Yakun Chen
Listwise Preference Alignment Optimization for Tail Item Recommendation
Jul 03, 2025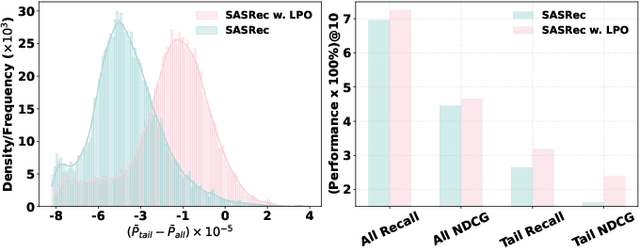
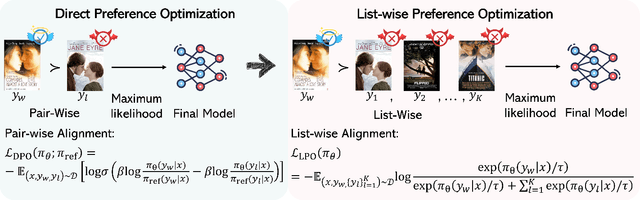
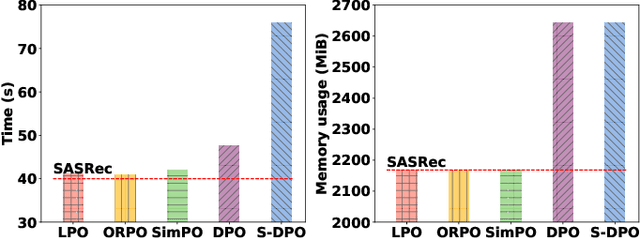
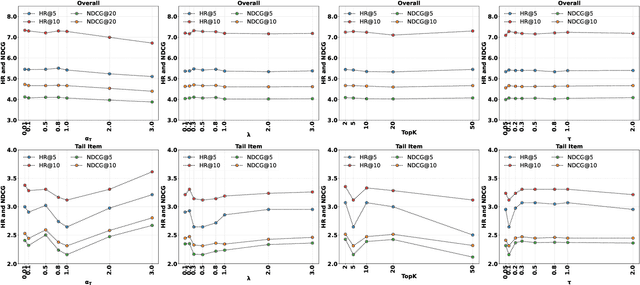
Abstract:Preference alignment has achieved greater success on Large Language Models (LLMs) and drawn broad interest in recommendation research. Existing preference alignment methods for recommendation either require explicit reward modeling or only support pairwise preference comparison. The former directly increases substantial computational costs, while the latter hinders training efficiency on negative samples. Moreover, no existing effort has explored preference alignment solutions for tail-item recommendation. To bridge the above gaps, we propose LPO4Rec, which extends the Bradley-Terry model from pairwise comparison to listwise comparison, to improve the efficiency of model training. Specifically, we derive a closed form optimal policy to enable more efficient and effective training without explicit reward modeling. We also present an adaptive negative sampling and reweighting strategy to prioritize tail items during optimization and enhance performance in tail-item recommendations. Besides, we theoretically prove that optimizing the listwise preference optimization (LPO) loss is equivalent to maximizing the upper bound of the optimal reward. Our experiments on three public datasets show that our method outperforms 10 baselines by a large margin, achieving up to 50% performance improvement while reducing 17.9% GPU memory usage when compared with direct preference optimization (DPO) in tail-item recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yuhanleeee/LPO4Rec.
Graph and Sequential Neural Networks in Session-based Recommendation: A Survey
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the remarkable success of recommendation systems (RSs) in alleviating the information overload problem. As a new paradigm of RSs, session-based recommendation (SR) specializes in users' short-term preference capture and aims to provide a more dynamic and timely recommendation based on the ongoing interacted actions. In this survey, we will give a comprehensive overview of the recent works on SR. First, we clarify the definitions of various SR tasks and introduce the characteristics of session-based recommendation against other recommendation tasks. Then, we summarize the existing methods in two categories: sequential neural network based methods and graph neural network (GNN) based methods. The standard frameworks and technical are also introduced. Finally, we discuss the challenges of SR and new research directions in this area.
Temporal Disentangled Contrastive Diffusion Model for Spatiotemporal Imputation
Feb 18, 2024



Abstract:Spatiotemporal data analysis is pivotal across various domains, including transportation, meteorology, and healthcare. However, the data collected in real-world scenarios often suffers incompleteness due to sensor malfunctions and network transmission errors. Spatiotemporal imputation endeavours to predict missing values by exploiting the inherent spatial and temporal dependencies present in the observed data. Traditional approaches, which rely on classical statistical and machine learning techniques, are often inadequate, particularly when the data fails to meet strict distributional assumptions. In contrast, recent deep learning-based methods, leveraging graph and recurrent neural networks, have demonstrated enhanced efficacy. Nonetheless, these approaches are prone to error accumulation. Generative models have been increasingly adopted to circumvent the reliance on potentially inaccurate historical imputed values for future predictions. These models grapple with the challenge of producing unstable results, a particular issue in diffusion-based models. We aim to address these challenges by designing conditional features to guide the generative process and expedite training. Specifically, we introduce C$^2$TSD, a novel approach incorporating trend and seasonal information as conditional features and employing contrastive learning to improve model generalizability. The extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superior performance of C$^2$TSD over various state-of-the-art baselines.
GATGPT: A Pre-trained Large Language Model with Graph Attention Network for Spatiotemporal Imputation
Nov 24, 2023Abstract:The analysis of spatiotemporal data is increasingly utilized across diverse domains, including transportation, healthcare, and meteorology. In real-world settings, such data often contain missing elements due to issues like sensor malfunctions and data transmission errors. The objective of spatiotemporal imputation is to estimate these missing values by understanding the inherent spatial and temporal relationships in the observed multivariate time series. Traditionally, spatiotemporal imputation has relied on specific, intricate architectures designed for this purpose, which suffer from limited applicability and high computational complexity. In contrast, our approach integrates pre-trained large language models (LLMs) into spatiotemporal imputation, introducing a groundbreaking framework, GATGPT. This framework merges a graph attention mechanism with LLMs. We maintain most of the LLM parameters unchanged to leverage existing knowledge for learning temporal patterns, while fine-tuning the upper layers tailored to various applications. The graph attention component enhances the LLM's ability to understand spatial relationships. Through tests on three distinct real-world datasets, our innovative approach demonstrates comparable results to established deep learning benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge