Usha Bhalla
Interpretability Illusions with Sparse Autoencoders: Evaluating Robustness of Concept Representations
May 21, 2025Abstract:Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) are commonly used to interpret the internal activations of large language models (LLMs) by mapping them to human-interpretable concept representations. While existing evaluations of SAEs focus on metrics such as the reconstruction-sparsity tradeoff, human (auto-)interpretability, and feature disentanglement, they overlook a critical aspect: the robustness of concept representations to input perturbations. We argue that robustness must be a fundamental consideration for concept representations, reflecting the fidelity of concept labeling. To this end, we formulate robustness quantification as input-space optimization problems and develop a comprehensive evaluation framework featuring realistic scenarios in which adversarial perturbations are crafted to manipulate SAE representations. Empirically, we find that tiny adversarial input perturbations can effectively manipulate concept-based interpretations in most scenarios without notably affecting the outputs of the base LLMs themselves. Overall, our results suggest that SAE concept representations are fragile and may be ill-suited for applications in model monitoring and oversight.
Building Bridges, Not Walls -- Advancing Interpretability by Unifying Feature, Data, and Model Component Attribution
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The increasing complexity of AI systems has made understanding their behavior a critical challenge. Numerous methods have been developed to attribute model behavior to three key aspects: input features, training data, and internal model components. However, these attribution methods are studied and applied rather independently, resulting in a fragmented landscape of approaches and terminology. This position paper argues that feature, data, and component attribution methods share fundamental similarities, and bridging them can benefit interpretability research. We conduct a detailed analysis of successful methods across three domains and present a unified view to demonstrate that these seemingly distinct methods employ similar approaches, such as perturbations, gradients, and linear approximations, differing primarily in their perspectives rather than core techniques. Our unified perspective enhances understanding of existing attribution methods, identifies shared concepts and challenges, makes this field more accessible to newcomers, and highlights new directions not only for attribution and interpretability but also for broader AI research, including model editing, steering, and regulation.
Towards Unifying Interpretability and Control: Evaluation via Intervention
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:With the growing complexity and capability of large language models, a need to understand model reasoning has emerged, often motivated by an underlying goal of controlling and aligning models. While numerous interpretability and steering methods have been proposed as solutions, they are typically designed either for understanding or for control, seldom addressing both, with the connection between interpretation and control more broadly remaining tenuous. Additionally, the lack of standardized applications, motivations, and evaluation metrics makes it difficult to assess these methods' practical utility and efficacy. To address this, we propose intervention as a fundamental goal of interpretability and introduce success criteria to evaluate how well methods are able to control model behavior through interventions. We unify and extend four popular interpretability methods--sparse autoencoders, logit lens, tuned lens, and probing--into an abstract encoder-decoder framework. This framework maps intermediate latent representations to human-interpretable feature spaces, enabling interventions on these interpretable features, which can then be mapped back to latent representations to control model outputs. We introduce two new evaluation metrics: intervention success rate and the coherence-intervention tradeoff, designed to measure the accuracy of explanations and their utility in controlling model behavior. Our findings reveal that (1) although current methods allow for intervention, they are inconsistent across models and features, (2) lens-based methods outperform others in achieving simple, concrete interventions, and (3) interventions often compromise model performance and coherence, underperforming simpler alternatives, such as prompting, for steering model behavior and highlighting a critical shortcoming of current interpretability approaches in real-world applications requiring control.
All Roads Lead to Rome? Exploring Representational Similarities Between Latent Spaces of Generative Image Models
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:Do different generative image models secretly learn similar underlying representations? We investigate this by measuring the latent space similarity of four different models: VAEs, GANs, Normalizing Flows (NFs), and Diffusion Models (DMs). Our methodology involves training linear maps between frozen latent spaces to "stitch" arbitrary pairs of encoders and decoders and measuring output-based and probe-based metrics on the resulting "stitched'' models. Our main findings are that linear maps between latent spaces of performant models preserve most visual information even when latent sizes differ; for CelebA models, gender is the most similarly represented probe-able attribute. Finally we show on an NF that latent space representations converge early in training.
Operationalizing the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights: Recommendations for Practitioners, Researchers, and Policy Makers
Jul 11, 2024Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools are increasingly employed in diverse real-world applications, there has been significant interest in regulating these tools. To this end, several regulatory frameworks have been introduced by different countries worldwide. For example, the European Union recently passed the AI Act, the White House issued an Executive Order on safe, secure, and trustworthy AI, and the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy issued the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (AI BoR). Many of these frameworks emphasize the need for auditing and improving the trustworthiness of AI tools, underscoring the importance of safety, privacy, explainability, fairness, and human fallback options. Although these regulatory frameworks highlight the necessity of enforcement, practitioners often lack detailed guidance on implementing them. Furthermore, the extensive research on operationalizing each of these aspects is frequently buried in technical papers that are difficult for practitioners to parse. In this write-up, we address this shortcoming by providing an accessible overview of existing literature related to operationalizing regulatory principles. We provide easy-to-understand summaries of state-of-the-art literature and highlight various gaps that exist between regulatory guidelines and existing AI research, including the trade-offs that emerge during operationalization. We hope that this work not only serves as a starting point for practitioners interested in learning more about operationalizing the regulatory guidelines outlined in the Blueprint for an AI BoR but also provides researchers with a list of critical open problems and gaps between regulations and state-of-the-art AI research. Finally, we note that this is a working paper and we invite feedback in line with the purpose of this document as described in the introduction.
Interpreting CLIP with Sparse Linear Concept Embeddings (SpLiCE)
Feb 16, 2024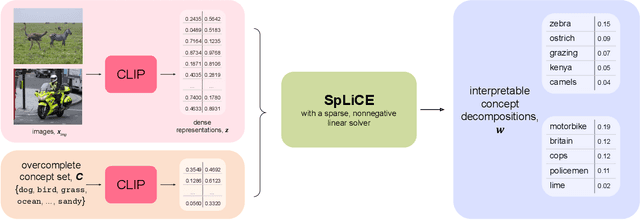
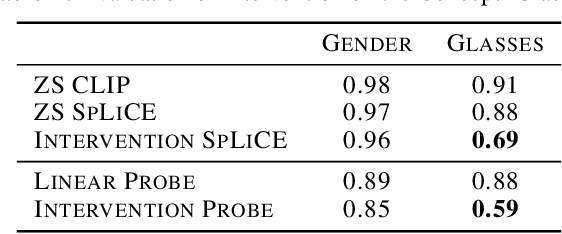

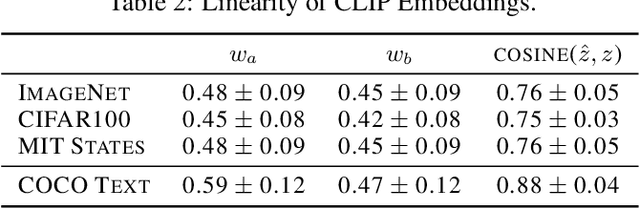
Abstract:CLIP embeddings have demonstrated remarkable performance across a wide range of computer vision tasks. However, these high-dimensional, dense vector representations are not easily interpretable, restricting their usefulness in downstream applications that require transparency. In this work, we empirically show that CLIP's latent space is highly structured, and consequently that CLIP representations can be decomposed into their underlying semantic components. We leverage this understanding to propose a novel method, Sparse Linear Concept Embeddings (SpLiCE), for transforming CLIP representations into sparse linear combinations of human-interpretable concepts. Distinct from previous work, SpLiCE does not require concept labels and can be applied post hoc. Through extensive experimentation with multiple real-world datasets, we validate that the representations output by SpLiCE can explain and even replace traditional dense CLIP representations, maintaining equivalent downstream performance while significantly improving their interpretability. We also demonstrate several use cases of SpLiCE representations including detecting spurious correlations, model editing, and quantifying semantic shifts in datasets.
Verifiable Feature Attributions: A Bridge between Post Hoc Explainability and Inherent Interpretability
Jul 27, 2023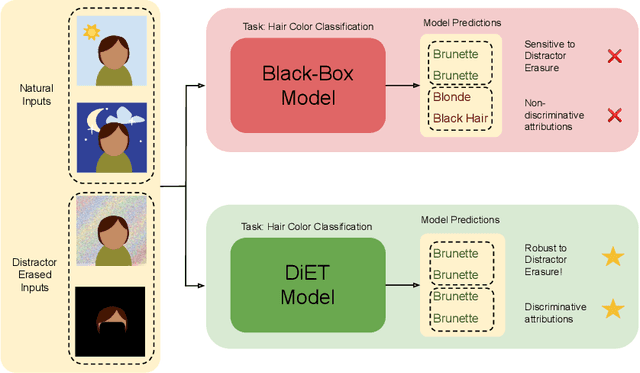

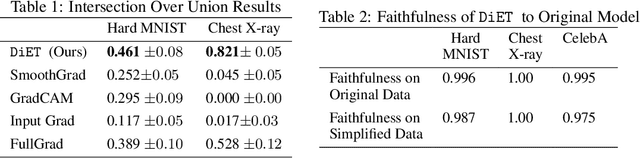
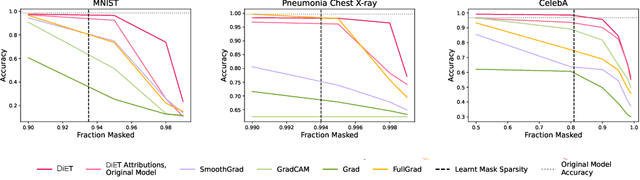
Abstract:With the increased deployment of machine learning models in various real-world applications, researchers and practitioners alike have emphasized the need for explanations of model behaviour. To this end, two broad strategies have been outlined in prior literature to explain models. Post hoc explanation methods explain the behaviour of complex black-box models by highlighting features that are critical to model predictions; however, prior work has shown that these explanations may not be faithful, and even more concerning is our inability to verify them. Specifically, it is nontrivial to evaluate if a given attribution is correct with respect to the underlying model. Inherently interpretable models, on the other hand, circumvent these issues by explicitly encoding explanations into model architecture, meaning their explanations are naturally faithful and verifiable, but they often exhibit poor predictive performance due to their limited expressive power. In this work, we aim to bridge the gap between the aforementioned strategies by proposing Verifiability Tuning (VerT), a method that transforms black-box models into models that naturally yield faithful and verifiable feature attributions. We begin by introducing a formal theoretical framework to understand verifiability and show that attributions produced by standard models cannot be verified. We then leverage this framework to propose a method to build verifiable models and feature attributions out of fully trained black-box models. Finally, we perform extensive experiments on semi-synthetic and real-world datasets, and show that VerT produces models that (1) yield explanations that are correct and verifiable and (2) are faithful to the original black-box models they are meant to explain.
Do Vision-Language Pretrained Models Learn Primitive Concepts?
Mar 31, 2022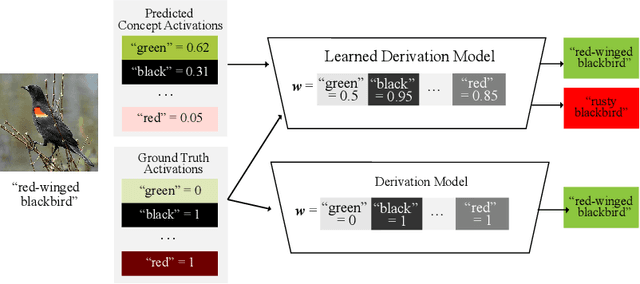
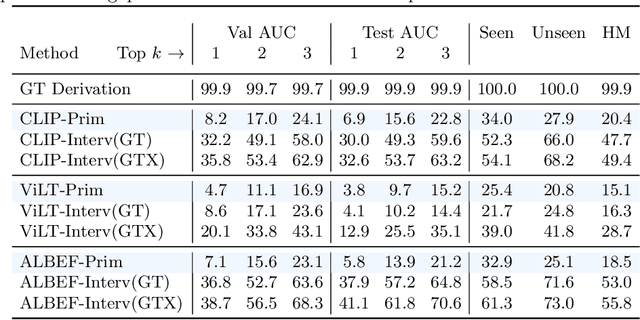
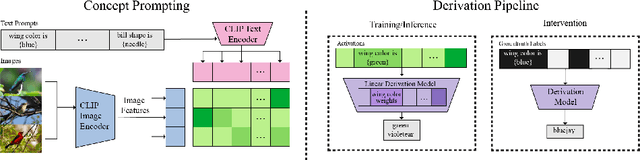
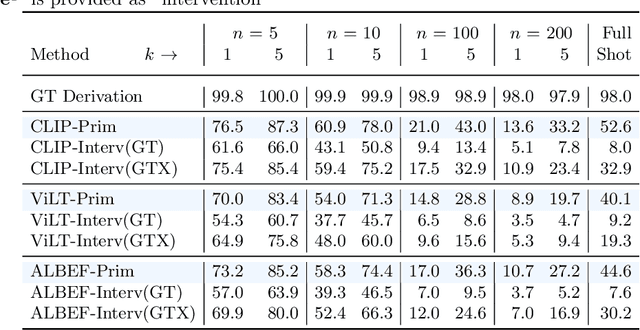
Abstract:Vision-language pretrained models have achieved impressive performance on multimodal reasoning and zero-shot recognition tasks. Many of these VL models are pretrained on unlabeled image and caption pairs from the internet. In this paper, we study whether the notion of primitive concepts, such as color and shape attributes, emerges automatically from these pretrained VL models. We propose to learn compositional derivations that map primitive concept activations into composite concepts, a task which we demonstrate to be straightforward given true primitive concept annotations. This compositional derivation learning (CompDL) framework allows us to quantitively measure the usefulness and interpretability of the learned derivations, by jointly considering the entire set of candidate primitive concepts. Our study reveals that state-of-the-art VL pretrained models learn primitive concepts that are highly useful as visual descriptors, as demonstrated by their strong performance on fine-grained visual recognition tasks, but those concepts struggle to provide interpretable compositional derivations, which highlights limitations of existing VL models. Code and models will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge