Weichung Wang
Federated Learning with Partially Labeled Data: A Conditional Distillation Approach
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:In medical imaging, developing generalized segmentation models that can handle multiple organs and lesions is crucial. However, the scarcity of fully annotated datasets and strict privacy regulations present significant barriers to data sharing. Federated Learning (FL) allows decentralized model training, but existing FL methods often struggle with partial labeling, leading to model divergence and catastrophic forgetting. We propose ConDistFL, a novel FL framework incorporating conditional distillation to address these challenges. ConDistFL enables effective learning from partially labeled datasets, significantly improving segmentation accuracy across distributed and non-uniform datasets. In addition to its superior segmentation performance, ConDistFL maintains computational and communication efficiency, ensuring its scalability for real-world applications. Furthermore, ConDistFL demonstrates remarkable generalizability, significantly outperforming existing FL methods in out-of-federation tests, even adapting to unseen contrast phases (e.g., non-contrast CT images) in our experiments. Extensive evaluations on 3D CT and 2D chest X-ray datasets show that ConDistFL is an efficient, adaptable solution for collaborative medical image segmentation in privacy-constrained settings.
ConDistFL: Conditional Distillation for Federated Learning from Partially Annotated Data
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Developing a generalized segmentation model capable of simultaneously delineating multiple organs and diseases is highly desirable. Federated learning (FL) is a key technology enabling the collaborative development of a model without exchanging training data. However, the limited access to fully annotated training data poses a major challenge to training generalizable models. We propose "ConDistFL", a framework to solve this problem by combining FL with knowledge distillation. Local models can extract the knowledge of unlabeled organs and tumors from partially annotated data from the global model with an adequately designed conditional probability representation. We validate our framework on four distinct partially annotated abdominal CT datasets from the MSD and KiTS19 challenges. The experimental results show that the proposed framework significantly outperforms FedAvg and FedOpt baselines. Moreover, the performance on an external test dataset demonstrates superior generalizability compared to models trained on each dataset separately. Our ablation study suggests that ConDistFL can perform well without frequent aggregation, reducing the communication cost of FL. Our implementation will be available at https://github.com/NVIDIA/NVFlare/tree/dev/research/condist-fl.
Multi-task Federated Learning for Heterogeneous Pancreas Segmentation
Aug 19, 2021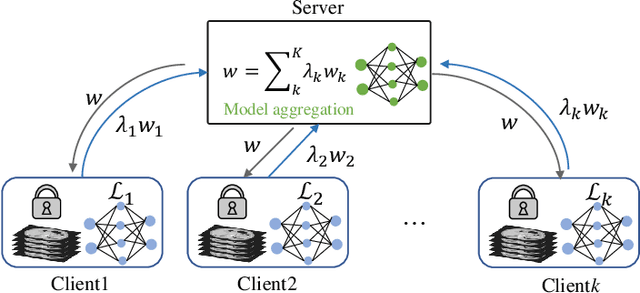
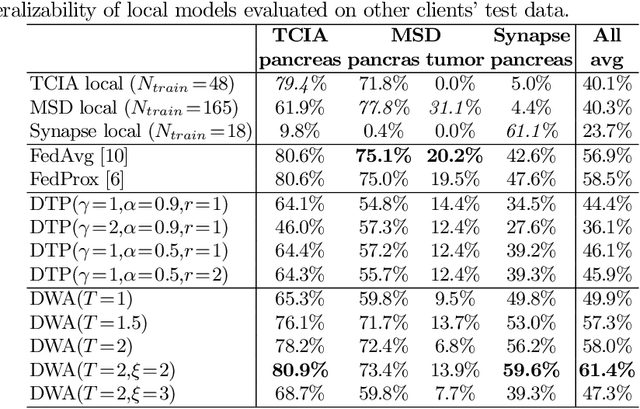
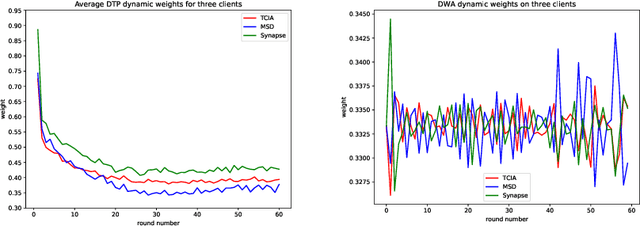
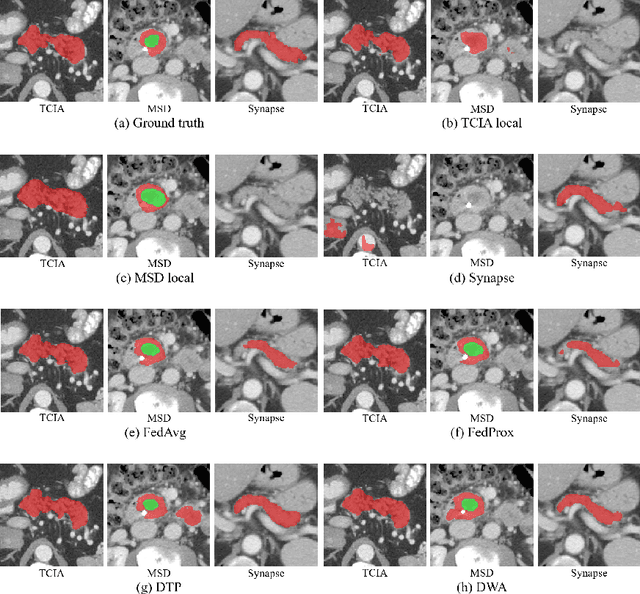
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) for medical image segmentation becomes more challenging in multi-task settings where clients might have different categories of labels represented in their data. For example, one client might have patient data with "healthy'' pancreases only while datasets from other clients may contain cases with pancreatic tumors. The vanilla federated averaging algorithm makes it possible to obtain more generalizable deep learning-based segmentation models representing the training data from multiple institutions without centralizing datasets. However, it might be sub-optimal for the aforementioned multi-task scenarios. In this paper, we investigate heterogeneous optimization methods that show improvements for the automated segmentation of pancreas and pancreatic tumors in abdominal CT images with FL settings.
Segmentation of Cardiac Structures via Successive Subspace Learning with Saab Transform from Cine MRI
Jul 22, 2021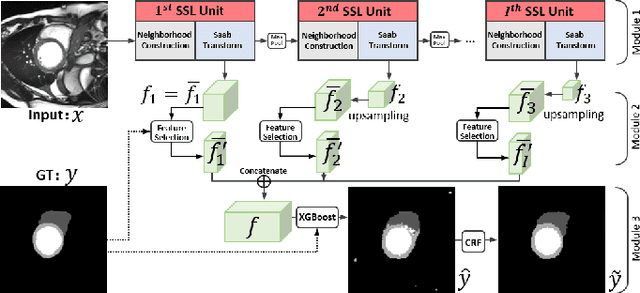

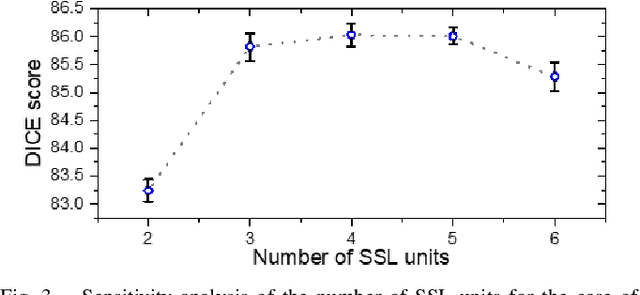
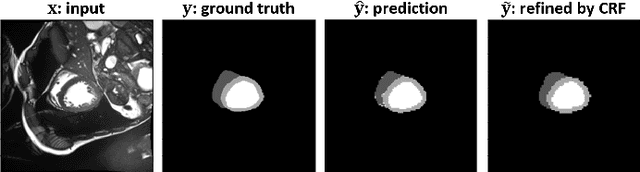
Abstract:Assessment of cardiovascular disease (CVD) with cine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been used to non-invasively evaluate detailed cardiac structure and function. Accurate segmentation of cardiac structures from cine MRI is a crucial step for early diagnosis and prognosis of CVD, and has been greatly improved with convolutional neural networks (CNN). There, however, are a number of limitations identified in CNN models, such as limited interpretability and high complexity, thus limiting their use in clinical practice. In this work, to address the limitations, we propose a lightweight and interpretable machine learning model, successive subspace learning with the subspace approximation with adjusted bias (Saab) transform, for accurate and efficient segmentation from cine MRI. Specifically, our segmentation framework is comprised of the following steps: (1) sequential expansion of near-to-far neighborhood at different resolutions; (2) channel-wise subspace approximation using the Saab transform for unsupervised dimension reduction; (3) class-wise entropy guided feature selection for supervised dimension reduction; (4) concatenation of features and pixel-wise classification with gradient boost; and (5) conditional random field for post-processing. Experimental results on the ACDC 2017 segmentation database, showed that our framework performed better than state-of-the-art U-Net models with 200$\times$ fewer parameters in delineating the left ventricle, right ventricle, and myocardium, thus showing its potential to be used in clinical practice.
Spectral Machine Learning for Pancreatic Mass Imaging Classification
May 03, 2021



Abstract:We present a novel spectral machine learning (SML) method in screening for pancreatic mass using CT imaging. Our algorithm is trained with approximately 30,000 images from 250 patients (50 patients with normal pancreas and 200 patients with abnormal pancreas findings) based on public data sources. A test accuracy of 94.6 percents was achieved in the out-of-sample diagnosis classification based on a total of approximately 15,000 images from 113 patients, whereby 26 out of 32 patients with normal pancreas and all 81 patients with abnormal pancreas findings were correctly diagnosed. SML is able to automatically choose fundamental images (on average 5 or 9 images for each patient) in the diagnosis classification and achieve the above mentioned accuracy. The computational time is 75 seconds for diagnosing 113 patients in a laptop with standard CPU running environment. Factors that influenced high performance of a well-designed integration of spectral learning and machine learning included: 1) use of eigenvectors corresponding to several of the largest eigenvalues of sample covariance matrix (spike eigenvectors) to choose input attributes in classification training, taking into account only the fundamental information of the raw images with less noise; 2) removal of irrelevant pixels based on mean-level spectral test to lower the challenges of memory capacity and enhance computational efficiency while maintaining superior classification accuracy; 3) adoption of state-of-the-art machine learning classification, gradient boosting and random forest. Our methodology showcases practical utility and improved accuracy of image diagnosis in pancreatic mass screening in the era of AI.
Automated Pancreas Segmentation Using Multi-institutional Collaborative Deep Learning
Sep 28, 2020



Abstract:The performance of deep learning-based methods strongly relies on the number of datasets used for training. Many efforts have been made to increase the data in the medical image analysis field. However, unlike photography images, it is hard to generate centralized databases to collect medical images because of numerous technical, legal, and privacy issues. In this work, we study the use of federated learning between two institutions in a real-world setting to collaboratively train a model without sharing the raw data across national boundaries. We quantitatively compare the segmentation models obtained with federated learning and local training alone. Our experimental results show that federated learning models have higher generalizability than standalone training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge