Xiangkun Wang
ErrorEraser: Unlearning Data Bias for Improved Continual Learning
Jun 11, 2025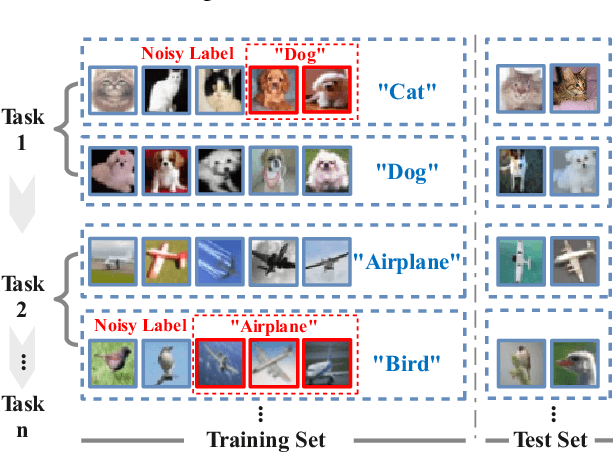
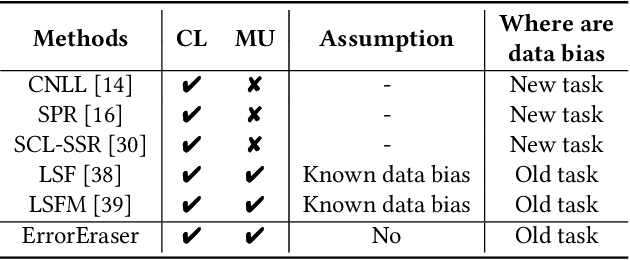
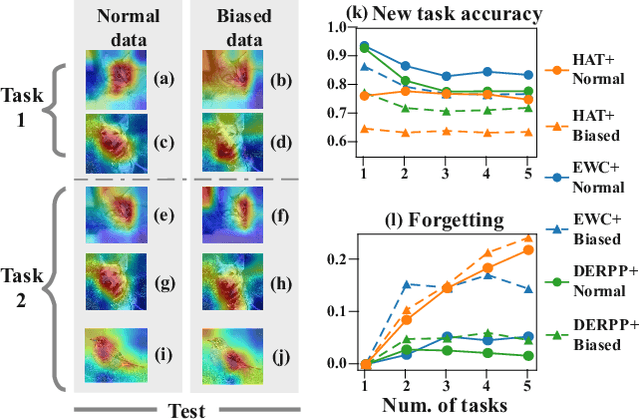
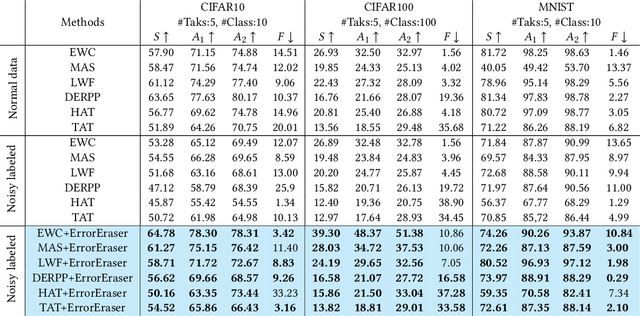
Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) primarily aims to retain knowledge to prevent catastrophic forgetting and transfer knowledge to facilitate learning new tasks. Unlike traditional methods, we propose a novel perspective: CL not only needs to prevent forgetting, but also requires intentional forgetting.This arises from existing CL methods ignoring biases in real-world data, leading the model to learn spurious correlations that transfer and amplify across tasks. From feature extraction and prediction results, we find that data biases simultaneously reduce CL's ability to retain and transfer knowledge. To address this, we propose ErrorEraser, a universal plugin that removes erroneous memories caused by biases in CL, enhancing performance in both new and old tasks. ErrorEraser consists of two modules: Error Identification and Error Erasure. The former learns the probability density distribution of task data in the feature space without prior knowledge, enabling accurate identification of potentially biased samples. The latter ensures only erroneous knowledge is erased by shifting the decision space of representative outlier samples. Additionally, an incremental feature distribution learning strategy is designed to reduce the resource overhead during error identification in downstream tasks. Extensive experimental results show that ErrorEraser significantly mitigates the negative impact of data biases, achieving higher accuracy and lower forgetting rates across three types of CL methods. The code is available at https://github.com/diadai/ErrorEraser.
Improving Open-world Continual Learning under the Constraints of Scarce Labeled Data
Feb 28, 2025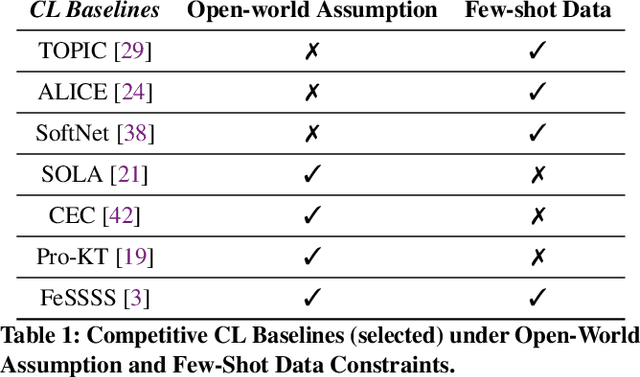
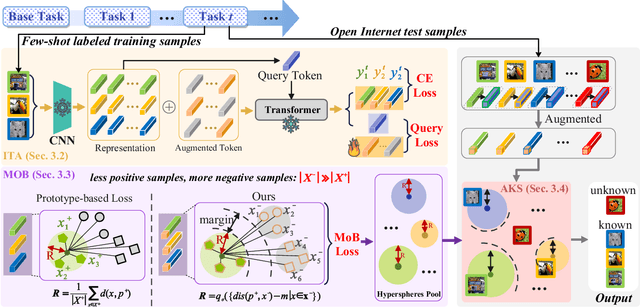
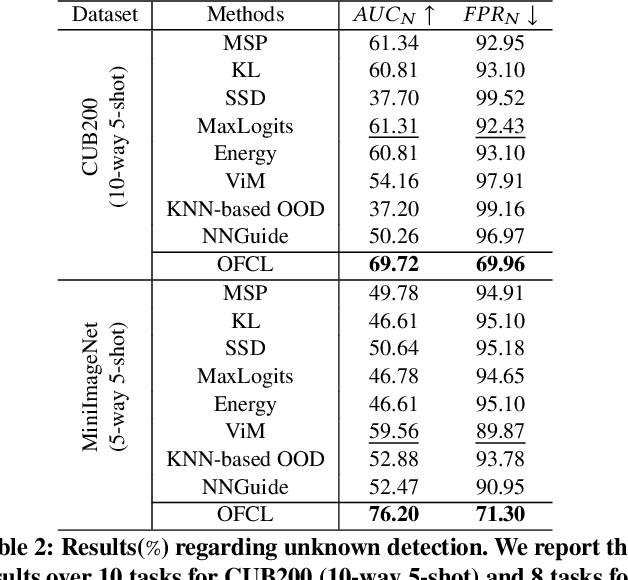
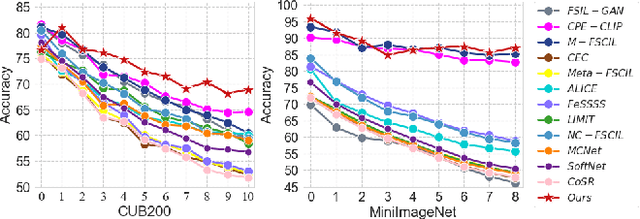
Abstract:Open-world continual learning (OWCL) adapts to sequential tasks with open samples, learning knowledge incrementally while preventing forgetting. However, existing OWCL still requires a large amount of labeled data for training, which is often impractical in real-world applications. Given that new categories/entities typically come with limited annotations and are in small quantities, a more realistic situation is OWCL with scarce labeled data, i.e., few-shot training samples. Hence, this paper investigates the problem of open-world few-shot continual learning (OFCL), challenging in (i) learning unbounded tasks without forgetting previous knowledge and avoiding overfitting, (ii) constructing compact decision boundaries for open detection with limited labeled data, and (iii) transferring knowledge about knowns and unknowns and even update the unknowns to knowns once the labels of open samples are learned. In response, we propose a novel OFCL framework that integrates three key components: (1) an instance-wise token augmentation (ITA) that represents and enriches sample representations with additional knowledge, (2) a margin-based open boundary (MOB) that supports open detection with new tasks emerge over time, and (3) an adaptive knowledge space (AKS) that endows unknowns with knowledge for the updating from unknowns to knowns. Finally, extensive experiments show the proposed OFCL framework outperforms all baselines remarkably with practical importance and reproducibility. The source code is released at https://github.com/liyj1201/OFCL.
Order-Robust Class Incremental Learning: Graph-Driven Dynamic Similarity Grouping
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Class Incremental Learning (CIL) requires a model to continuously learn new classes without forgetting previously learned ones. While recent studies have significantly alleviated the problem of catastrophic forgetting (CF), more and more research reveals that the order in which classes appear have significant influences on CIL models. Specifically, prioritizing the learning of classes with lower similarity will enhance the model's generalization performance and its ability to mitigate forgetting. Hence, it is imperative to develop an order-robust class incremental learning model that maintains stable performance even when faced with varying levels of class similarity in different orders. In response, we first provide additional theoretical analysis, which reveals that when the similarity among a group of classes is lower, the model demonstrates increased robustness to the class order. Then, we introduce a novel \textbf{G}raph-\textbf{D}riven \textbf{D}ynamic \textbf{S}imilarity \textbf{G}rouping (\textbf{GDDSG}) method, which leverages a graph coloring algorithm for class-based similarity grouping. The proposed approach trains independent CIL models for each group of classes, ultimately combining these models to facilitate joint prediction. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively addresses the issue of class order sensitivity while achieving optimal performance in both model accuracy and anti-forgetting capability. Our code is available at https://github.com/AIGNLAI/GDDSG.
Learning to Prompt Knowledge Transfer for Open-World Continual Learning
Dec 22, 2023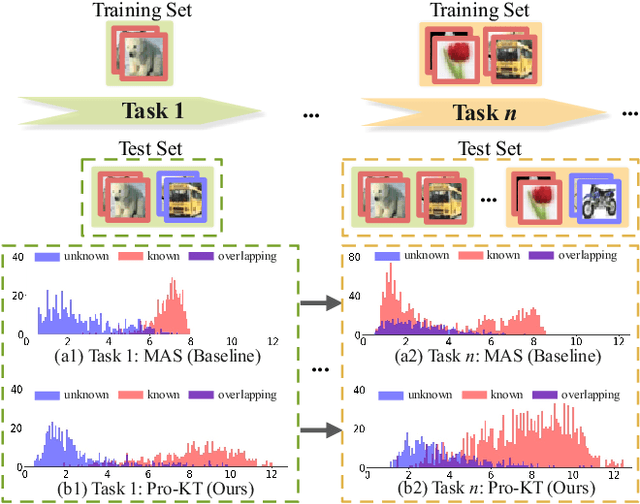
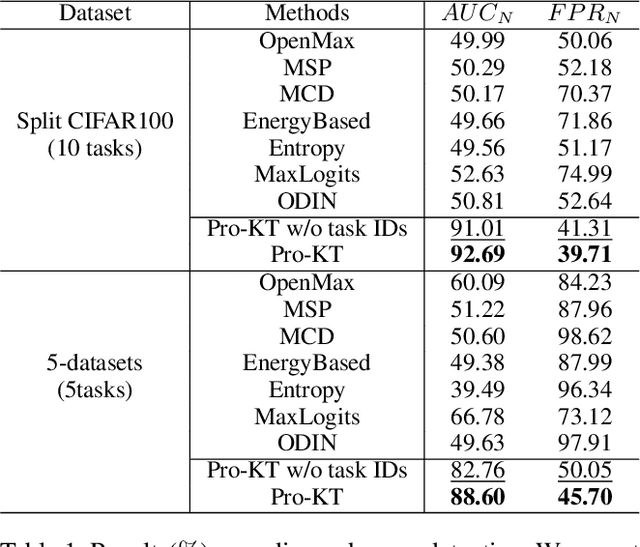
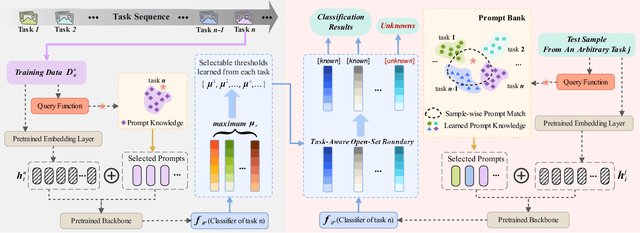
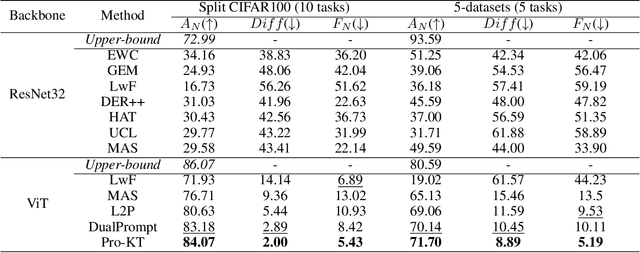
Abstract:This paper studies the problem of continual learning in an open-world scenario, referred to as Open-world Continual Learning (OwCL). OwCL is increasingly rising while it is highly challenging in two-fold: i) learning a sequence of tasks without forgetting knowns in the past, and ii) identifying unknowns (novel objects/classes) in the future. Existing OwCL methods suffer from the adaptability of task-aware boundaries between knowns and unknowns, and do not consider the mechanism of knowledge transfer. In this work, we propose Pro-KT, a novel prompt-enhanced knowledge transfer model for OwCL. Pro-KT includes two key components: (1) a prompt bank to encode and transfer both task-generic and task-specific knowledge, and (2) a task-aware open-set boundary to identify unknowns in the new tasks. Experimental results using two real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed Pro-KT outperforms the state-of-the-art counterparts in both the detection of unknowns and the classification of knowns markedly.
Deep learning-based person re-identification methods: A survey and outlook of recent works
Oct 16, 2021



Abstract:In recent years, with the increasing demand for public safety and the rapid development of intelligent surveillance networks, person re-identification (Re-ID) has become one of the hot research topics in the field of computer vision. The main research goal of person Re-ID is to retrieve persons with the same identity from different cameras. However, traditional person Re-ID methods require manual marking of person targets, which consumes a lot of labor cost. With the widespread application of deep neural networks in the field of computer vision, a large number of deep learning-based person Re-ID methods have emerged. Therefore, this paper is to facilitate researchers to better understand the latest research results and the future trends in the field. Firstly, we summarize the main study of several recently published person re-identification surveys and try to fill the gaps between them. Secondly, We propose a multi-dimensional taxonomy to categorize the most current deep learning-based person Re-ID methods according to different characteristics, including methods for deep metric learning, local feature learning, generate adversarial networks, sequence feature learning and graph convolutional networks. Furthermore, we subdivide the above five categories according to their technique types, discussing and comparing the experimental performance of part subcategories. Finally, we conclude this paper and discuss future research directions for person Re-ID.
Global-Local Dynamic Feature Alignment Network for Person Re-Identification
Sep 13, 2021
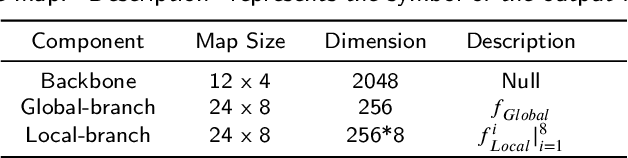
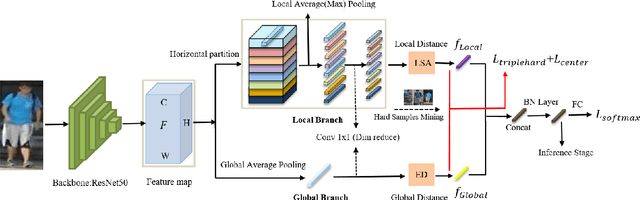
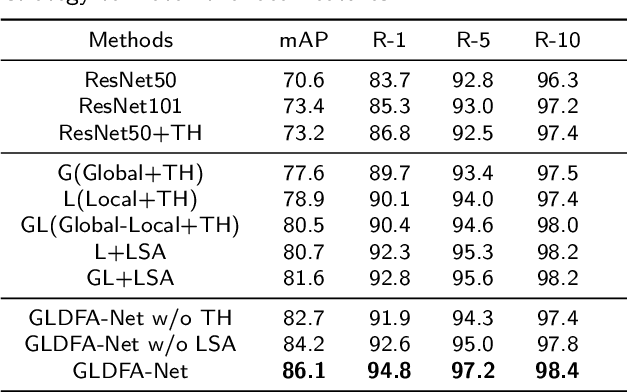
Abstract:The misalignment of human images caused by pedestrian detection bounding box errors or partial occlusions is one of the main challenges in person Re-Identification (Re-ID) tasks. Previous local-based methods mainly focus on learning local features in predefined semantic regions of pedestrians, usually use local hard alignment methods or introduce auxiliary information such as key human pose points to match local features. These methods are often not applicable when large scene differences are encountered. Targeting to solve these problems, we propose a simple and efficient Local Sliding Alignment (LSA) strategy to dynamically align the local features of two images by setting a sliding window on the local stripes of the pedestrian. LSA can effectively suppress spatial misalignment and does not need to introduce extra supervision information. Then, we design a Global-Local Dynamic Feature Alignment Network (GLDFA-Net) framework, which contains both global and local branches. We introduce LSA into the local branch of GLDFA-Net to guide the computation of distance metrics, which can further improve the accuracy of the testing phase. Evaluation experiments on several mainstream evaluation datasets including Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and CUHK03 show that our method has competitive accuracy over the several state-of-the-art person Re-ID methods. Additionally, it achieves 86.1% mAP and 94.8% Rank-1 accuracy on Market1501.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge