Xiangheng He
ProsodyFM: Unsupervised Phrasing and Intonation Control for Intelligible Speech Synthesis
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Prosody contains rich information beyond the literal meaning of words, which is crucial for the intelligibility of speech. Current models still fall short in phrasing and intonation; they not only miss or misplace breaks when synthesizing long sentences with complex structures but also produce unnatural intonation. We propose ProsodyFM, a prosody-aware text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) model with a flow-matching (FM) backbone that aims to enhance the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody. ProsodyFM introduces two key components: a Phrase Break Encoder to capture initial phrase break locations, followed by a Duration Predictor for the flexible adjustment of break durations; and a Terminal Intonation Encoder which integrates a set of intonation shape tokens combined with a novel Pitch Processor for more robust modeling of human-perceived intonation change. ProsodyFM is trained with no explicit prosodic labels and yet can uncover a broad spectrum of break durations and intonation patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that ProsodyFM can effectively improve the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody, thereby enhancing the overall intelligibility compared to four state-of-the-art (SOTA) models. Out-of-distribution experiments show that this prosody improvement can further bring ProsodyFM superior generalizability for unseen complex sentences and speakers. Our case study intuitively illustrates the powerful and fine-grained controllability of ProsodyFM over phrasing and intonation.
Improving Unsupervised Constituency Parsing via Maximizing Semantic Information
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised constituency parsers organize phrases within a sentence into a tree-shaped syntactic constituent structure that reflects the organization of sentence semantics. However, the traditional objective of maximizing sentence log-likelihood (LL) does not explicitly account for the close relationship between the constituent structure and the semantics, resulting in a weak correlation between LL values and parsing accuracy. In this paper, we introduce a novel objective for training unsupervised parsers: maximizing the information between constituent structures and sentence semantics (SemInfo). We introduce a bag-of-substrings model to represent the semantics and apply the probability-weighted information metric to estimate the SemInfo. Additionally, we develop a Tree Conditional Random Field (TreeCRF)-based model to apply the SemInfo maximization objective to Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar (PCFG) induction, the state-of-the-art method for unsupervised constituency parsing. Experiments demonstrate that SemInfo correlates more strongly with parsing accuracy than LL. Our algorithm significantly enhances parsing accuracy by an average of 7.85 points across five PCFG variants and in four languages, achieving new state-of-the-art results in three of the four languages.
Constituents Correspond to Word Sequence Patterns among Sentences with Equivalent Predicate-Argument Structures: Unsupervised Constituency Parsing by Span Matching
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised constituency parsing is about identifying word sequences that form a syntactic unit (i.e., constituents) in a target sentence. Linguists identify the constituent by evaluating a set of Predicate-Argument Structure (PAS) equivalent sentences where we find the constituent corresponds to frequent word sequences. However, such information is unavailable to previous parsing methods which identify the constituent by observing sentences with diverse PAS. In this study, we empirically verify that \textbf{constituents correspond to word sequence patterns in the PAS-equivalent sentence set}. We propose a frequency-based method \emph{span-overlap}, applying the word sequence pattern to computational unsupervised parsing for the first time. Parsing experiments show that the span-overlap parser outperforms state-of-the-art parsers in eight out of ten languages. Further discrimination analysis confirms that the span-overlap method can non-trivially separate constituents from non-constituents. This result highlights the utility of the word sequence pattern. Additionally, we discover a multilingual phenomenon: \textbf{participant-denoting constituents are more frequent than event-denoting constituents}. The phenomenon indicates a behavioral difference between the two constituent types, laying the foundation for future labeled unsupervised parsing.
Task Selection and Assignment for Multi-modal Multi-task Dialogue Act Classification with Non-stationary Multi-armed Bandits
Sep 18, 2023Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) aims to improve the performance of a primary task by jointly learning with related auxiliary tasks. Traditional MTL methods select tasks randomly during training. However, both previous studies and our results suggest that such the random selection of tasks may not be helpful, and can even be harmful to performance. Therefore, new strategies for task selection and assignment in MTL need to be explored. This paper studies the multi-modal, multi-task dialogue act classification task, and proposes a method for selecting and assigning tasks based on non-stationary multi-armed bandits (MAB) with discounted Thompson Sampling (TS) using Gaussian priors. Our experimental results show that in different training stages, different tasks have different utility. Our proposed method can effectively identify the task utility, actively avoid useless or harmful tasks, and realise the task assignment during training. Our proposed method is significantly superior in terms of UAR and F1 to the single-task and multi-task baselines with p-values < 0.05. Further analysis of experiments indicates that for the dataset with the data imbalance problem, our proposed method has significantly higher stability and can obtain consistent and decent performance for minority classes. Our proposed method is superior to the current state-of-the-art model.
An Overview of Affective Speech Synthesis and Conversion in the Deep Learning Era
Oct 06, 2022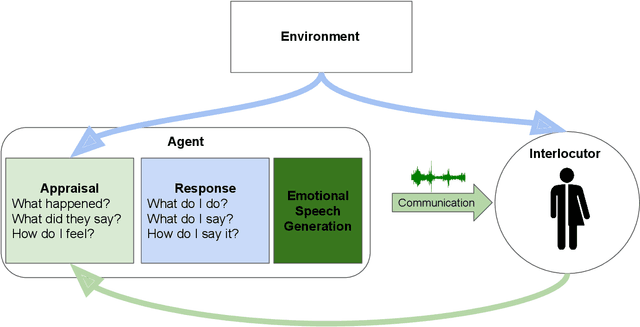
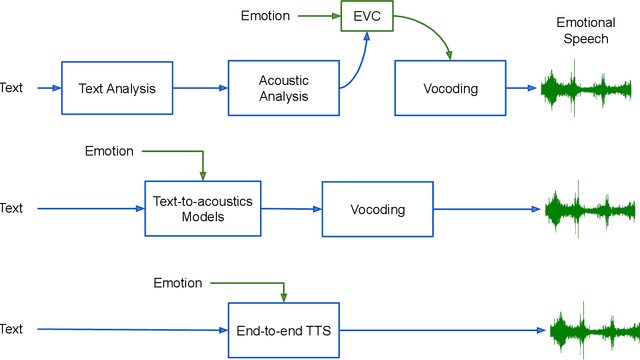
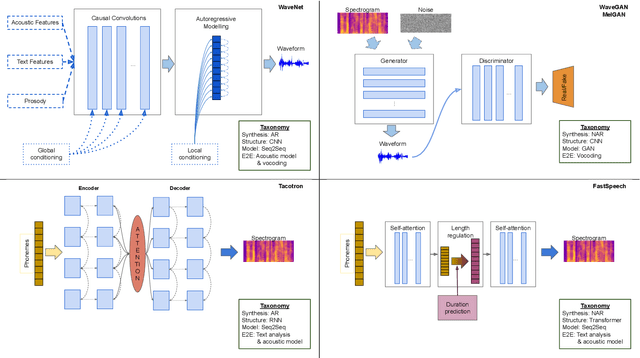
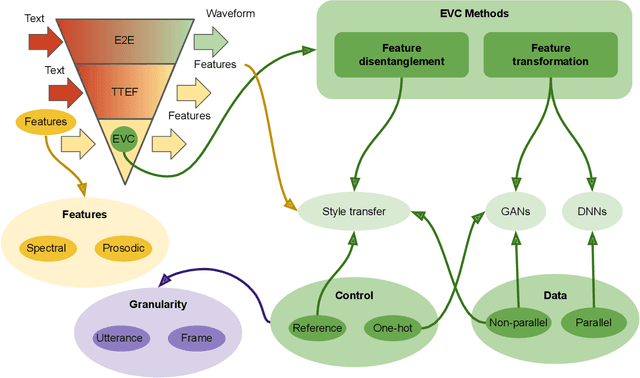
Abstract:Speech is the fundamental mode of human communication, and its synthesis has long been a core priority in human-computer interaction research. In recent years, machines have managed to master the art of generating speech that is understandable by humans. But the linguistic content of an utterance encompasses only a part of its meaning. Affect, or expressivity, has the capacity to turn speech into a medium capable of conveying intimate thoughts, feelings, and emotions -- aspects that are essential for engaging and naturalistic interpersonal communication. While the goal of imparting expressivity to synthesised utterances has so far remained elusive, following recent advances in text-to-speech synthesis, a paradigm shift is well under way in the fields of affective speech synthesis and conversion as well. Deep learning, as the technology which underlies most of the recent advances in artificial intelligence, is spearheading these efforts. In the present overview, we outline ongoing trends and summarise state-of-the-art approaches in an attempt to provide a comprehensive overview of this exciting field.
Depression Diagnosis and Forecast based on Mobile Phone Sensor Data
May 10, 2022
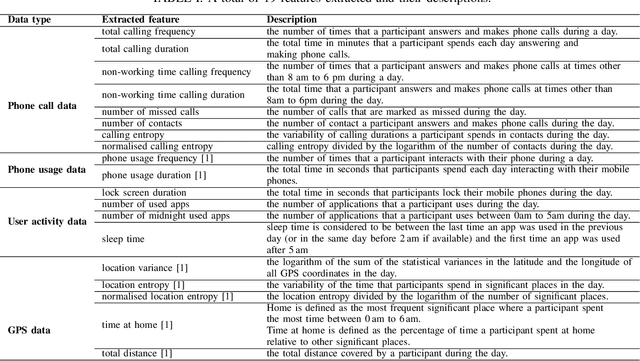
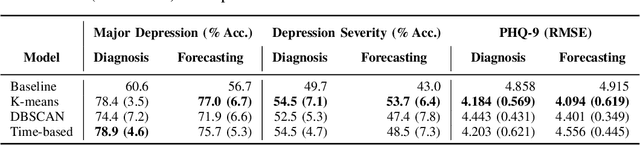
Abstract:Previous studies have shown the correlation between sensor data collected from mobile phones and human depression states. Compared to the traditional self-assessment questionnaires, the passive data collected from mobile phones is easier to access and less time-consuming. In particular, passive mobile phone data can be collected on a flexible time interval, thus detecting moment-by-moment psychological changes and helping achieve earlier interventions. Moreover, while previous studies mainly focused on depression diagnosis using mobile phone data, depression forecasting has not received sufficient attention. In this work, we extract four types of passive features from mobile phone data, including phone call, phone usage, user activity, and GPS features. We implement a long short-term memory (LSTM) network in a subject-independent 10-fold cross-validation setup to model both a diagnostic and a forecasting tasks. Experimental results show that the forecasting task achieves comparable results with the diagnostic task, which indicates the possibility of forecasting depression from mobile phone sensor data. Our model achieves an accuracy of 77.0 % for major depression forecasting (binary), an accuracy of 53.7 % for depression severity forecasting (5 classes), and a best RMSE score of 4.094 (PHQ-9, range from 0 to 27).
Journaling Data for Daily PHQ-2 Depression Prediction and Forecasting
May 06, 2022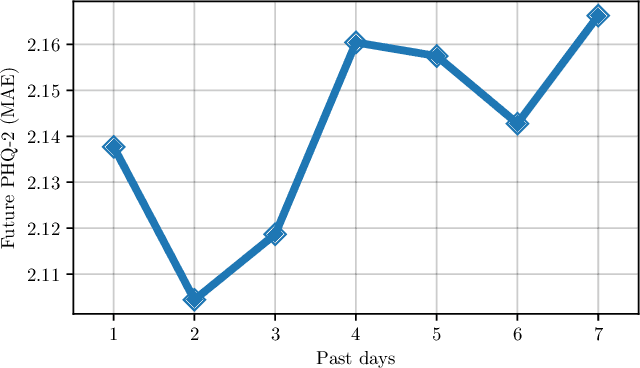
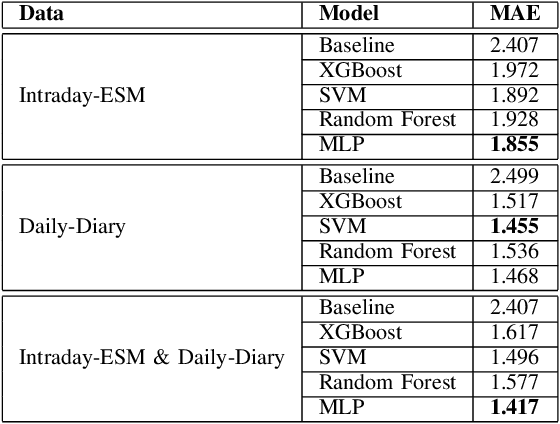
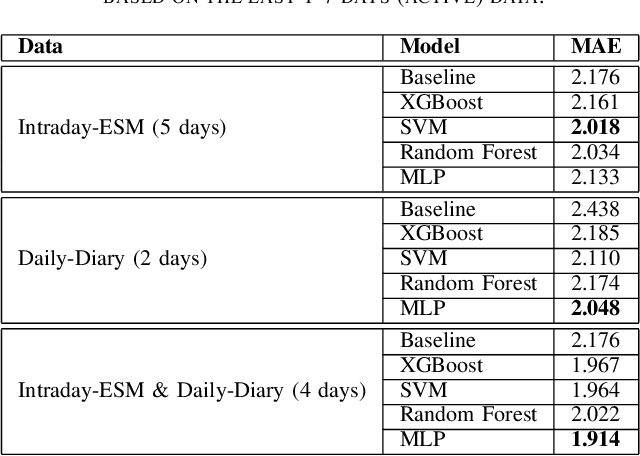
Abstract:Digital health applications are becoming increasingly important for assessing and monitoring the wellbeing of people suffering from mental health conditions like depression. A common target of said applications is to predict the results of self-assessed Patient-Health-Questionnaires (PHQ), indicating current symptom severity of depressive individuals. In this work, we explore the potential of using actively-collected data to predict and forecast daily PHQ-2 scores on a newly-collected longitudinal dataset. We obtain a best MAE of 1.417 for daily prediction of PHQ-2 scores, which specifically in the used dataset have a range of 0 to 12, using leave-one-subject-out cross-validation, as well as a best MAE of 1.914 for forecasting PHQ-2 scores using data from up to the last 7 days. This illustrates the additive value that can be obtained by incorporating actively-collected data in a depression monitoring application.
An Improved StarGAN for Emotional Voice Conversion: Enhancing Voice Quality and Data Augmentation
Jul 18, 2021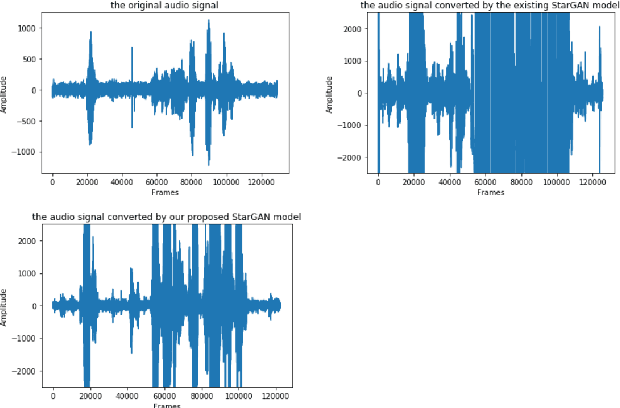


Abstract:Emotional Voice Conversion (EVC) aims to convert the emotional style of a source speech signal to a target style while preserving its content and speaker identity information. Previous emotional conversion studies do not disentangle emotional information from emotion-independent information that should be preserved, thus transforming it all in a monolithic manner and generating audio of low quality, with linguistic distortions. To address this distortion problem, we propose a novel StarGAN framework along with a two-stage training process that separates emotional features from those independent of emotion by using an autoencoder with two encoders as the generator of the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). The proposed model achieves favourable results in both the objective evaluation and the subjective evaluation in terms of distortion, which reveals that the proposed model can effectively reduce distortion. Furthermore, in data augmentation experiments for end-to-end speech emotion recognition, the proposed StarGAN model achieves an increase of 2% in Micro-F1 and 5% in Macro-F1 compared to the baseline StarGAN model, which indicates that the proposed model is more valuable for data augmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge