Xiaobo Gao
TexRO: Generating Delicate Textures of 3D Models by Recursive Optimization
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:This paper presents TexRO, a novel method for generating delicate textures of a known 3D mesh by optimizing its UV texture. The key contributions are two-fold. We propose an optimal viewpoint selection strategy, that finds the most miniature set of viewpoints covering all the faces of a mesh. Our viewpoint selection strategy guarantees the completeness of a generated result. We propose a recursive optimization pipeline that optimizes a UV texture at increasing resolutions, with an adaptive denoising method that re-uses existing textures for new texture generation. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate the superior performance of TexRO in terms of texture quality, detail preservation, visual consistency, and, notably runtime speed, outperforming other current methods. The broad applicability of TexRO is further confirmed through its successful use on diverse 3D models.
HD-Fusion: Detailed Text-to-3D Generation Leveraging Multiple Noise Estimation
Jul 30, 2023
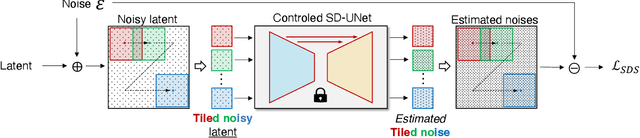
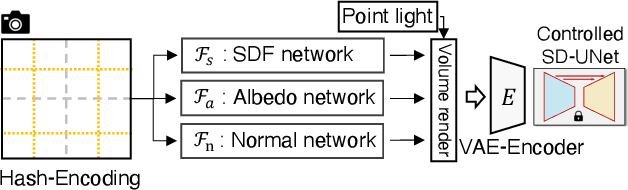
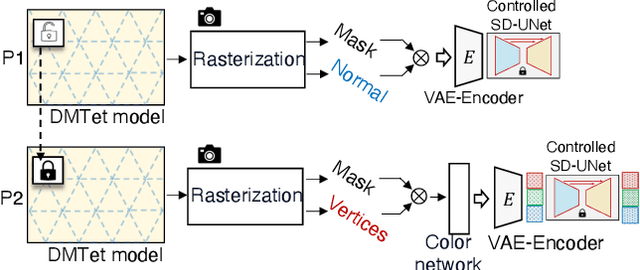
Abstract:In this paper, we study Text-to-3D content generation leveraging 2D diffusion priors to enhance the quality and detail of the generated 3D models. Recent progress (Magic3D) in text-to-3D has shown that employing high-resolution (e.g., 512 x 512) renderings can lead to the production of high-quality 3D models using latent diffusion priors. To enable rendering at even higher resolutions, which has the potential to further augment the quality and detail of the models, we propose a novel approach that combines multiple noise estimation processes with a pretrained 2D diffusion prior. Distinct from the Bar-Tal et al.s' study which binds multiple denoised results to generate images from texts, our approach integrates the computation of scoring distillation losses such as SDS loss and VSD loss which are essential techniques for the 3D content generation with 2D diffusion priors. We experimentally evaluated the proposed approach. The results show that the proposed approach can generate high-quality details compared to the baselines.
Aesthetics Driven Autonomous Time-Lapse Photography Generation by Virtual and Real Robots
Aug 22, 2022



Abstract:Time-lapse photography is employed in movies and promotional films because it can reflect the passage of time in a short time and strengthen the visual attraction. However, since it takes a long time and requires the stable shooting, it is a great challenge for the photographer. In this article, we propose a time-lapse photography system with virtual and real robots. To help users shoot time-lapse videos efficiently, we first parameterize the time-lapse photography and propose a parameter optimization method. For different parameters, different aesthetic models, including image and video aesthetic quality assessment networks, are used to generate optimal parameters. Then we propose a time-lapse photography interface to facilitate users to view and adjust parameters and use virtual robots to conduct virtual photography in a three-dimensional scene. The system can also export the parameters and provide them to real robots so that the time-lapse videos can be filmed in the real world. In addition, we propose a time-lapse photography aesthetic assessment method that can automatically evaluate the aesthetic quality of time-lapse video. The experimental results show that our method can efficiently obtain the time-lapse videos. We also conduct a user study. The results show that our system has the similar effect as professional photographers and is more efficient.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge