Journaling Data for Daily PHQ-2 Depression Prediction and Forecasting
Paper and Code
May 06, 2022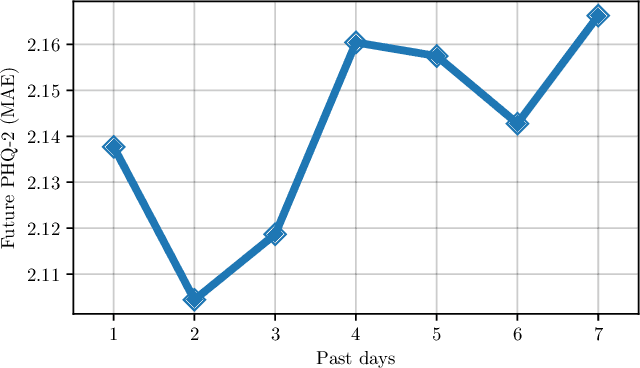
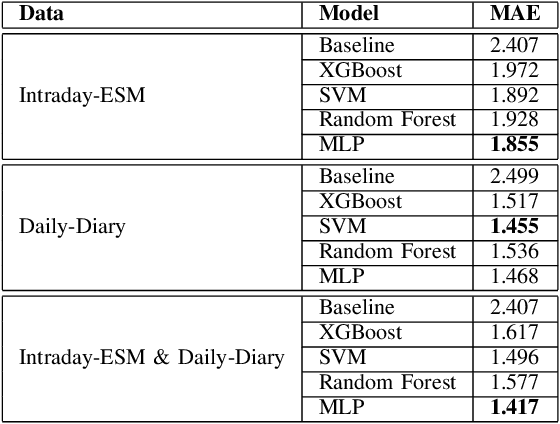
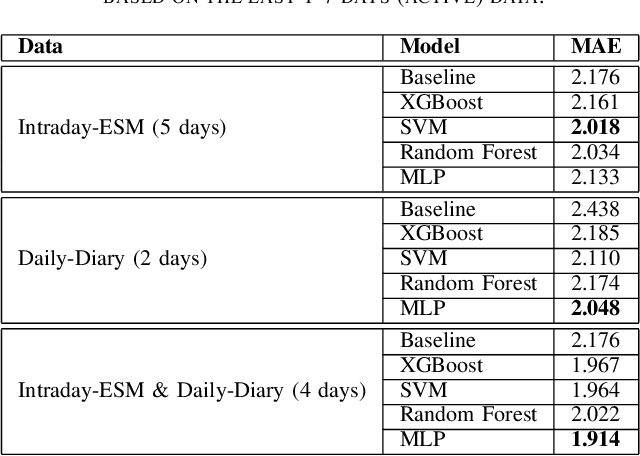
Digital health applications are becoming increasingly important for assessing and monitoring the wellbeing of people suffering from mental health conditions like depression. A common target of said applications is to predict the results of self-assessed Patient-Health-Questionnaires (PHQ), indicating current symptom severity of depressive individuals. In this work, we explore the potential of using actively-collected data to predict and forecast daily PHQ-2 scores on a newly-collected longitudinal dataset. We obtain a best MAE of 1.417 for daily prediction of PHQ-2 scores, which specifically in the used dataset have a range of 0 to 12, using leave-one-subject-out cross-validation, as well as a best MAE of 1.914 for forecasting PHQ-2 scores using data from up to the last 7 days. This illustrates the additive value that can be obtained by incorporating actively-collected data in a depression monitoring application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge