Zhongwu Chen
On the Evolution of Knowledge Graphs: A Survey and Perspective
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) are structured representations of diversified knowledge. They are widely used in various intelligent applications. In this article, we provide a comprehensive survey on the evolution of various types of knowledge graphs (i.e., static KGs, dynamic KGs, temporal KGs, and event KGs) and techniques for knowledge extraction and reasoning. Furthermore, we introduce the practical applications of different types of KGs, including a case study in financial analysis. Finally, we propose our perspective on the future directions of knowledge engineering, including the potential of combining the power of knowledge graphs and large language models (LLMs), and the evolution of knowledge extraction, reasoning, and representation.
Incorporating Structured Sentences with Time-enhanced BERT for Fully-inductive Temporal Relation Prediction
Apr 10, 2023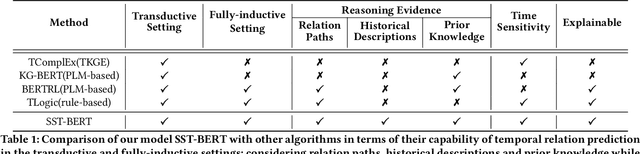
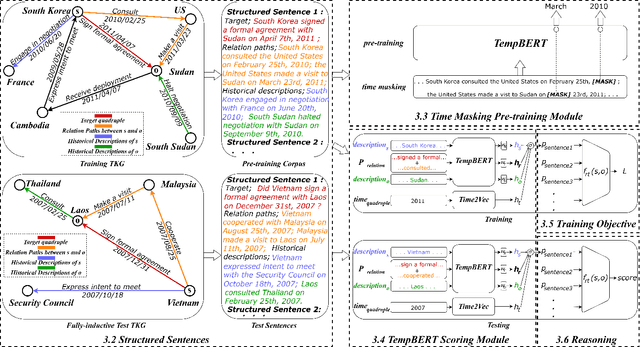
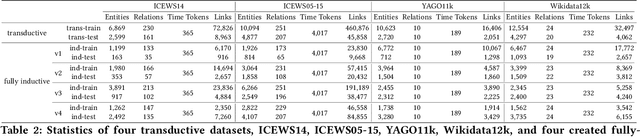
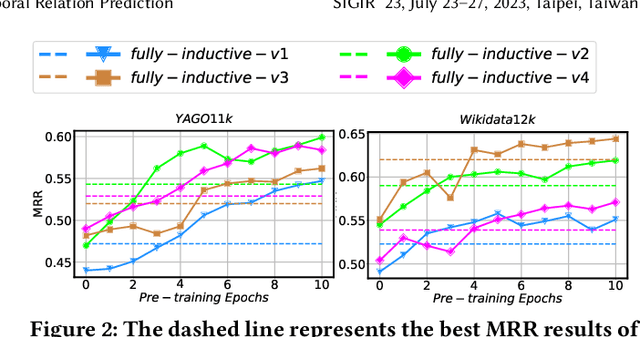
Abstract:Temporal relation prediction in incomplete temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) is a popular temporal knowledge graph completion (TKGC) problem in both transductive and inductive settings. Traditional embedding-based TKGC models (TKGE) rely on structured connections and can only handle a fixed set of entities, i.e., the transductive setting. In the inductive setting where test TKGs contain emerging entities, the latest methods are based on symbolic rules or pre-trained language models (PLMs). However, they suffer from being inflexible and not time-specific, respectively. In this work, we extend the fully-inductive setting, where entities in the training and test sets are totally disjoint, into TKGs and take a further step towards a more flexible and time-sensitive temporal relation prediction approach SST-BERT, incorporating Structured Sentences with Time-enhanced BERT. Our model can obtain the entity history and implicitly learn rules in the semantic space by encoding structured sentences, solving the problem of inflexibility. We propose to use a time masking MLM task to pre-train BERT in a corpus rich in temporal tokens specially generated for TKGs, enhancing the time sensitivity of SST-BERT. To compute the probability of occurrence of a target quadruple, we aggregate all its structured sentences from both temporal and semantic perspectives into a score. Experiments on the transductive datasets and newly generated fully-inductive benchmarks show that SST-BERT successfully improves over state-of-the-art baselines.
Meta-Learning Based Knowledge Extrapolation for Temporal Knowledge Graph
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:In the last few years, the solution to Knowledge Graph (KG) completion via learning embeddings of entities and relations has attracted a surge of interest. Temporal KGs(TKGs) extend traditional Knowledge Graphs (KGs) by associating static triples with timestamps forming quadruples. Different from KGs and TKGs in the transductive setting, constantly emerging entities and relations in incomplete TKGs create demand to predict missing facts with unseen components, which is the extrapolation setting. Traditional temporal knowledge graph embedding (TKGE) methods are limited in the extrapolation setting since they are trained within a fixed set of components. In this paper, we propose a Meta-Learning based Temporal Knowledge Graph Extrapolation (MTKGE) model, which is trained on link prediction tasks sampled from the existing TKGs and tested in the emerging TKGs with unseen entities and relations. Specifically, we meta-train a GNN framework that captures relative position patterns and temporal sequence patterns between relations. The learned embeddings of patterns can be transferred to embed unseen components. Experimental results on two different TKG extrapolation datasets show that MTKGE consistently outperforms both the existing state-of-the-art models for knowledge graph extrapolation and specifically adapted KGE and TKGE baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge