Wenxin Shao
Solving Motion Planning Tasks with a Scalable Generative Model
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:As autonomous driving systems being deployed to millions of vehicles, there is a pressing need of improving the system's scalability, safety and reducing the engineering cost. A realistic, scalable, and practical simulator of the driving world is highly desired. In this paper, we present an efficient solution based on generative models which learns the dynamics of the driving scenes. With this model, we can not only simulate the diverse futures of a given driving scenario but also generate a variety of driving scenarios conditioned on various prompts. Our innovative design allows the model to operate in both full-Autoregressive and partial-Autoregressive modes, significantly improving inference and training speed without sacrificing generative capability. This efficiency makes it ideal for being used as an online reactive environment for reinforcement learning, an evaluator for planning policies, and a high-fidelity simulator for testing. We evaluated our model against two real-world datasets: the Waymo motion dataset and the nuPlan dataset. On the simulation realism and scene generation benchmark, our model achieves the state-of-the-art performance. And in the planning benchmarks, our planner outperforms the prior arts. We conclude that the proposed generative model may serve as a foundation for a variety of motion planning tasks, including data generation, simulation, planning, and online training. Source code is public at https://github.com/HorizonRobotics/GUMP/
Imitation with Spatial-Temporal Heatmap: 2nd Place Solution for NuPlan Challenge
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:This paper presents our 2nd place solution for the NuPlan Challenge 2023. Autonomous driving in real-world scenarios is highly complex and uncertain. Achieving safe planning in the complex multimodal scenarios is a highly challenging task. Our approach, Imitation with Spatial-Temporal Heatmap, adopts the learning form of behavior cloning, innovatively predicts the future multimodal states with a heatmap representation, and uses trajectory refinement techniques to ensure final safety. The experiment shows that our method effectively balances the vehicle's progress and safety, generating safe and comfortable trajectories. In the NuPlan competition, we achieved the second highest overall score, while obtained the best scores in the ego progress and comfort metrics.
HOPE: Hierarchical Spatial-temporal Network for Occupancy Flow Prediction
Jun 21, 2022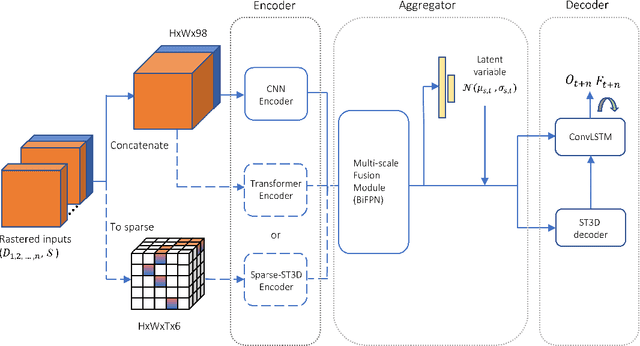
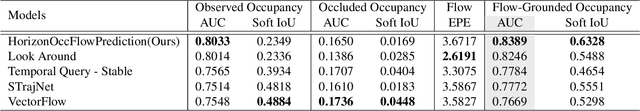
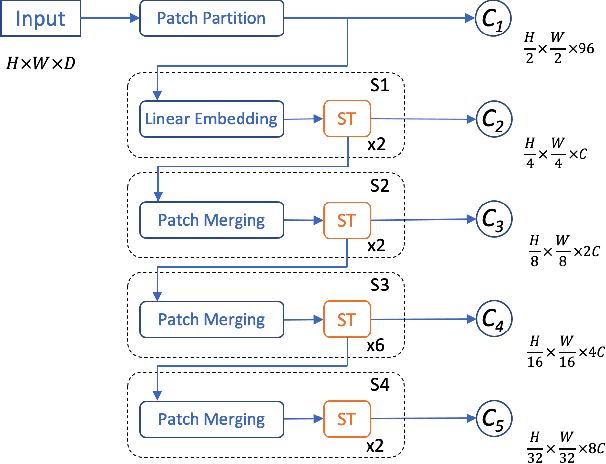
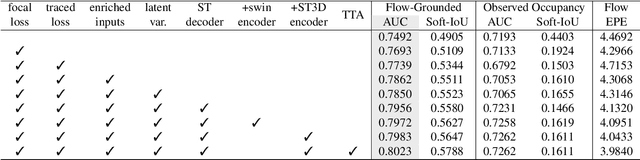
Abstract:In this report, we introduce our solution to the Occupancy and Flow Prediction challenge in the Waymo Open Dataset Challenges at CVPR 2022, which ranks 1st on the leaderboard. We have developed a novel hierarchical spatial-temporal network featured with spatial-temporal encoders, a multi-scale aggregator enriched with latent variables, and a recursive hierarchical 3D decoder. We use multiple losses including focal loss and modified flow trace loss to efficiently guide the training process. Our method achieves a Flow-Grounded Occupancy AUC of 0.8389 and outperforms all the other teams on the leaderboard.
AFDetV2: Rethinking the Necessity of the Second Stage for Object Detection from Point Clouds
Dec 16, 2021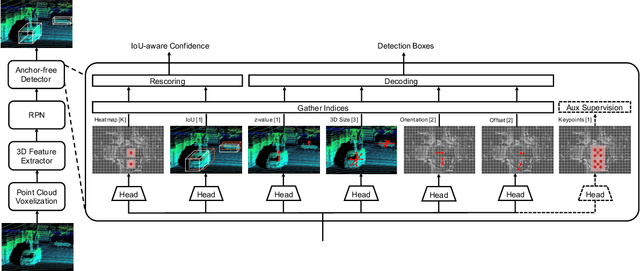
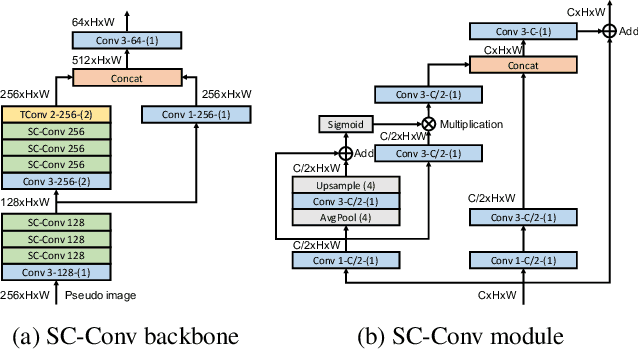
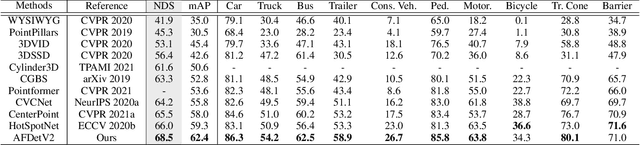
Abstract:There have been two streams in the 3D detection from point clouds: single-stage methods and two-stage methods. While the former is more computationally efficient, the latter usually provides better detection accuracy. By carefully examining the two-stage approaches, we have found that if appropriately designed, the first stage can produce accurate box regression. In this scenario, the second stage mainly rescores the boxes such that the boxes with better localization get selected. From this observation, we have devised a single-stage anchor-free network that can fulfill these requirements. This network, named AFDetV2, extends the previous work by incorporating a self-calibrated convolution block in the backbone, a keypoint auxiliary supervision, and an IoU prediction branch in the multi-task head. As a result, the detection accuracy is drastically boosted in the single-stage. To evaluate our approach, we have conducted extensive experiments on the Waymo Open Dataset and the nuScenes Dataset. We have observed that our AFDetV2 achieves the state-of-the-art results on these two datasets, superior to all the prior arts, including both the single-stage and the two-stage se3D detectors. AFDetV2 won the 1st place in the Real-Time 3D Detection of the Waymo Open Dataset Challenge 2021. In addition, a variant of our model AFDetV2-Base was entitled the "Most Efficient Model" by the Challenge Sponsor, showing a superior computational efficiency. To demonstrate the generality of this single-stage method, we have also applied it to the first stage of the two-stage networks. Without exception, the results show that with the strengthened backbone and the rescoring approach, the second stage refinement is no longer needed.
Real-Time Anchor-Free Single-Stage 3D Detection with IoU-Awareness
Aug 03, 2021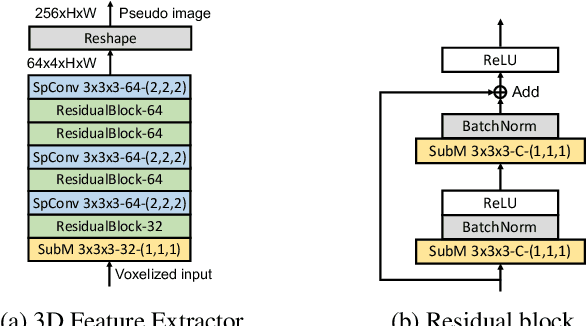
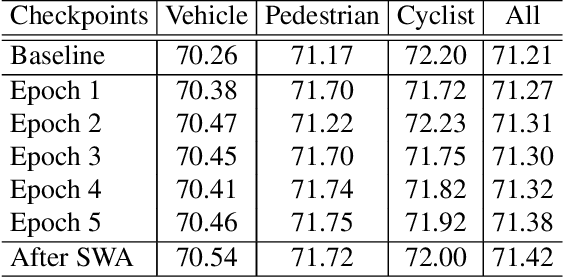
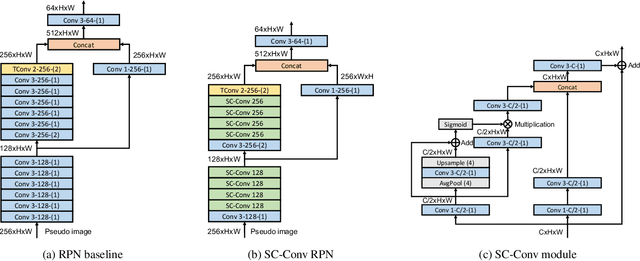
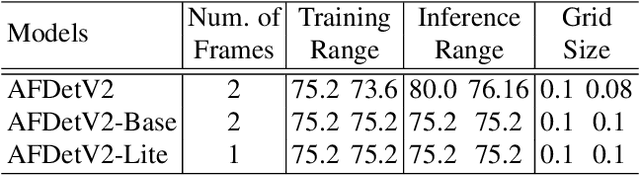
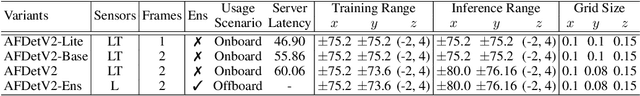
Abstract:In this report, we introduce our winning solution to the Real-time 3D Detection and also the "Most Efficient Model" in the Waymo Open Dataset Challenges at CVPR 2021. Extended from our last year's award-winning model AFDet, we have made a handful of modifications to the base model, to improve the accuracy and at the same time to greatly reduce the latency. The modified model, named as AFDetV2, is featured with a lite 3D Feature Extractor, an improved RPN with extended receptive field and an added sub-head that produces an IoU-aware confidence score. These model enhancements, together with enriched data augmentation, stochastic weights averaging, and a GPU-based implementation of voxelization, lead to a winning accuracy of 73.12 mAPH/L2 for our AFDetV2 with a latency of 60.06 ms, and an accuracy of 72.57 mAPH/L2 for our AFDetV2-base, entitled as the "Most Efficient Model" by the challenge sponsor, with a winning latency of 55.86 ms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge