Wonsuk Yang
Trillion Labs
Trillion 7B Technical Report
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:We introduce Trillion-7B, the most token-efficient Korean-centric multilingual LLM available. Our novel Cross-lingual Document Attention (XLDA) mechanism enables highly efficient and effective knowledge transfer from English to target languages like Korean and Japanese. Combined with optimized data mixtures, language-specific filtering, and tailored tokenizer construction, Trillion-7B achieves competitive performance while dedicating only 10\% of its 2T training tokens to multilingual data and requiring just 59.4K H100 GPU hours (\$148K) for full training. Comprehensive evaluations across 27 benchmarks in four languages demonstrate Trillion-7B's robust multilingual performance and exceptional cross-lingual consistency.
Fashion Style Editing with Generative Human Prior
Apr 02, 2024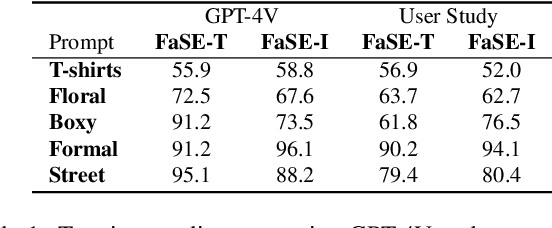
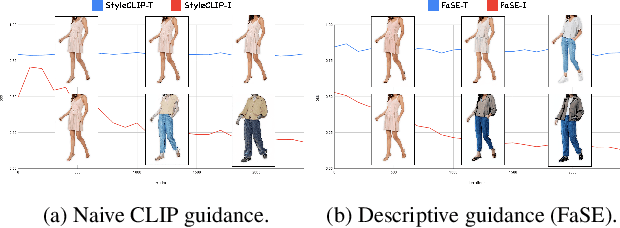
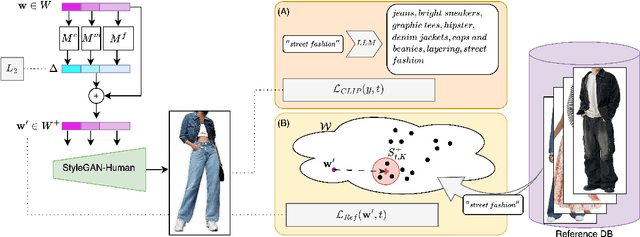
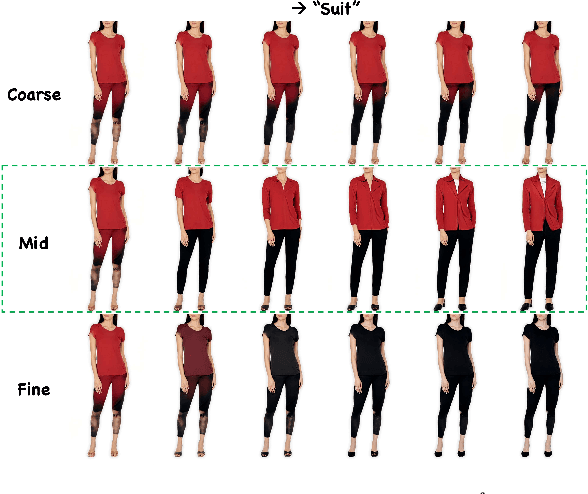
Abstract:Image editing has been a long-standing challenge in the research community with its far-reaching impact on numerous applications. Recently, text-driven methods started to deliver promising results in domains like human faces, but their applications to more complex domains have been relatively limited. In this work, we explore the task of fashion style editing, where we aim to manipulate the fashion style of human imagery using text descriptions. Specifically, we leverage a generative human prior and achieve fashion style editing by navigating its learned latent space. We first verify that the existing text-driven editing methods fall short for our problem due to their overly simplified guidance signal, and propose two directions to reinforce the guidance: textual augmentation and visual referencing. Combined with our empirical findings on the latent space structure, our Fashion Style Editing framework (FaSE) successfully projects abstract fashion concepts onto human images and introduces exciting new applications to the field.
A Prompt Array Keeps the Bias Away: Debiasing Vision-Language Models with Adversarial Learning
Apr 01, 2022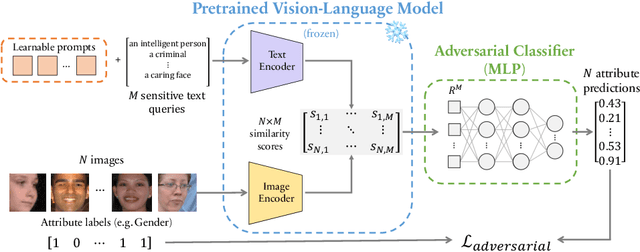
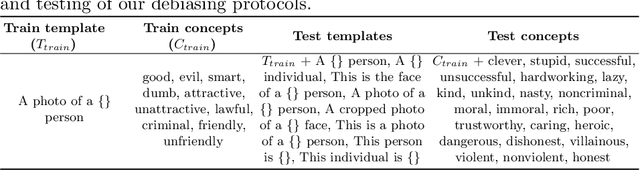
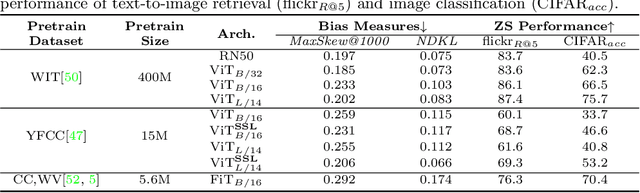

Abstract:Vision-language models can encode societal biases and stereotypes, but there are challenges to measuring and mitigating these harms. Prior proposed bias measurements lack robustness and feature degradation occurs when mitigating bias without access to pretraining data. We address both of these challenges in this paper: First, we evaluate different bias measures and propose the use of retrieval metrics to image-text representations via a bias measuring framework. Second, we investigate debiasing methods and show that optimizing for adversarial loss via learnable token embeddings minimizes various bias measures without substantially degrading feature representations.
Pano-AVQA: Grounded Audio-Visual Question Answering on 360$^\circ$ Videos
Oct 11, 2021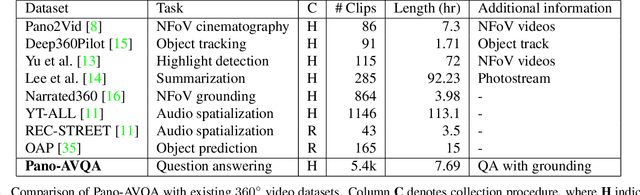
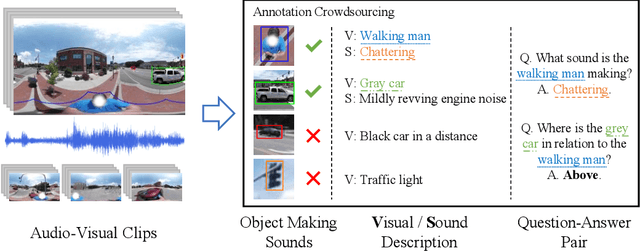
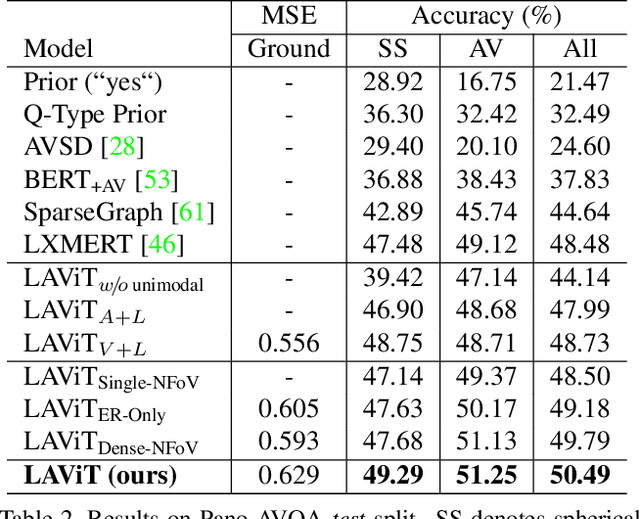
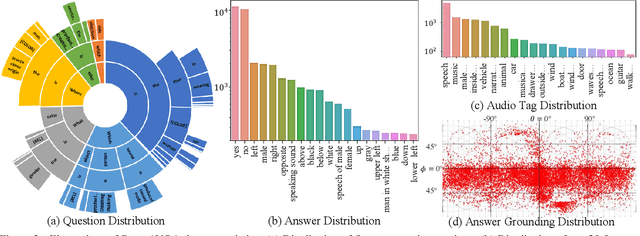
Abstract:360$^\circ$ videos convey holistic views for the surroundings of a scene. It provides audio-visual cues beyond pre-determined normal field of views and displays distinctive spatial relations on a sphere. However, previous benchmark tasks for panoramic videos are still limited to evaluate the semantic understanding of audio-visual relationships or spherical spatial property in surroundings. We propose a novel benchmark named Pano-AVQA as a large-scale grounded audio-visual question answering dataset on panoramic videos. Using 5.4K 360$^\circ$ video clips harvested online, we collect two types of novel question-answer pairs with bounding-box grounding: spherical spatial relation QAs and audio-visual relation QAs. We train several transformer-based models from Pano-AVQA, where the results suggest that our proposed spherical spatial embeddings and multimodal training objectives fairly contribute to a better semantic understanding of the panoramic surroundings on the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge