Weili Guo
Robust Semi-Supervised Learning for Self-learning Open-World Classes
Jan 15, 2024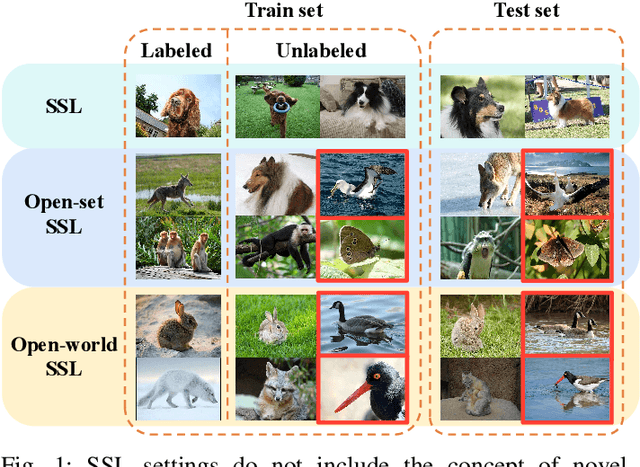
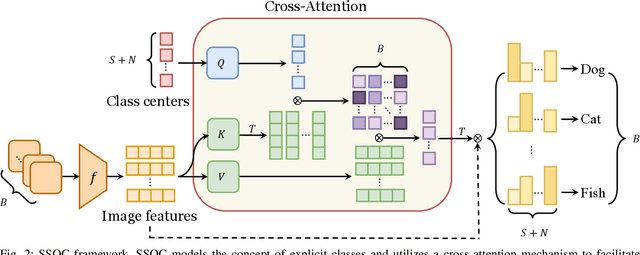
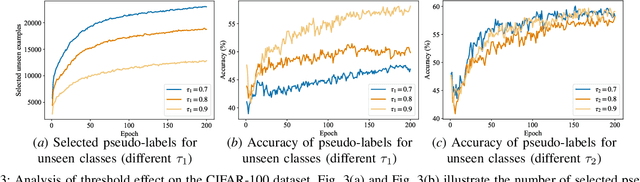
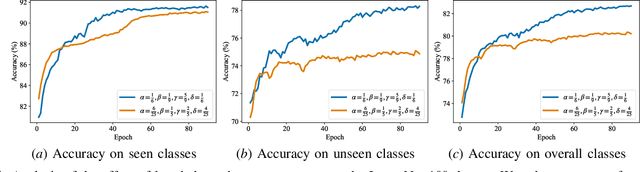
Abstract:Existing semi-supervised learning (SSL) methods assume that labeled and unlabeled data share the same class space. However, in real-world applications, unlabeled data always contain classes not present in the labeled set, which may cause classification performance degradation of known classes. Therefore, open-world SSL approaches are researched to handle the presence of multiple unknown classes in the unlabeled data, which aims to accurately classify known classes while fine-grained distinguishing different unknown classes. To address this challenge, in this paper, we propose an open-world SSL method for Self-learning Open-world Classes (SSOC), which can explicitly self-learn multiple unknown classes. Specifically, SSOC first defines class center tokens for both known and unknown classes and autonomously learns token representations according to all samples with the cross-attention mechanism. To effectively discover novel classes, SSOC further designs a pairwise similarity loss in addition to the entropy loss, which can wisely exploit the information available in unlabeled data from instances' predictions and relationships. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SSOC outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on multiple popular classification benchmarks. Specifically, on the ImageNet-100 dataset with a novel ratio of 90%, SSOC achieves a remarkable 22% improvement.
The Solution for the CVPR2023 NICE Image Captioning Challenge
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present our solution to the New frontiers for Zero-shot Image Captioning Challenge. Different from the traditional image captioning datasets, this challenge includes a larger new variety of visual concepts from many domains (such as COVID-19) as well as various image types (photographs, illustrations, graphics). For the data level, we collect external training data from Laion-5B, a large-scale CLIP-filtered image-text dataset. For the model level, we use OFA, a large-scale visual-language pre-training model based on handcrafted templates, to perform the image captioning task. In addition, we introduce contrastive learning to align image-text pairs to learn new visual concepts in the pre-training stage. Then, we propose a similarity-bucket strategy and incorporate this strategy into the template to force the model to generate higher quality and more matching captions. Finally, by retrieval-augmented strategy, we construct a content-rich template, containing the most relevant top-k captions from other image-text pairs, to guide the model in generating semantic-rich captions. Our method ranks first on the leaderboard, achieving 105.17 and 325.72 Cider-Score in the validation and test phase, respectively.
NICE: CVPR 2023 Challenge on Zero-shot Image Captioning
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:In this report, we introduce NICE (New frontiers for zero-shot Image Captioning Evaluation) project and share the results and outcomes of 2023 challenge. This project is designed to challenge the computer vision community to develop robust image captioning models that advance the state-of-the-art both in terms of accuracy and fairness. Through the challenge, the image captioning models were tested using a new evaluation dataset that includes a large variety of visual concepts from many domains. There was no specific training data provided for the challenge, and therefore the challenge entries were required to adapt to new types of image descriptions that had not been seen during training. This report includes information on the newly proposed NICE dataset, evaluation methods, challenge results, and technical details of top-ranking entries. We expect that the outcomes of the challenge will contribute to the improvement of AI models on various vision-language tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge