Xumin Huang
Tiny Multi-Agent DRL for Twins Migration in UAV Metaverses: A Multi-Leader Multi-Follower Stackelberg Game Approach
Jan 18, 2024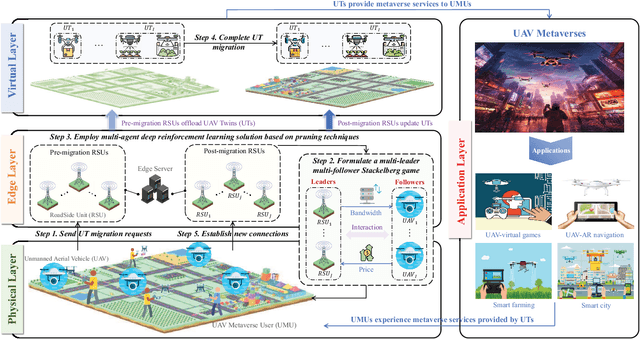
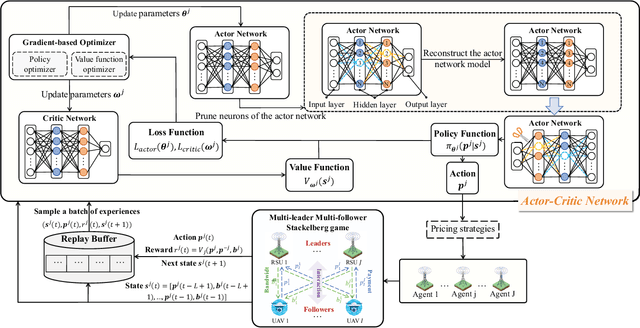
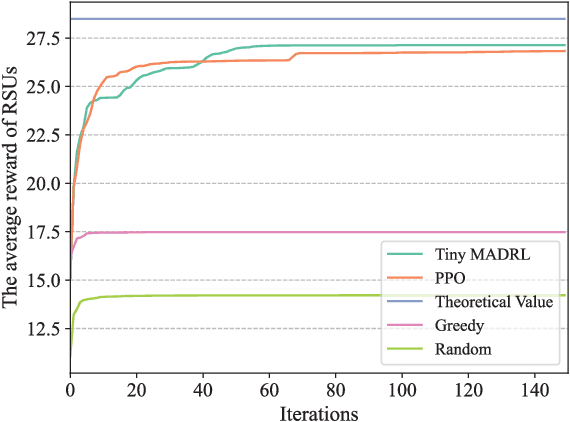
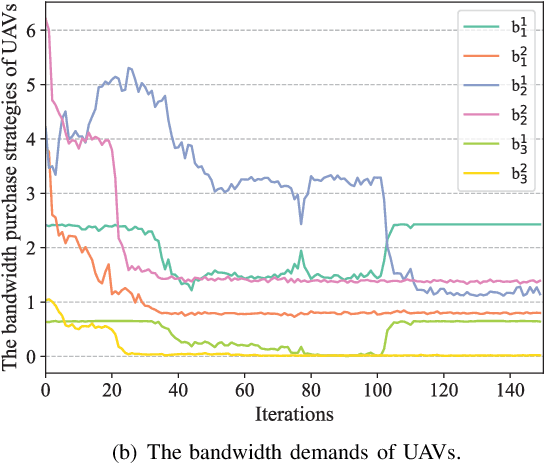
Abstract:The synergy between Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and metaverses is giving rise to an emerging paradigm named UAV metaverses, which create a unified ecosystem that blends physical and virtual spaces, transforming drone interaction and virtual exploration. UAV Twins (UTs), as the digital twins of UAVs that revolutionize UAV applications by making them more immersive, realistic, and informative, are deployed and updated on ground base stations, e.g., RoadSide Units (RSUs), to offer metaverse services for UAV Metaverse Users (UMUs). Due to the dynamic mobility of UAVs and limited communication coverages of RSUs, it is essential to perform real-time UT migration to ensure seamless immersive experiences for UMUs. However, selecting appropriate RSUs and optimizing the required bandwidth is challenging for achieving reliable and efficient UT migration. To address the challenges, we propose a tiny machine learning-based Stackelberg game framework based on pruning techniques for efficient UT migration in UAV metaverses. Specifically, we formulate a multi-leader multi-follower Stackelberg model considering a new immersion metric of UMUs in the utilities of UAVs. Then, we design a Tiny Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (Tiny MADRL) algorithm to obtain the tiny networks representing the optimal game solution. Specifically, the actor-critic network leverages the pruning techniques to reduce the number of network parameters and achieve model size and computation reduction, allowing for efficient implementation of Tiny MADRL. Numerical results demonstrate that our proposed schemes have better performance than traditional schemes.
Service Reservation and Pricing for Green Metaverses: A Stackelberg Game Approach
Aug 09, 2023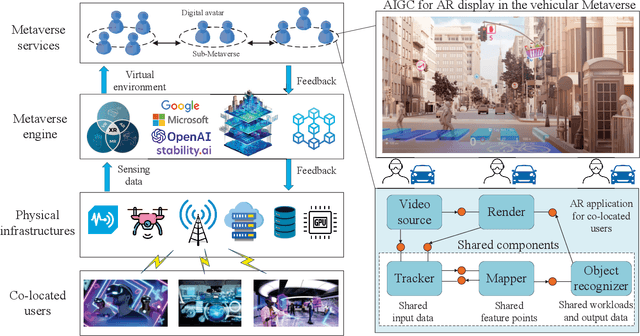
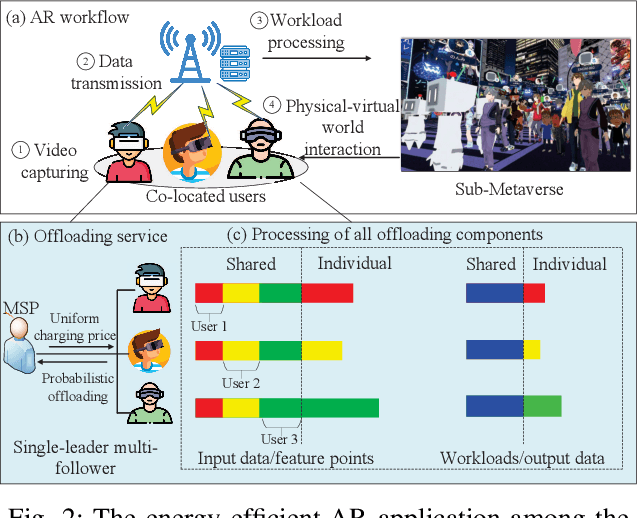
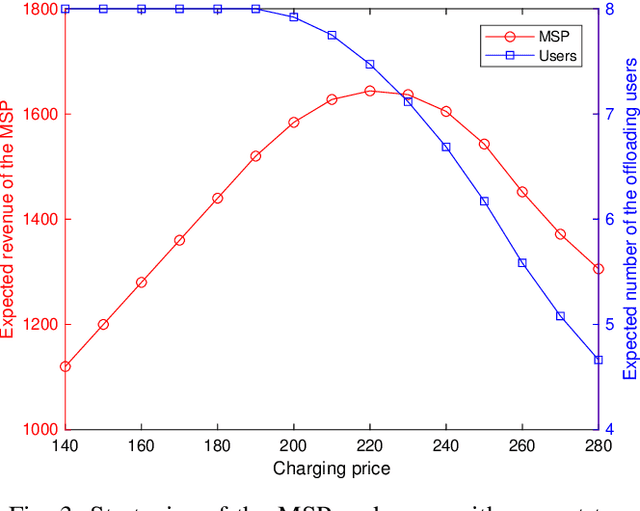
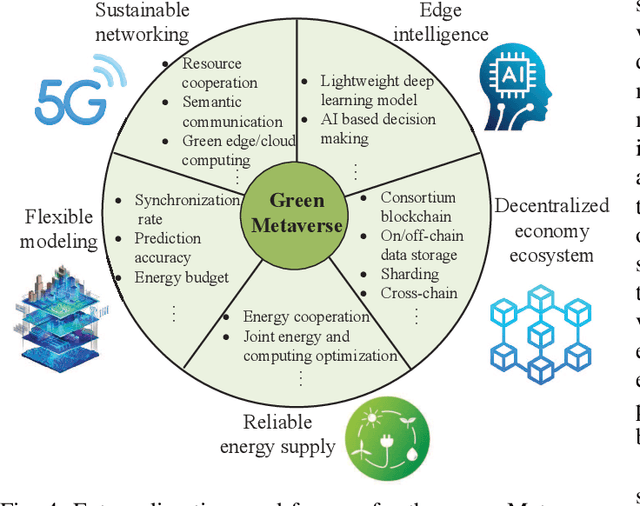
Abstract:Metaverse enables users to communicate, collaborate and socialize with each other through their digital avatars. Due to the spatio-temporal characteristics, co-located users are served well by performing their software components in a collaborative manner such that a Metaverse service provider (MSP) eliminates redundant data transmission and processing, ultimately reducing the total energy consumption. The energyefficient service provision is crucial for enabling the green and sustainable Metaverse. In this article, we take an augmented reality (AR) application as an example to achieve this goal. Moreover, we study an economic issue on how the users reserve offloading services from the MSP and how the MSP determines an optimal charging price since each user is rational to decide whether to accept the offloading service by taking into account the monetary cost. A single-leader multi-follower Stackelberg game is formulated between the MSP and users while each user optimizes an offloading probability to minimize the weighted sum of time, energy consumption and monetary cost. Numerical results show that our scheme achieves energy savings and satisfies individual rationality simultaneously compared with the conventional schemes. Finally, we identify and discuss open directions on how several emerging technologies are combined with the sustainable green Metaverse.
Federated Learning-Empowered AI-Generated Content in Wireless Networks
Jul 14, 2023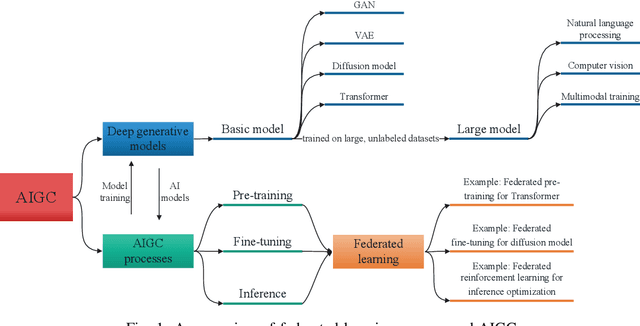
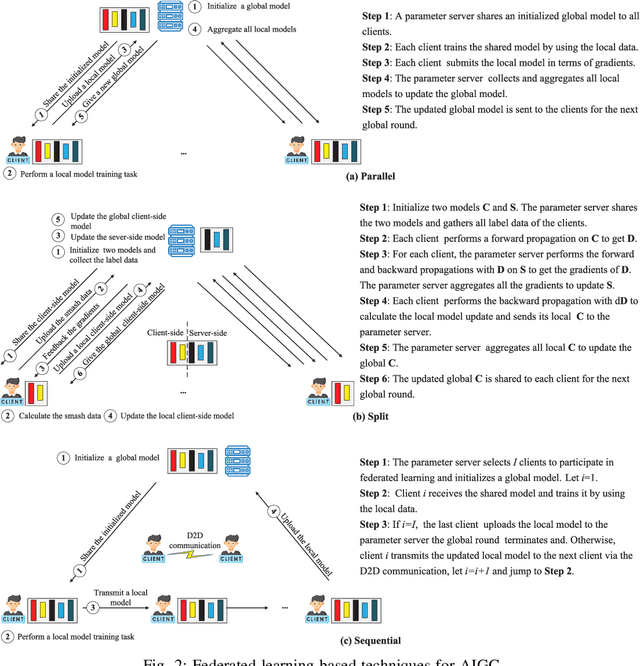
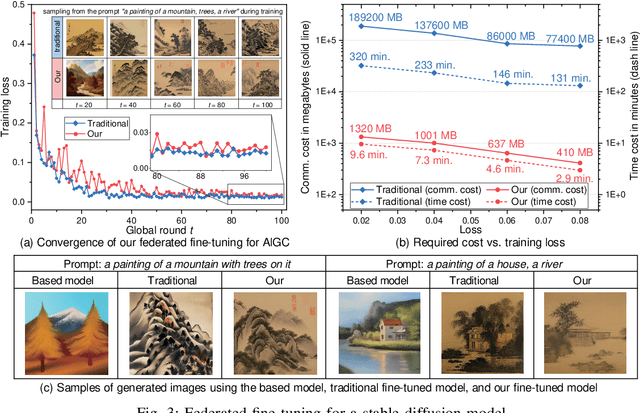
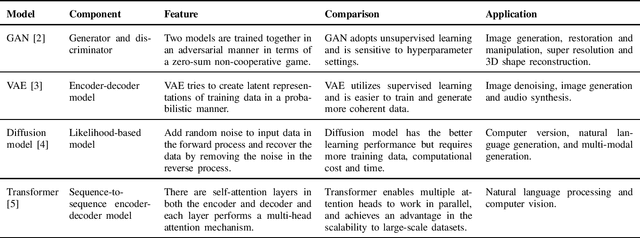
Abstract:Artificial intelligence generated content (AIGC) has emerged as a promising technology to improve the efficiency, quality, diversity and flexibility of the content creation process by adopting a variety of generative AI models. Deploying AIGC services in wireless networks has been expected to enhance the user experience. However, the existing AIGC service provision suffers from several limitations, e.g., the centralized training in the pre-training, fine-tuning and inference processes, especially their implementations in wireless networks with privacy preservation. Federated learning (FL), as a collaborative learning framework where the model training is distributed to cooperative data owners without the need for data sharing, can be leveraged to simultaneously improve learning efficiency and achieve privacy protection for AIGC. To this end, we present FL-based techniques for empowering AIGC, and aim to enable users to generate diverse, personalized, and high-quality content. Furthermore, we conduct a case study of FL-aided AIGC fine-tuning by using the state-of-the-art AIGC model, i.e., stable diffusion model. Numerical results show that our scheme achieves advantages in effectively reducing the communication cost and training latency and privacy protection. Finally, we highlight several major research directions and open issues for the convergence of FL and AIGC.
Adversarial Attacks and Defenses for Semantic Communication in Vehicular Metaverses
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:For vehicular metaverses, one of the ultimate user-centric goals is to optimize the immersive experience and Quality of Service (QoS) for users on board. Semantic Communication (SemCom) has been introduced as a revolutionary paradigm that significantly eases communication resource pressure for vehicular metaverse applications to achieve this goal. SemCom enables high-quality and ultra-efficient vehicular communication, even with explosively increasing data traffic among vehicles. In this article, we propose a hierarchical SemCom-enabled vehicular metaverses framework consisting of the global metaverse, local metaverses, SemCom module, and resource pool. The global and local metaverses are brand-new concepts from the metaverse's distribution standpoint. Considering the QoS of users, this article explores the potential security vulnerabilities of the proposed framework. To that purpose, this study highlights a specific security risk to the framework's SemCom module and offers a viable defense solution, so encouraging community researchers to focus more on vehicular metaverse security. Finally, we provide an overview of the open issues of secure SemCom in the vehicular metaverses, notably pointing out potential future research directions.
AnycostFL: Efficient On-Demand Federated Learning over Heterogeneous Edge Devices
Jan 08, 2023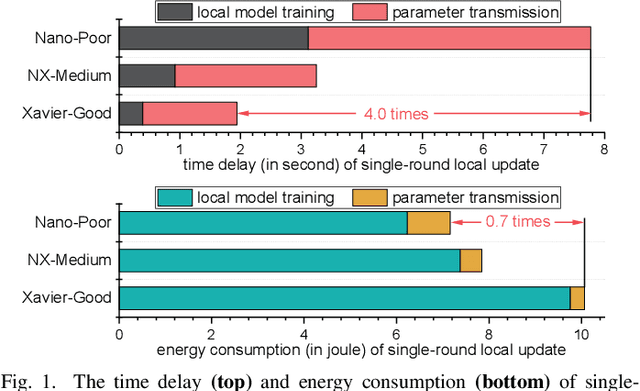
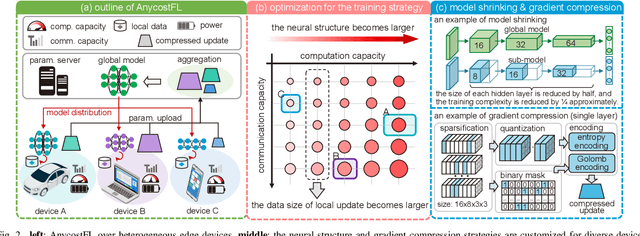
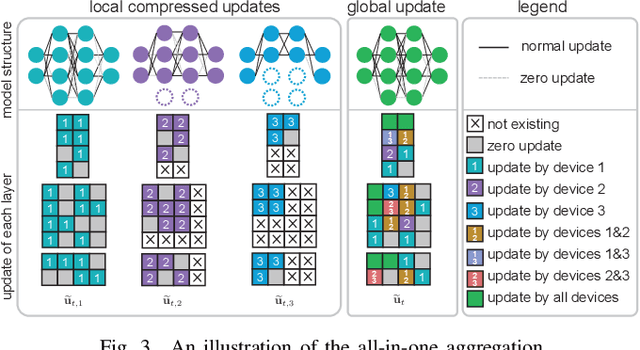
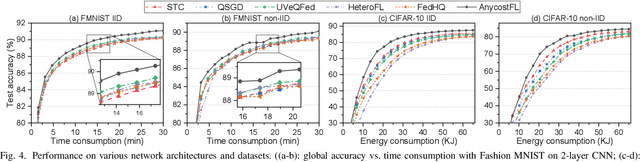
Abstract:In this work, we investigate the challenging problem of on-demand federated learning (FL) over heterogeneous edge devices with diverse resource constraints. We propose a cost-adjustable FL framework, named AnycostFL, that enables diverse edge devices to efficiently perform local updates under a wide range of efficiency constraints. To this end, we design the model shrinking to support local model training with elastic computation cost, and the gradient compression to allow parameter transmission with dynamic communication overhead. An enhanced parameter aggregation is conducted in an element-wise manner to improve the model performance. Focusing on AnycostFL, we further propose an optimization design to minimize the global training loss with personalized latency and energy constraints. By revealing the theoretical insights of the convergence analysis, personalized training strategies are deduced for different devices to match their locally available resources. Experiment results indicate that, when compared to the state-of-the-art efficient FL algorithms, our learning framework can reduce up to 1.9 times of the training latency and energy consumption for realizing a reasonable global testing accuracy. Moreover, the results also demonstrate that, our approach significantly improves the converged global accuracy.
FedGreen: Federated Learning with Fine-Grained Gradient Compression for Green Mobile Edge Computing
Nov 11, 2021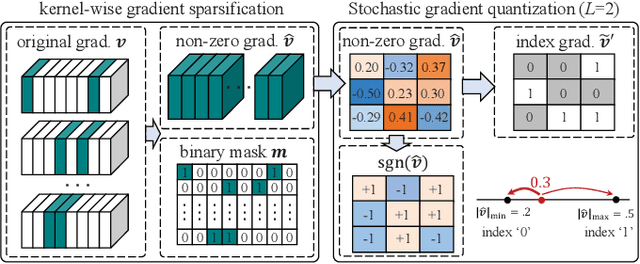
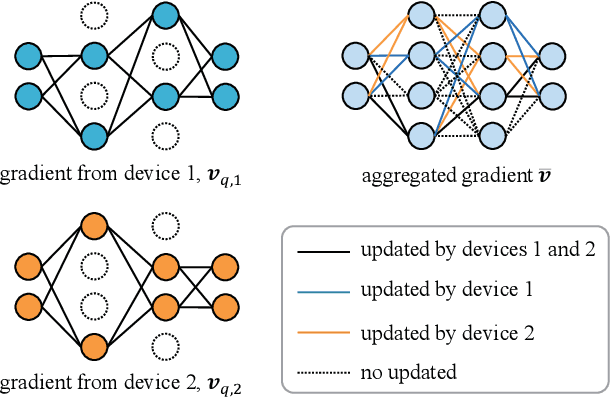
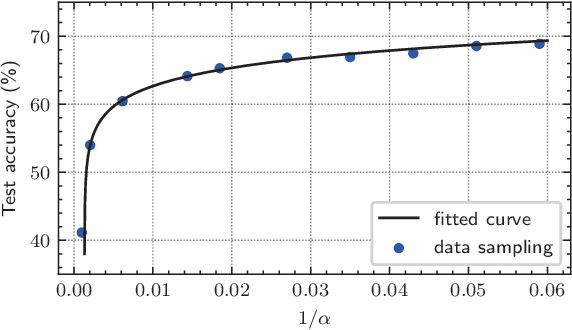
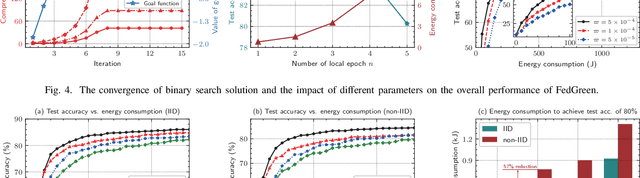
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables devices in mobile edge computing (MEC) to collaboratively train a shared model without uploading the local data. Gradient compression may be applied to FL to alleviate the communication overheads but current FL with gradient compression still faces great challenges. To deploy green MEC, we propose FedGreen, which enhances the original FL with fine-grained gradient compression to efficiently control the total energy consumption of the devices. Specifically, we introduce the relevant operations including device-side gradient reduction and server-side element-wise aggregation to facilitate the gradient compression in FL. According to a public dataset, we investigate the contributions of the compressed local gradients with respect to different compression ratios. After that, we formulate and tackle a learning accuracy-energy efficiency tradeoff problem where the optimal compression ratio and computing frequency are derived for each device. Experiments results demonstrate that given the 80% test accuracy requirement, compared with the baseline schemes, FedGreen reduces at least 32% of the total energy consumption of the devices.
FedParking: A Federated Learning based Parking Space Estimation with Parked Vehicle assisted Edge Computing
Oct 19, 2021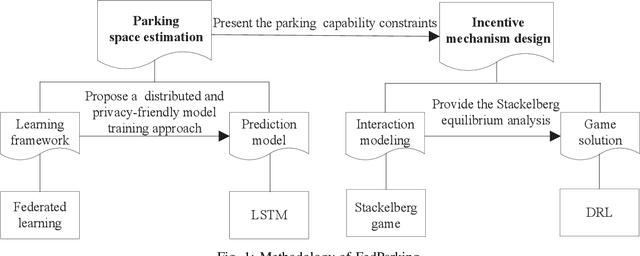
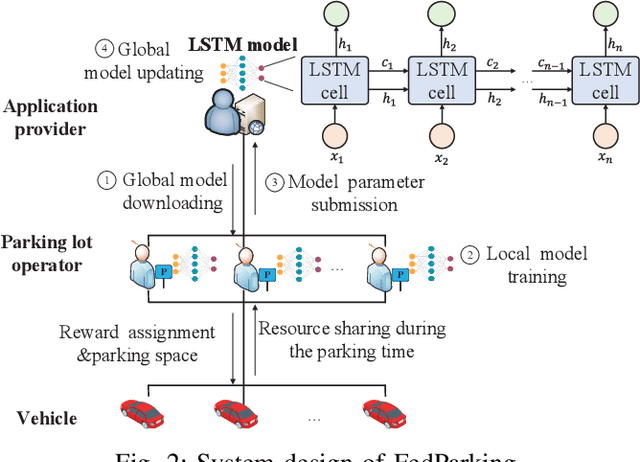
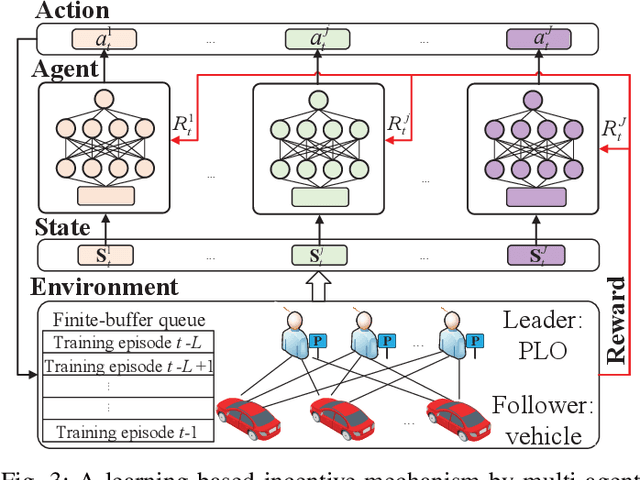
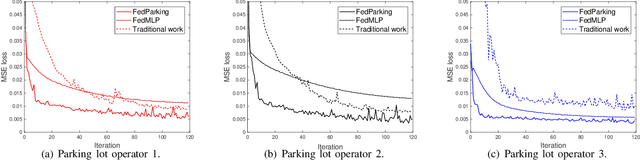
Abstract:As a distributed learning approach, federated learning trains a shared learning model over distributed datasets while preserving the training data privacy. We extend the application of federated learning to parking management and introduce FedParking in which Parking Lot Operators (PLOs) collaborate to train a long short-term memory model for parking space estimation without exchanging the raw data. Furthermore, we investigate the management of Parked Vehicle assisted Edge Computing (PVEC) by FedParking. In PVEC, different PLOs recruit PVs as edge computing nodes for offloading services through an incentive mechanism, which is designed according to the computation demand and parking capacity constraints derived from FedParking. We formulate the interactions among the PLOs and vehicles as a multi-lead multi-follower Stackelberg game. Considering the dynamic arrivals of the vehicles and time-varying parking capacity constraints, we present a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approach to gradually reach the Stackelberg equilibrium in a distributed yet privacy-preserving manner. Finally, numerical results are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge