Yinghan Shen
Related Knowledge Perturbation Matters: Rethinking Multiple Pieces of Knowledge Editing in Same-Subject
Feb 08, 2025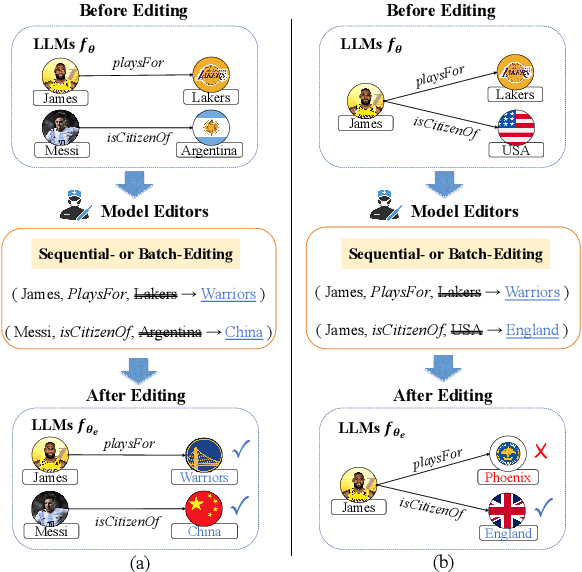
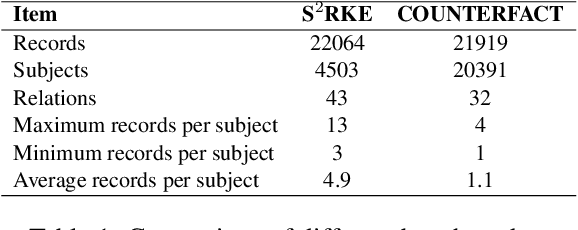
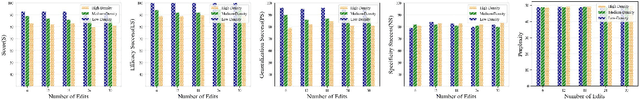
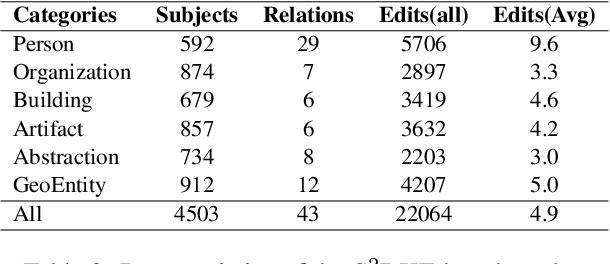
Abstract:Knowledge editing has become a promising approach for efficiently and precisely updating knowledge embedded in large language models (LLMs). In this work, we focus on Same-Subject Editing, which involves modifying multiple attributes of a single entity to ensure comprehensive and consistent updates to entity-centric knowledge. Through preliminary observation, we identify a significant challenge: Current state-of-the-art editing methods struggle when tasked with editing multiple related knowledge pieces for the same subject. To address the lack of relevant editing data for identical subjects in traditional benchmarks, we introduce the $\text{S}^2\text{RKE}$(Same-Subject Related Knowledge Editing) benchmark. Our extensive experiments reveal that only mainstream locate-then-edit methods, such as ROME and MEMIT, exhibit "related knowledge perturbation," where subsequent edits interfere with earlier ones. Further analysis reveals that these methods over-rely on subject information, neglecting other critical factors, resulting in reduced editing effectiveness.
A Survey on LLM-as-a-Judge
Nov 23, 2024Abstract:Accurate and consistent evaluation is crucial for decision-making across numerous fields, yet it remains a challenging task due to inherent subjectivity, variability, and scale. Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across diverse domains, leading to the emergence of "LLM-as-a-Judge," where LLMs are employed as evaluators for complex tasks. With their ability to process diverse data types and provide scalable, cost-effective, and consistent assessments, LLMs present a compelling alternative to traditional expert-driven evaluations. However, ensuring the reliability of LLM-as-a-Judge systems remains a significant challenge that requires careful design and standardization. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of LLM-as-a-Judge, addressing the core question: How can reliable LLM-as-a-Judge systems be built? We explore strategies to enhance reliability, including improving consistency, mitigating biases, and adapting to diverse assessment scenarios. Additionally, we propose methodologies for evaluating the reliability of LLM-as-a-Judge systems, supported by a novel benchmark designed for this purpose. To advance the development and real-world deployment of LLM-as-a-Judge systems, we also discussed practical applications, challenges, and future directions. This survey serves as a foundational reference for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.
Unlocking the Power of Large Language Models for Entity Alignment
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:Entity Alignment (EA) is vital for integrating diverse knowledge graph (KG) data, playing a crucial role in data-driven AI applications. Traditional EA methods primarily rely on comparing entity embeddings, but their effectiveness is constrained by the limited input KG data and the capabilities of the representation learning techniques. Against this backdrop, we introduce ChatEA, an innovative framework that incorporates large language models (LLMs) to improve EA. To address the constraints of limited input KG data, ChatEA introduces a KG-code translation module that translates KG structures into a format understandable by LLMs, thereby allowing LLMs to utilize their extensive background knowledge to improve EA accuracy. To overcome the over-reliance on entity embedding comparisons, ChatEA implements a two-stage EA strategy that capitalizes on LLMs' capability for multi-step reasoning in a dialogue format, thereby enhancing accuracy while preserving efficiency. Our experimental results affirm ChatEA's superior performance, highlighting LLMs' potential in facilitating EA tasks.
On the Evolution of Knowledge Graphs: A Survey and Perspective
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) are structured representations of diversified knowledge. They are widely used in various intelligent applications. In this article, we provide a comprehensive survey on the evolution of various types of knowledge graphs (i.e., static KGs, dynamic KGs, temporal KGs, and event KGs) and techniques for knowledge extraction and reasoning. Furthermore, we introduce the practical applications of different types of KGs, including a case study in financial analysis. Finally, we propose our perspective on the future directions of knowledge engineering, including the potential of combining the power of knowledge graphs and large language models (LLMs), and the evolution of knowledge extraction, reasoning, and representation.
Rethinking GNN-based Entity Alignment on Heterogeneous Knowledge Graphs: New Datasets and A New Method
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:The development of knowledge graph (KG) applications has led to a rising need for entity alignment (EA) between heterogeneous KGs that are extracted from various sources. Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have been widely adopted in EA tasks due to GNNs' impressive ability to capture structure information. However, we have observed that the oversimplified settings of the existing common EA datasets are distant from real-world scenarios, which obstructs a full understanding of the advancements achieved by recent methods. This phenomenon makes us ponder: Do existing GNN-based EA methods really make great progress? In this paper, to study the performance of EA methods in realistic settings, we focus on the alignment of highly heterogeneous KGs (HHKGs) (e.g., event KGs and general KGs) which are different with regard to the scale and structure, and share fewer overlapping entities. First, we sweep the unreasonable settings, and propose two new HHKG datasets that closely mimic real-world EA scenarios. Then, based on the proposed datasets, we conduct extensive experiments to evaluate previous representative EA methods, and reveal interesting findings about the progress of GNN-based EA methods. We find that the structural information becomes difficult to exploit but still valuable in aligning HHKGs. This phenomenon leads to inferior performance of existing EA methods, especially GNN-based methods. Our findings shed light on the potential problems resulting from an impulsive application of GNN-based methods as a panacea for all EA datasets. Finally, we introduce a simple but effective method: Simple-HHEA, which comprehensively utilizes entity name, structure, and temporal information. Experiment results show Simple-HHEA outperforms previous models on HHKG datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge