Wenbin Duan
Circular Reasoning: Understanding Self-Reinforcing Loops in Large Reasoning Models
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Despite the success of test-time scaling, Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) frequently encounter repetitive loops that lead to computational waste and inference failure. In this paper, we identify a distinct failure mode termed Circular Reasoning. Unlike traditional model degeneration, this phenomenon manifests as a self-reinforcing trap where generated content acts as a logical premise for its own recurrence, compelling the reiteration of preceding text. To systematically analyze this phenomenon, we introduce LoopBench, a dataset designed to capture two distinct loop typologies: numerical loops and statement loops. Mechanistically, we characterize circular reasoning as a state collapse exhibiting distinct boundaries, where semantic repetition precedes textual repetition. We reveal that reasoning impasses trigger the loop onset, which subsequently persists as an inescapable cycle driven by a self-reinforcing V-shaped attention mechanism. Guided by these findings, we employ the Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) algorithm to capture these precursors for early loop prediction. Experiments across diverse LRMs validate its accuracy and elucidate the stability of long-chain reasoning.
Related Knowledge Perturbation Matters: Rethinking Multiple Pieces of Knowledge Editing in Same-Subject
Feb 08, 2025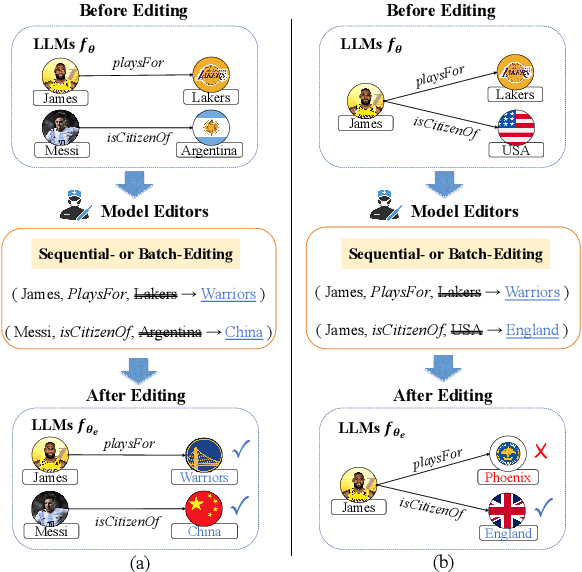
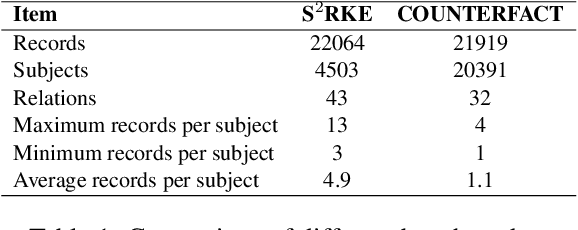
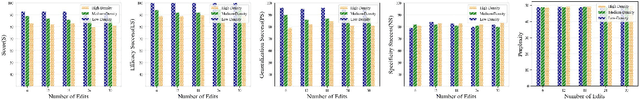
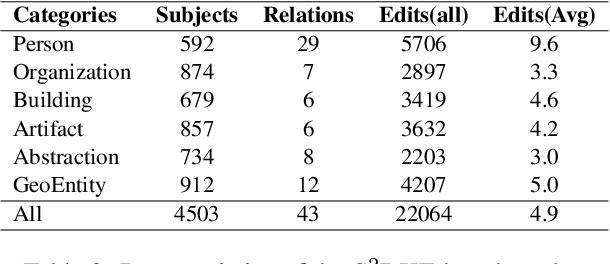
Abstract:Knowledge editing has become a promising approach for efficiently and precisely updating knowledge embedded in large language models (LLMs). In this work, we focus on Same-Subject Editing, which involves modifying multiple attributes of a single entity to ensure comprehensive and consistent updates to entity-centric knowledge. Through preliminary observation, we identify a significant challenge: Current state-of-the-art editing methods struggle when tasked with editing multiple related knowledge pieces for the same subject. To address the lack of relevant editing data for identical subjects in traditional benchmarks, we introduce the $\text{S}^2\text{RKE}$(Same-Subject Related Knowledge Editing) benchmark. Our extensive experiments reveal that only mainstream locate-then-edit methods, such as ROME and MEMIT, exhibit "related knowledge perturbation," where subsequent edits interfere with earlier ones. Further analysis reveals that these methods over-rely on subject information, neglecting other critical factors, resulting in reduced editing effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge