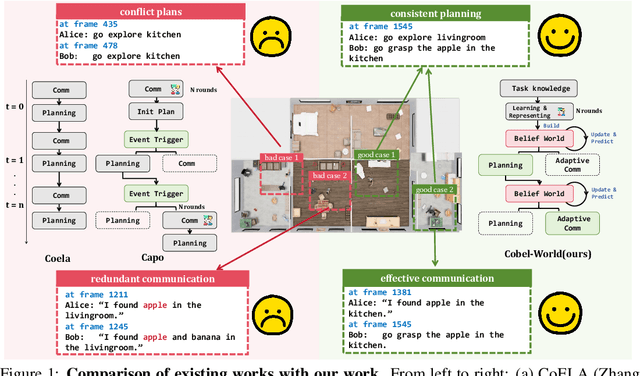
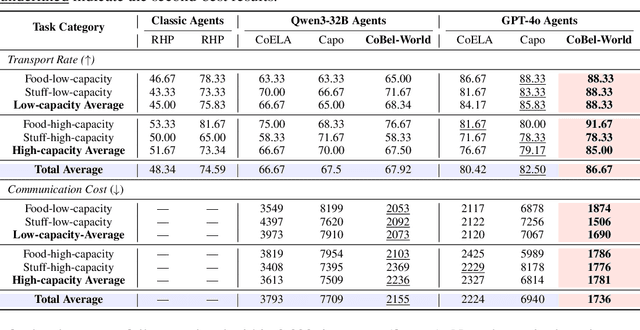
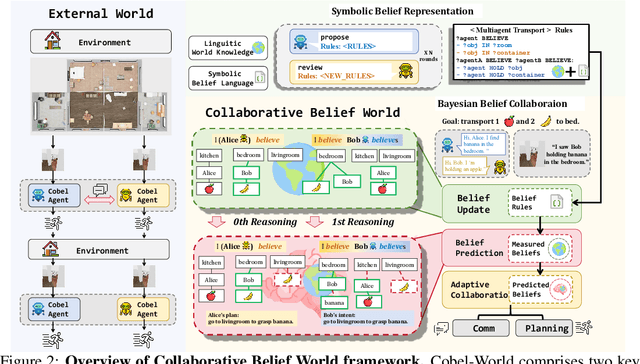
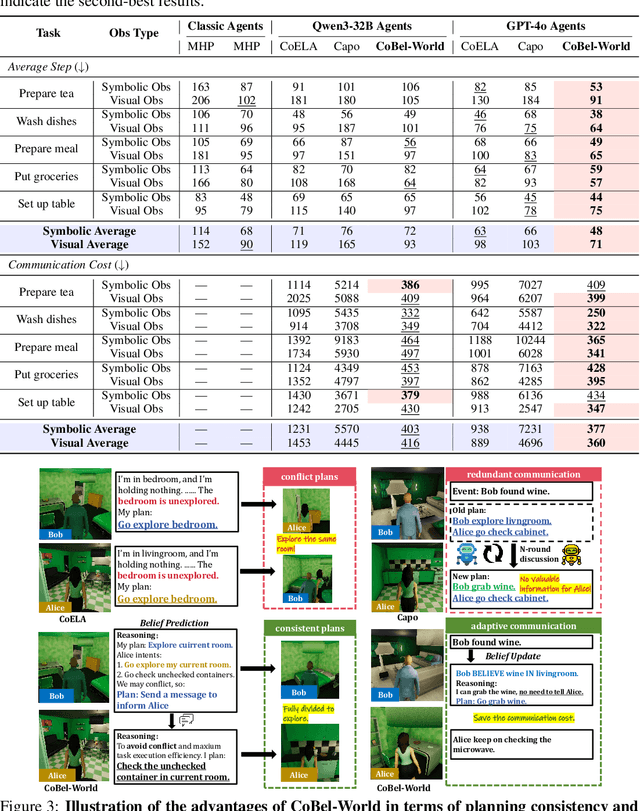
Abstract:Effective real-world multi-agent collaboration requires not only accurate planning but also the ability to reason about collaborators' intents -- a crucial capability for avoiding miscoordination and redundant communication under partial observable environments. Due to their strong planning and reasoning capabilities, large language models (LLMs) have emerged as promising autonomous agents for collaborative task solving. However, existing collaboration frameworks for LLMs overlook their reasoning potential for dynamic intent inference, and thus produce inconsistent plans and redundant communication, reducing collaboration efficiency. To bridge this gap, we propose CoBel-World, a novel framework that equips LLM agents with a collaborative belief world -- an internal representation jointly modeling the physical environment and collaborators' mental states. CoBel-World enables agents to parse open-world task knowledge into structured beliefs via a symbolic belief language, and perform zero-shot Bayesian-style belief updates through LLM reasoning. This allows agents to proactively detect potential miscoordination (e.g., conflicting plans) and communicate adaptively. Evaluated on challenging embodied benchmarks (i.e., TDW-MAT and C-WAH), CoBel-World significantly reduces communication costs by 22-60% and improves task completion efficiency by 4-28% compared to the strongest baseline. Our results show that explicit, intent-aware belief modeling is essential for efficient and human-like collaboration in LLM-based multi-agent systems.
CATP-LLM: Empowering Large Language Models for Cost-Aware Tool Planning
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Utilizing large language models (LLMs) for tool planning has emerged as a promising avenue for developing general AI systems, where LLMs automatically schedule external tools (e.g. vision models) to tackle complex tasks based on task descriptions. To push this paradigm toward practical applications, it is crucial for LLMs to consider tool execution costs (e.g. execution time) for tool planning. Unfortunately, prior studies overlook the tool execution costs, leading to the generation of expensive plans of which the costs outweigh task performance. To fill this gap, we propose the Cost-Aware Tool Planning with LLMs (CATP-LLM) framework, which for the first time provides a coherent design to empower LLMs for cost-aware tool planning. Specifically, CATP-LLM incorporates a tool planning language to enhance the LLM to generate non-sequential plans of multiple branches for efficient concurrent tool execution and cost reduction. Moreover, it further designs a cost-aware offline reinforcement learning algorithm to fine-tune the LLM to optimize the performance-cost trade-off in tool planning. In lack of public cost-related datasets, we further present OpenCATP, the first platform for cost-aware planning evaluation. Experiments on OpenCATP show that CATP-LLM outperforms GPT-4 even when using Llama2-7B as its backbone, with the average improvement of 28.2%-30.2% higher plan performance and 24.7%-45.8% lower costs even on the challenging planning tasks. The codes of CATP-LLM and OpenCATP will be publicly available.
Design of a W-band High-PAE Class A&AB Power Amplifier in 150nm GaAs Technology
Feb 11, 2024Abstract:Nanometer scale power amplifiers (PA) at sub-THz suffer from severe parasitic effects that lead to experience limited maximum frequency and reduced power performance at the device transceiver front end. The integrated circuits researchers proposed different PA design architecture combinations at scaled down technologies to overcome these limitations. Although the designs meet the minimum requirements, the power added efficiency (PAE) of PA is still quite low. In this paper, a W-band single-ended common-source (CS) and cascode integrated 3-stage 2-way PA design is proposed. The design integrated different key design methodologies to mitigate the parasitic; such as combined Class AB and Class A stages for gain-boosting and efficiency enhancement, Wilkinson power combiner for higher output power, linearity, and bandwidth, and transmission line (TL)-based wide band matching network for better inter-stage matching and compact size. The proposed PA design is validated using UMS 150-nm GaAs pHEMT using advanced design system (ADS) simulator. The results show that the proposed PA achieved a gain of 20.1 dB, an output power of 17.2 dBm, a PAE of 33 % and a 21 GHz bandwidth at 90 GHz Sub-THz band. The PA layout consumes only 5.66 X 2.51 mm2 die space including pads. Our proposed PA design will boost the research on sub-THz integrated circuits research and will smooth the wide spread adoption of 6G in near future.
Large Language Model Adaptation for Networking
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Many networking tasks now employ deep learning (DL) to solve complex prediction and system optimization problems. However, current design philosophy of DL-based algorithms entails intensive engineering overhead due to the manual design of deep neural networks (DNNs) for different networking tasks. Besides, DNNs tend to achieve poor generalization performance on unseen data distributions/environments. Motivated by the recent success of large language models (LLMs), for the first time, this work studies the LLM adaptation for networking to explore a more sustainable design philosophy. With the massive pre-trained knowledge and powerful inference ability, LLM can serve as the foundation model, and is expected to achieve "one model for all" with even better performance and stronger generalization for various tasks. In this paper, we present NetLLM, the first LLM adaptation framework that efficiently adapts LLMs to solve networking problems. NetLLM addresses many practical challenges in LLM adaptation, from how to process task-specific information with LLMs, to how to improve the efficiency of answer generation and acquiring domain knowledge for networking. Across three networking-related use cases - viewport prediction (VP), adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) and cluster job scheduling (CJS), we showcase the effectiveness of NetLLM in LLM adaptation for networking. Results show that the adapted LLM surpasses state-of-the-art algorithms by 10.1-36.6% for VP, 14.5-36.6% for ABR, 6.8-41.3% for CJS, and also achieves superior generalization performance.
ILCAS: Imitation Learning-Based Configuration-Adaptive Streaming for Live Video Analytics with Cross-Camera Collaboration
Aug 19, 2023Abstract:The high-accuracy and resource-intensive deep neural networks (DNNs) have been widely adopted by live video analytics (VA), where camera videos are streamed over the network to resource-rich edge/cloud servers for DNN inference. Common video encoding configurations (e.g., resolution and frame rate) have been identified with significant impacts on striking the balance between bandwidth consumption and inference accuracy and therefore their adaption scheme has been a focus of optimization. However, previous profiling-based solutions suffer from high profiling cost, while existing deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based solutions may achieve poor performance due to the usage of fixed reward function for training the agent, which fails to craft the application goals in various scenarios. In this paper, we propose ILCAS, the first imitation learning (IL) based configuration-adaptive VA streaming system. Unlike DRL-based solutions, ILCAS trains the agent with demonstrations collected from the expert which is designed as an offline optimal policy that solves the configuration adaption problem through dynamic programming. To tackle the challenge of video content dynamics, ILCAS derives motion feature maps based on motion vectors which allow ILCAS to visually ``perceive'' video content changes. Moreover, ILCAS incorporates a cross-camera collaboration scheme to exploit the spatio-temporal correlations of cameras for more proper configuration selection. Extensive experiments confirm the superiority of ILCAS compared with state-of-the-art solutions, with 2-20.9% improvement of mean accuracy and 19.9-85.3% reduction of chunk upload lag.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge