Xu Bao
PoSynDA: Multi-Hypothesis Pose Synthesis Domain Adaptation for Robust 3D Human Pose Estimation
Aug 18, 2023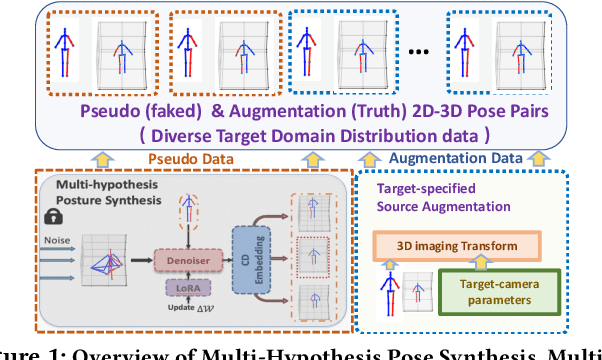
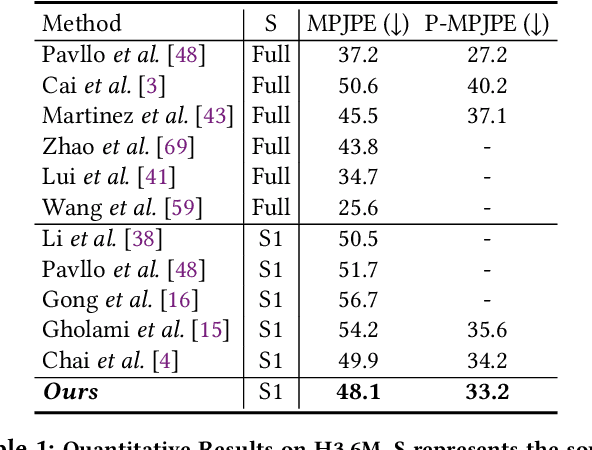
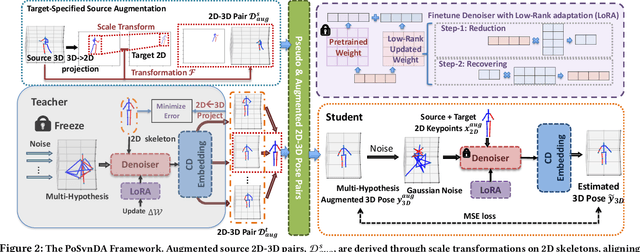
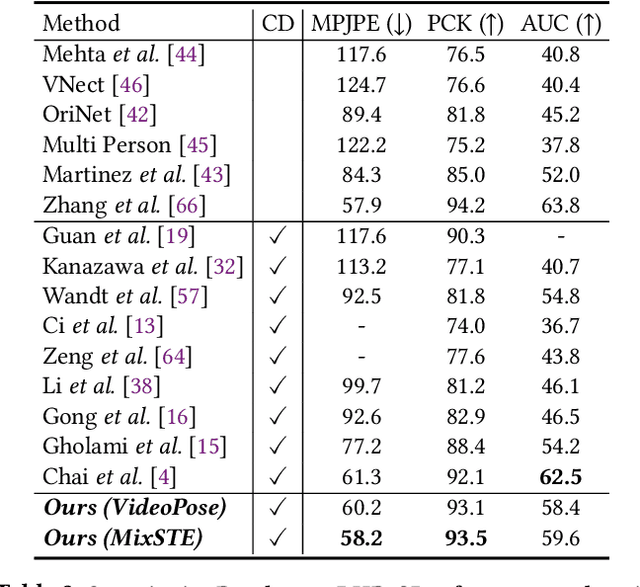
Abstract:The current 3D human pose estimators face challenges in adapting to new datasets due to the scarcity of 2D-3D pose pairs in target domain training sets. We present the \textit{Multi-Hypothesis \textbf{P}ose \textbf{Syn}thesis \textbf{D}omain \textbf{A}daptation} (\textbf{PoSynDA}) framework to overcome this issue without extensive target domain annotation. Utilizing a diffusion-centric structure, PoSynDA simulates the 3D pose distribution in the target domain, filling the data diversity gap. By incorporating a multi-hypothesis network, it creates diverse pose hypotheses and aligns them with the target domain. Target-specific source augmentation obtains the target domain distribution data from the source domain by decoupling the scale and position parameters. The teacher-student paradigm and low-rank adaptation further refine the process. PoSynDA demonstrates competitive performance on benchmarks, such as Human3.6M, MPI-INF-3DHP, and 3DPW, even comparable with the target-trained MixSTE model~\cite{zhang2022mixste}. This work paves the way for the practical application of 3D human pose estimation. The code is available at https://github.com/hbing-l/PoSynDA.
KeyPosS: Plug-and-Play Facial Landmark Detection through GPS-Inspired True-Range Multilateration
May 25, 2023



Abstract:In the realm of facial analysis, accurate landmark detection is crucial for various applications, ranging from face recognition and expression analysis to animation. Conventional heatmap or coordinate regression-based techniques, however, often face challenges in terms of computational burden and quantization errors. To address these issues, we present the KeyPoint Positioning System (KeyPosS), a groundbreaking facial landmark detection framework that stands out from existing methods. For the first time, KeyPosS employs the True-range Multilateration algorithm, a technique originally used in GPS systems, to achieve rapid and precise facial landmark detection without relying on computationally intensive regression approaches. The framework utilizes a fully convolutional network to predict a distance map, which computes the distance between a Point of Interest (POI) and multiple anchor points. These anchor points are ingeniously harnessed to triangulate the POI's position through the True-range Multilateration algorithm. Notably, the plug-and-play nature of KeyPosS enables seamless integration into any decoding stage, ensuring a versatile and adaptable solution. We conducted a thorough evaluation of KeyPosS's performance by benchmarking it against state-of-the-art models on four different datasets. The results show that KeyPosS substantially outperforms leading methods in low-resolution settings while requiring a minimal time overhead. The code is available at https://github.com/zhiqic/KeyPosS.
ProContEXT: Exploring Progressive Context Transformer for Tracking
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Existing Visual Object Tracking (VOT) only takes the target area in the first frame as a template. This causes tracking to inevitably fail in fast-changing and crowded scenes, as it cannot account for changes in object appearance between frames. To this end, we revamped the tracking framework with Progressive Context Encoding Transformer Tracker (ProContEXT), which coherently exploits spatial and temporal contexts to predict object motion trajectories. Specifically, ProContEXT leverages a context-aware self-attention module to encode the spatial and temporal context, refining and updating the multi-scale static and dynamic templates to progressively perform accurate tracking. It explores the complementary between spatial and temporal context, raising a new pathway to multi-context modeling for transformer-based trackers. In addition, ProContEXT revised the token pruning technique to reduce computational complexity. Extensive experiments on popular benchmark datasets such as GOT-10k and TrackingNet demonstrate that the proposed ProContEXT achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Levenberg-Marquardt Method Based Cooperative Source Localization in SIMO Molecular Communication via Diffusion Systems
Mar 16, 2022



Abstract:Molecular communication underpins nano-scale communications in nanotechnology. The combination of multinanomachines to form nano-networks is one of the main enabling methods. Due to the importance of source localization in establishing nano-networks, this paper proposes a cooperative source localization method for Molecular Communication via Diffusion (MCvD) systems using multiple spherical absorption receivers. Since there is no exact mathematical expression of the channel impulse response for multiple absorbing receivers, we adopt an empirical expression and use Levenberg-Marquardt method to estimate the distance of the transmitter to each receiver, based on which the location of the transmitter is obtained using an iterative scheme where the initial point is obtained using a multi-point localization method. Particle based simulation is carried out to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. Simulation results show that the proposed method can accurately estimate the location of transmitter in short to medium communication ranges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge