Zhiyi Yin
PersonaAct: Simulating Short-Video Users with Personalized Agents for Counterfactual Filter Bubble Auditing
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Short-video platforms rely on personalized recommendation, raising concerns about filter bubbles that narrow content exposure. Auditing such phenomena at scale is challenging because real user studies are costly and privacy-sensitive, and existing simulators fail to reproduce realistic behaviors due to their reliance on textual signals and weak personalization. We propose PersonaAct, a framework for simulating short-video users with persona-conditioned multimodal agents trained on real behavioral traces for auditing filter bubbles in breadth and depth. PersonaAct synthesizes interpretable personas through automated interviews combining behavioral analysis with structured questioning, then trains agents on multimodal observations using supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. We deploy trained agents for filter bubble auditing and evaluate bubble breadth via content diversity and bubble depth via escape potential. The evaluation demonstrates substantial improvements in fidelity over generic LLM baselines, enabling realistic behavior reproduction. Results reveal significant content narrowing over interaction. However, we find that Bilibili demonstrates the strongest escape potential. We release the first open multimodal short-video dataset and code to support reproducible auditing of recommender systems.
Projecting Out the Malice: A Global Subspace Approach to LLM Detoxification
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit exceptional performance but pose inherent risks of generating toxic content, restricting their safe deployment. While traditional methods (e.g., alignment) adjust output preferences, they fail to eliminate underlying toxic regions in parameters, leaving models vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Prior mechanistic studies characterize toxic regions as "toxic vectors" or "layer-wise subspaces", yet our analysis identifies critical limitations: i) Removed toxic vectors can be reconstructed via linear combinations of non-toxic vectors, demanding targeting of entire toxic subspace; ii) Contrastive objective over limited samples inject noise into layer-wise subspaces, hindering stable extraction. These highlight the challenge of identifying robust toxic subspace and removing them. Therefore, we propose GLOSS (GLobal tOxic Subspace Suppression), a lightweight method that mitigates toxicity by identifying and eliminating this global subspace from FFN parameters. Experiments on LLMs (e.g., Qwen3) show GLOSS achieves SOTA detoxification while preserving general capabilities without requiring large-scale retraining. WARNING: This paper contains context which is toxic in nature.
Circular Reasoning: Understanding Self-Reinforcing Loops in Large Reasoning Models
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Despite the success of test-time scaling, Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) frequently encounter repetitive loops that lead to computational waste and inference failure. In this paper, we identify a distinct failure mode termed Circular Reasoning. Unlike traditional model degeneration, this phenomenon manifests as a self-reinforcing trap where generated content acts as a logical premise for its own recurrence, compelling the reiteration of preceding text. To systematically analyze this phenomenon, we introduce LoopBench, a dataset designed to capture two distinct loop typologies: numerical loops and statement loops. Mechanistically, we characterize circular reasoning as a state collapse exhibiting distinct boundaries, where semantic repetition precedes textual repetition. We reveal that reasoning impasses trigger the loop onset, which subsequently persists as an inescapable cycle driven by a self-reinforcing V-shaped attention mechanism. Guided by these findings, we employ the Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) algorithm to capture these precursors for early loop prediction. Experiments across diverse LRMs validate its accuracy and elucidate the stability of long-chain reasoning.
LLM4MEA: Data-free Model Extraction Attacks on Sequential Recommenders via Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the vulnerability of sequential recommender systems to Model Extraction Attacks (MEAs). MEAs collect responses from recommender systems to replicate their functionality, enabling unauthorized deployments and posing critical privacy and security risks. Black-box attacks in prior MEAs are ineffective at exposing recommender system vulnerabilities due to random sampling in data selection, which leads to misaligned synthetic and real-world distributions. To overcome this limitation, we propose LLM4MEA, a novel model extraction method that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) as human-like rankers to generate data. It generates data through interactions between the LLM ranker and target recommender system. In each interaction, the LLM ranker analyzes historical interactions to understand user behavior, and selects items from recommendations with consistent preferences to extend the interaction history, which serves as training data for MEA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLM4MEA significantly outperforms existing approaches in data quality and attack performance, reducing the divergence between synthetic and real-world data by up to 64.98% and improving MEA performance by 44.82% on average. From a defensive perspective, we propose a simple yet effective defense strategy and identify key hyperparameters of recommender systems that can mitigate the risk of MEAs.
Related Knowledge Perturbation Matters: Rethinking Multiple Pieces of Knowledge Editing in Same-Subject
Feb 08, 2025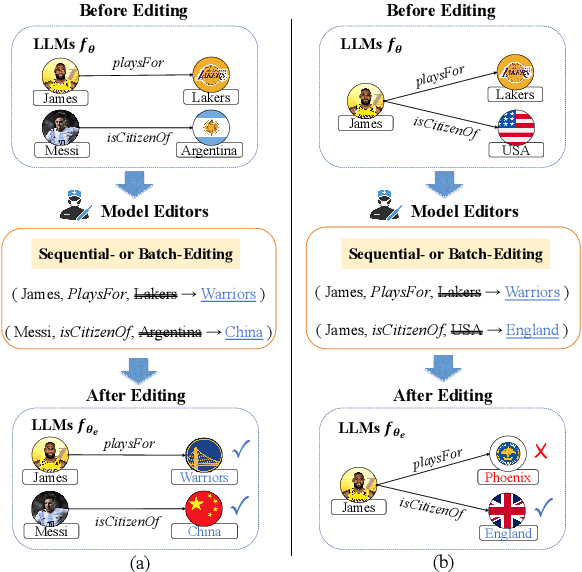
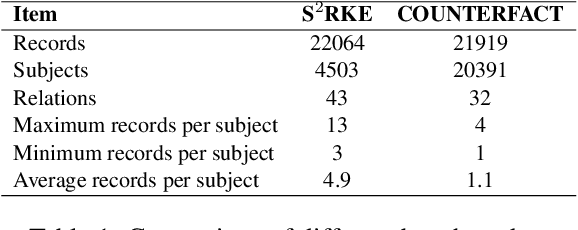
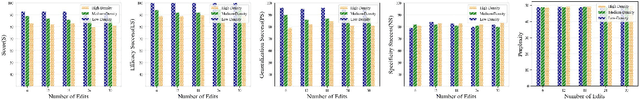
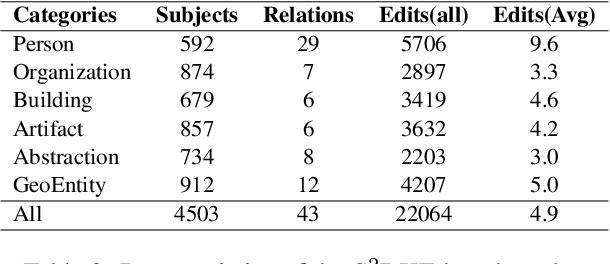
Abstract:Knowledge editing has become a promising approach for efficiently and precisely updating knowledge embedded in large language models (LLMs). In this work, we focus on Same-Subject Editing, which involves modifying multiple attributes of a single entity to ensure comprehensive and consistent updates to entity-centric knowledge. Through preliminary observation, we identify a significant challenge: Current state-of-the-art editing methods struggle when tasked with editing multiple related knowledge pieces for the same subject. To address the lack of relevant editing data for identical subjects in traditional benchmarks, we introduce the $\text{S}^2\text{RKE}$(Same-Subject Related Knowledge Editing) benchmark. Our extensive experiments reveal that only mainstream locate-then-edit methods, such as ROME and MEMIT, exhibit "related knowledge perturbation," where subsequent edits interfere with earlier ones. Further analysis reveals that these methods over-rely on subject information, neglecting other critical factors, resulting in reduced editing effectiveness.
Diversified Co-Attention towards Informative Live Video Commenting
Nov 07, 2019



Abstract:We focus on the task of Automatic Live Video Commenting (ALVC), which aims to generate real-time video comments based on both video frames and other viewers' remarks. An intractable challenge in this task is the appropriate modeling of complex dependencies between video and textual inputs. Previous work in the ALVC task applies separate attention on these two input sources to obtain their representations. In this paper, we argue that the information of video and text should be modeled integrally. We propose a novel model equipped with a Diversified Co-Attention layer (DCA) and a Gated Attention Module (GAM). DCA allows interactions between video and text from diversified perspectives via metric learning, while GAM collects an informative context for comment generation. We further introduce a parameter orthogonalization technique to allieviate information redundancy in DCA. Experiment results show that our model outperforms previous approaches in the ALVC task and the traditional co-attention model, achieving state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge