W. Dean Wallace
A Multi-resolution Model for Histopathology Image Classification and Localization with Multiple Instance Learning
Nov 05, 2020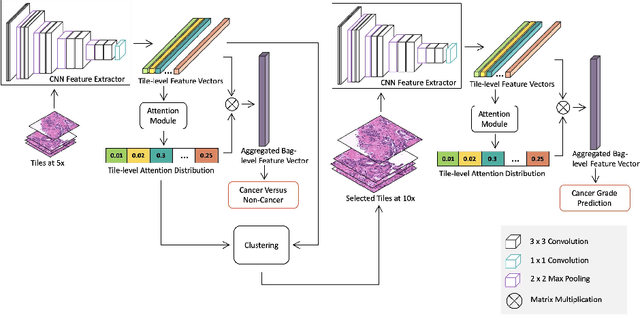
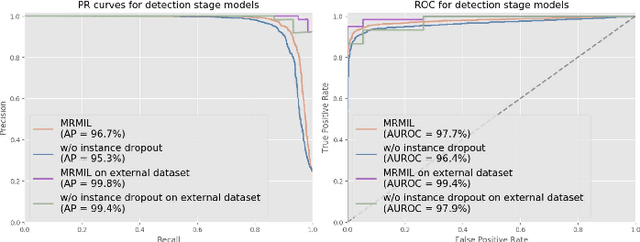
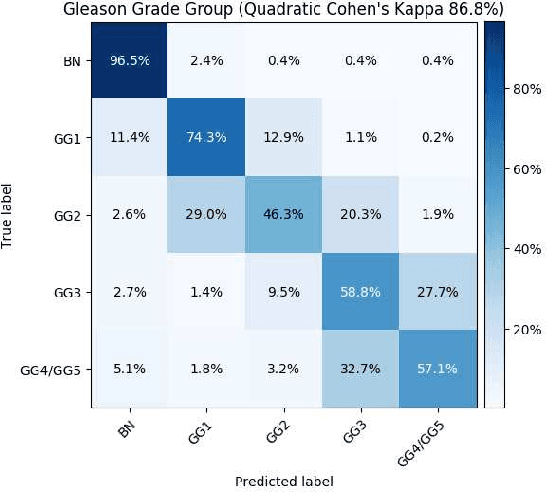
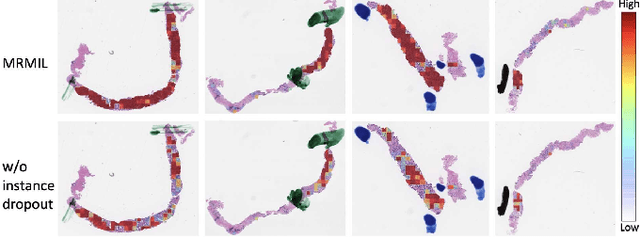
Abstract:Histopathological images provide rich information for disease diagnosis. Large numbers of histopathological images have been digitized into high resolution whole slide images, opening opportunities in developing computational image analysis tools to reduce pathologists' workload and potentially improve inter- and intra- observer agreement. Most previous work on whole slide image analysis has focused on classification or segmentation of small pre-selected regions-of-interest, which requires fine-grained annotation and is non-trivial to extend for large-scale whole slide analysis. In this paper, we proposed a multi-resolution multiple instance learning model that leverages saliency maps to detect suspicious regions for fine-grained grade prediction. Instead of relying on expensive region- or pixel-level annotations, our model can be trained end-to-end with only slide-level labels. The model is developed on a large-scale prostate biopsy dataset containing 20,229 slides from 830 patients. The model achieved 92.7% accuracy, 81.8% Cohen's Kappa for benign, low grade (i.e. Grade group 1) and high grade (i.e. Grade group >= 2) prediction, an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 98.2% and an average precision (AP) of 97.4% for differentiating malignant and benign slides. The model obtained an AUROC of 99.4% and an AP of 99.8% for cancer detection on an external dataset.
Deep learning-based transformation of the H&E stain into special stains improves kidney disease diagnosis
Aug 20, 2020
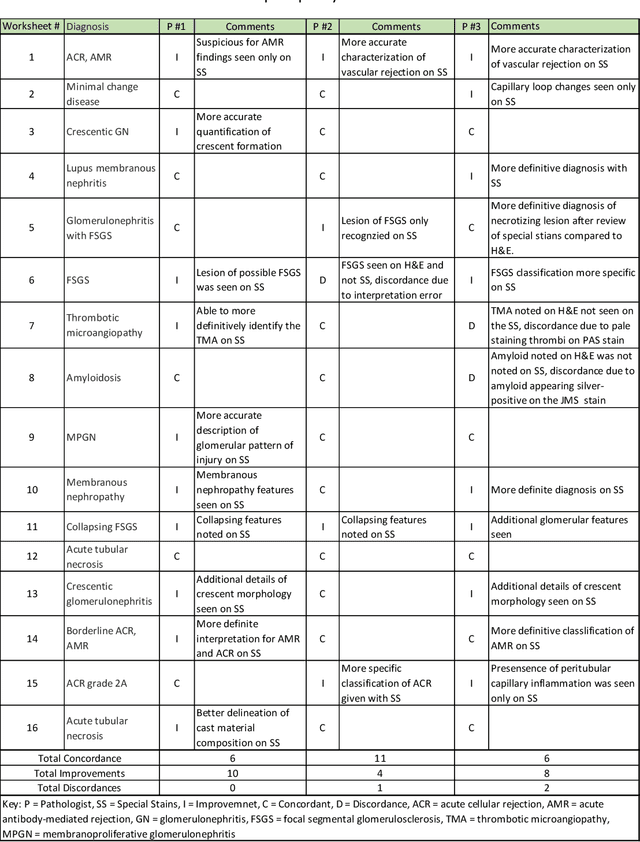


Abstract:Pathology is practiced by visual inspection of histochemically stained slides. Most commonly, the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain is used in the diagnostic workflow and it is the gold standard for cancer diagnosis. However, in many cases, especially for non-neoplastic diseases, additional "special stains" are used to provide different levels of contrast and color to tissue components and allow pathologists to get a clearer diagnostic picture. In this study, we demonstrate the utility of supervised learning-based computational stain transformation from H&E to different special stains (Masson's Trichrome, periodic acid-Schiff and Jones silver stain) using tissue sections from kidney needle core biopsies. Based on evaluation by three renal pathologists, followed by adjudication by a fourth renal pathologist, we show that the generation of virtual special stains from existing H&E images improves the diagnosis in several non-neoplastic kidney diseases, sampled from 16 unique subjects. Adjudication of N=48 diagnoses from the three pathologists revealed that the virtually generated special stains yielded 22 improvements (45.8%), 23 concordances (47.9%) and 3 discordances (6.3%), when compared against the use of H&E stained tissue only. As the virtual transformation of H&E images into special stains can be achieved in less than 1 min per patient core specimen slide, this stain-to-stain transformation framework can improve the quality of the preliminary diagnosis when additional special stains are needed, along with significant savings in time and cost, reducing the burden on healthcare system and patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge