Tanchao Zhu
Recommender Transformers with Behavior Pathways
Jun 13, 2022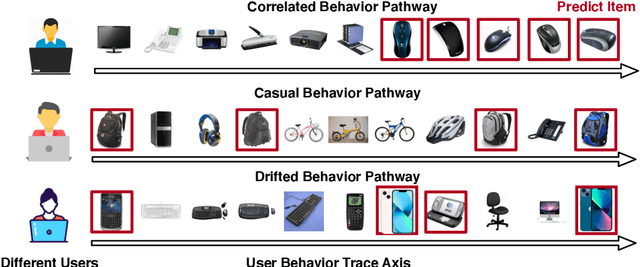
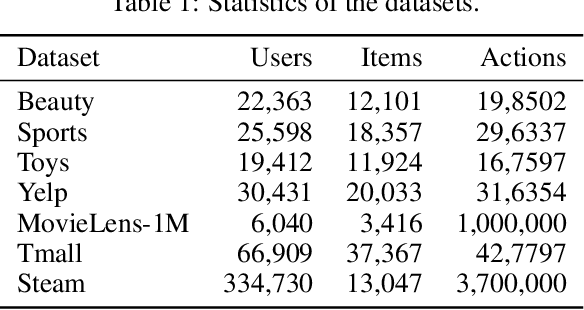
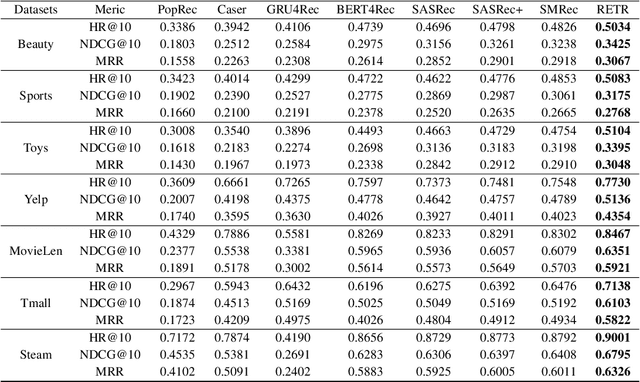
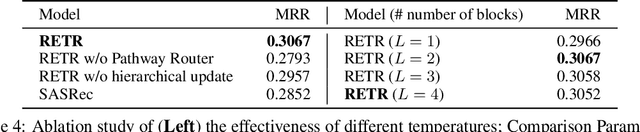
Abstract:Sequential recommendation requires the recommender to capture the evolving behavior characteristics from logged user behavior data for accurate recommendations. However, user behavior sequences are viewed as a script with multiple ongoing threads intertwined. We find that only a small set of pivotal behaviors can be evolved into the user's future action. As a result, the future behavior of the user is hard to predict. We conclude this characteristic for sequential behaviors of each user as the Behavior Pathway. Different users have their unique behavior pathways. Among existing sequential models, transformers have shown great capacity in capturing global-dependent characteristics. However, these models mainly provide a dense distribution over all previous behaviors using the self-attention mechanism, making the final predictions overwhelmed by the trivial behaviors not adjusted to each user. In this paper, we build the Recommender Transformer (RETR) with a novel Pathway Attention mechanism. RETR can dynamically plan the behavior pathway specified for each user, and sparingly activate the network through this behavior pathway to effectively capture evolving patterns useful for recommendation. The key design is a learned binary route to prevent the behavior pathway from being overwhelmed by trivial behaviors. We empirically verify the effectiveness of RETR on seven real-world datasets and RETR yields state-of-the-art performance.
MAMDR: A Model Agnostic Learning Method for Multi-Domain Recommendation
Mar 22, 2022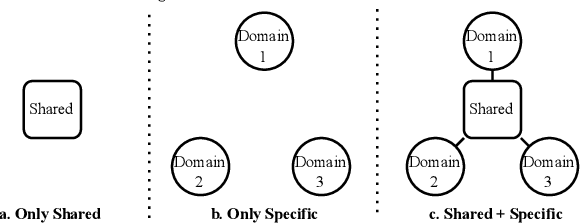
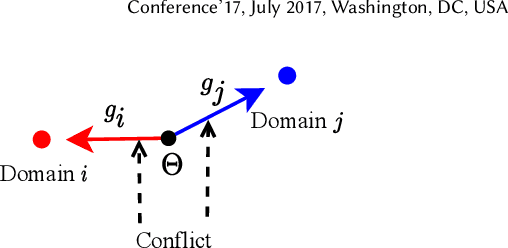
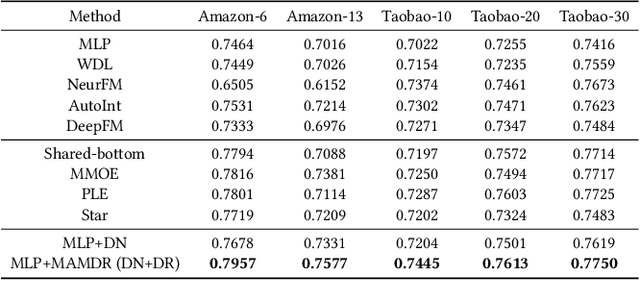
Abstract:Large-scale e-commercial platforms in the real-world usually contain various recommendation scenarios (domains) to meet demands of diverse customer groups. Multi-Domain Recommendation (MDR), which aims to jointly improve recommendations on all domains, has attracted increasing attention from practitioners and researchers. Existing MDR methods often employ a shared structure to leverage reusable features for all domains and several specific parts to capture domain-specific information. However, data from different domains may conflict with each other and cause shared parameters to stay at a compromised position on the optimization landscape. This could deteriorate the overall performance. Despite the specific parameters are separately learned for each domain, they can easily overfit on data sparsity domains. Furthermore, data distribution differs across domains, making it challenging to develop a general model that can be applied to all circumstances. To address these problems, we propose a novel model agnostic learning method, namely MAMDR, for the multi-domain recommendation. Specifically, we first propose a Domain Negotiation (DN) strategy to alleviate the conflict between domains and learn better shared parameters. Then, we develop a Domain Regularization (DR) scheme to improve the generalization ability of specific parameters by learning from other domains. Finally, we integrate these components into a unified framework and present MAMDR which can be applied to any model structure to perform multi-domain recommendation. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets and online applications demonstrate both the effectiveness and generalizability of MAMDR.
A General Method For Automatic Discovery of Powerful Interactions In Click-Through Rate Prediction
May 21, 2021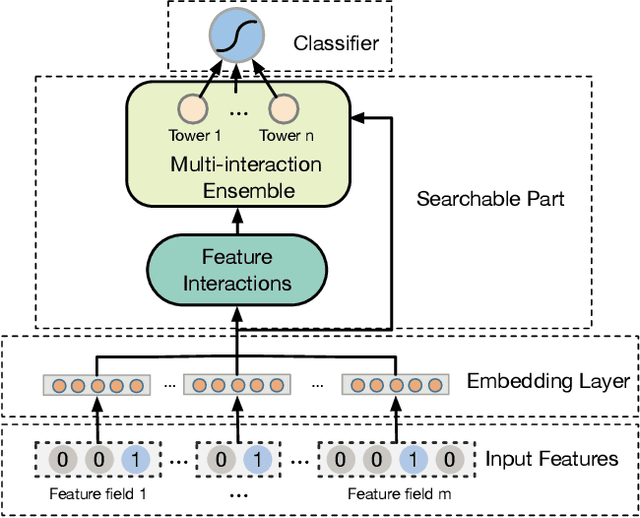
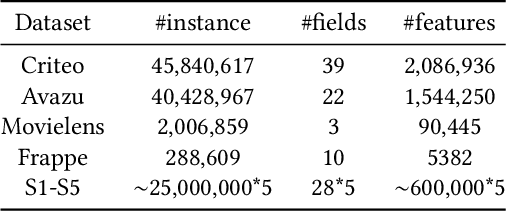
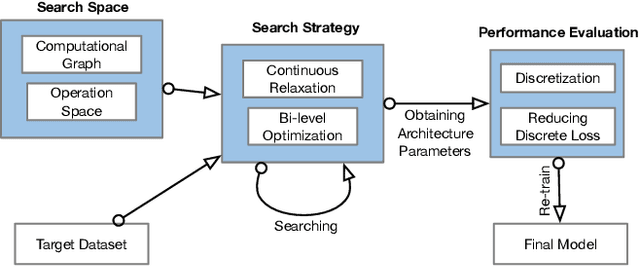
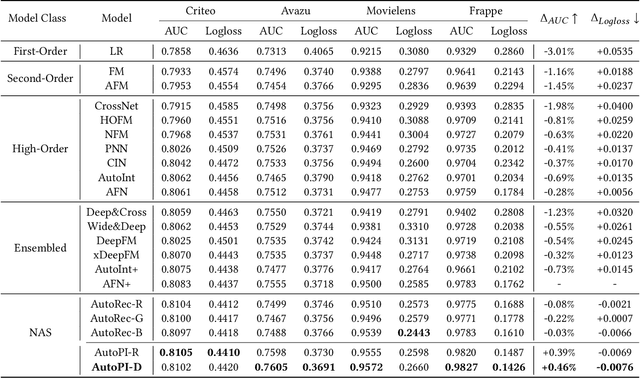
Abstract:Modeling powerful interactions is a critical challenge in Click-through rate (CTR) prediction, which is one of the most typical machine learning tasks in personalized advertising and recommender systems. Although developing hand-crafted interactions is effective for a small number of datasets, it generally requires laborious and tedious architecture engineering for extensive scenarios. In recent years, several neural architecture search (NAS) methods have been proposed for designing interactions automatically. However, existing methods only explore limited types and connections of operators for interaction generation, leading to low generalization ability. To address these problems, we propose a more general automated method for building powerful interactions named AutoPI. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: AutoPI adopts a more general search space in which the computational graph is generalized from existing network connections, and the interactive operators in the edges of the graph are extracted from representative hand-crafted works. It allows searching for various powerful feature interactions to produce higher AUC and lower Logloss in a wide variety of applications. Besides, AutoPI utilizes a gradient-based search strategy for exploration with a significantly low computational cost. Experimentally, we evaluate AutoPI on a diverse suite of benchmark datasets, demonstrating the generalizability and efficiency of AutoPI over hand-crafted architectures and state-of-the-art NAS algorithms.
Learning User Representations with Hypercuboids for Recommender Systems
Nov 11, 2020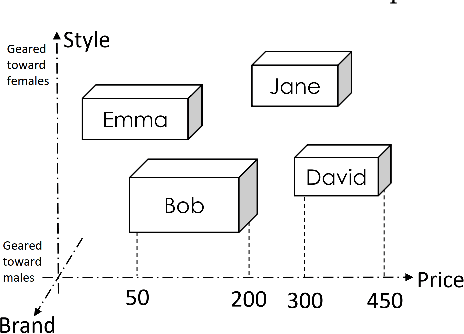
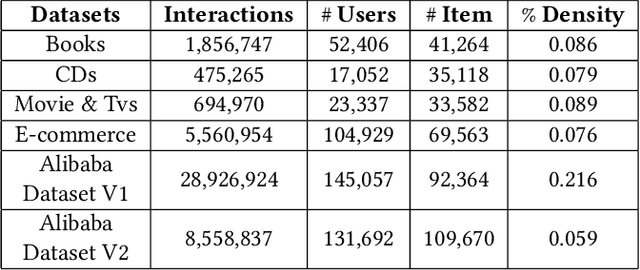
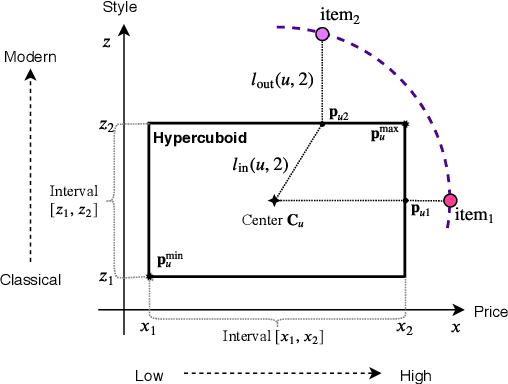
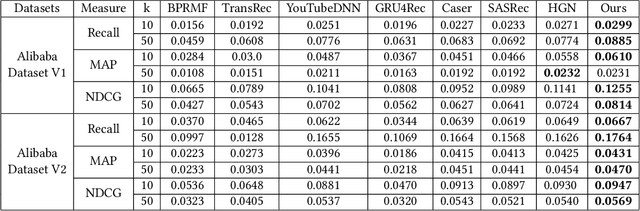
Abstract:Modeling user interests is crucial in real-world recommender systems. In this paper, we present a new user interest representation model for personalized recommendation. Specifically, the key novelty behind our model is that it explicitly models user interests as a hypercuboid instead of a point in the space. In our approach, the recommendation score is learned by calculating a compositional distance between the user hypercuboid and the item. This helps to alleviate the potential geometric inflexibility of existing collaborative filtering approaches, enabling a greater extent of modeling capability. Furthermore, we present two variants of hypercuboids to enhance the capability in capturing the diversities of user interests. A neural architecture is also proposed to facilitate user hypercuboid learning by capturing the activity sequences (e.g., buy and rate) of users. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model via extensive experiments on both public and commercial datasets. Empirical results show that our approach achieves very promising results, outperforming existing state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge