Tanaya Guha
Robust Understanding of Human-Robot Social Interactions through Multimodal Distillation
May 06, 2025Abstract:The need for social robots and agents to interact and assist humans is growing steadily. To be able to successfully interact with humans, they need to understand and analyse socially interactive scenes from their (robot's) perspective. Works that model social situations between humans and agents are few; and even those existing ones are often too computationally intensive to be suitable for deployment in real time or on real world scenarios with limited available information. We propose a robust knowledge distillation framework that models social interactions through various multimodal cues, yet is robust against incomplete and noisy information during inference. Our teacher model is trained with multimodal input (body, face and hand gestures, gaze, raw images) that transfers knowledge to a student model that relies solely on body pose. Extensive experiments on two publicly available human-robot interaction datasets demonstrate that the our student model achieves an average accuracy gain of 14.75\% over relevant baselines on multiple downstream social understanding task even with up to 51\% of its input being corrupted. The student model is highly efficient: it is $<1$\% in size of the teacher model in terms of parameters and uses $\sim 0.5$\textperthousand~FLOPs of that in the teacher model. Our code will be made public during publication.
Interact with me: Joint Egocentric Forecasting of Intent to Interact, Attitude and Social Actions
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:For efficient human-agent interaction, an agent should proactively recognize their target user and prepare for upcoming interactions. We formulate this challenging problem as the novel task of jointly forecasting a person's intent to interact with the agent, their attitude towards the agent and the action they will perform, from the agent's (egocentric) perspective. So we propose \emph{SocialEgoNet} - a graph-based spatiotemporal framework that exploits task dependencies through a hierarchical multitask learning approach. SocialEgoNet uses whole-body skeletons (keypoints from face, hands and body) extracted from only 1 second of video input for high inference speed. For evaluation, we augment an existing egocentric human-agent interaction dataset with new class labels and bounding box annotations. Extensive experiments on this augmented dataset, named JPL-Social, demonstrate \emph{real-time} inference and superior performance (average accuracy across all tasks: 83.15\%) of our model outperforming several competitive baselines. The additional annotations and code will be available upon acceptance.
Active Listener: Continuous Generation of Listener's Head Motion Response in Dyadic Interactions
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:A key component of dyadic spoken interactions is the contextually relevant non-verbal gestures, such as head movements that reflect a listener's response to the interlocutor's speech. Although significant progress has been made in the context of generating co-speech gestures, generating listener's response has remained a challenge. We introduce the task of generating continuous head motion response of a listener in response to the speaker's speech in real time. To this end, we propose a graph-based end-to-end crossmodal model that takes interlocutor's speech audio as input and directly generates head pose angles (roll, pitch, yaw) of the listener in real time. Different from previous work, our approach is completely data-driven, does not require manual annotations or oversimplify head motion to merely nods and shakes. Extensive evaluation on the dyadic interaction sessions on the IEMOCAP dataset shows that our model produces a low overall error (4.5 degrees) and a high frame rate, thereby indicating its deployability in real-world human-robot interaction systems. Our code is available at - https://github.com/bigzen/Active-Listener
WorkBench: a Benchmark Dataset for Agents in a Realistic Workplace Setting
May 01, 2024Abstract:We introduce WorkBench: a benchmark dataset for evaluating agents' ability to execute tasks in a workplace setting. WorkBench contains a sandbox environment with five databases, 26 tools, and 690 tasks. These tasks represent common business activities, such as sending emails and scheduling meetings. The tasks in WorkBench are challenging as they require planning, tool selection, and often multiple actions. If a task has been successfully executed, one (or more) of the database values may change. The correct outcome for each task is unique and unambiguous, which allows for robust, automated evaluation. We call this key contribution outcome-centric evaluation. We evaluate five existing ReAct agents on WorkBench, finding they successfully complete as few as 3% of tasks (Llama2-70B), and just 43% for the best-performing (GPT-4). We further find that agents' errors can result in the wrong action being taken, such as an email being sent to the wrong person. WorkBench reveals weaknesses in agents' ability to undertake common business activities, raising questions about their use in high-stakes workplace settings. WorkBench is publicly available as a free resource at https://github.com/olly-styles/WorkBench.
CLIP-EBC: CLIP Can Count Accurately through Enhanced Blockwise Classification
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:The CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) model has exhibited outstanding performance in recognition problems, such as zero-shot image classification and object detection. However, its ability to count remains understudied due to the inherent challenges of transforming counting--a regression task--into a recognition task. In this paper, we investigate CLIP's potential in counting, focusing specifically on estimating crowd sizes. Existing classification-based crowd-counting methods have encountered issues, including inappropriate discretization strategies, which impede the application of CLIP and result in suboptimal performance. To address these challenges, we propose the Enhanced Blockwise Classification (EBC) framework. In contrast to previous methods, EBC relies on integer-valued bins that facilitate the learning of robust decision boundaries. Within our model-agnostic EBC framework, we introduce CLIP-EBC, the first fully CLIP-based crowd-counting model capable of generating density maps. Comprehensive evaluations across diverse crowd-counting datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our methods. Particularly, EBC can improve existing models by up to 76.9%. Moreover, our CLIP-EBC model surpasses current crowd-counting methods, achieving mean absolute errors of 55.0 and 6.3 on ShanghaiTech part A and part B datasets, respectively. The code will be made publicly available.
Explainable Depression Detection via Head Motion Patterns
Jul 23, 2023



Abstract:While depression has been studied via multimodal non-verbal behavioural cues, head motion behaviour has not received much attention as a biomarker. This study demonstrates the utility of fundamental head-motion units, termed \emph{kinemes}, for depression detection by adopting two distinct approaches, and employing distinctive features: (a) discovering kinemes from head motion data corresponding to both depressed patients and healthy controls, and (b) learning kineme patterns only from healthy controls, and computing statistics derived from reconstruction errors for both the patient and control classes. Employing machine learning methods, we evaluate depression classification performance on the \emph{BlackDog} and \emph{AVEC2013} datasets. Our findings indicate that: (1) head motion patterns are effective biomarkers for detecting depressive symptoms, and (2) explanatory kineme patterns consistent with prior findings can be observed for the two classes. Overall, we achieve peak F1 scores of 0.79 and 0.82, respectively, over BlackDog and AVEC2013 for binary classification over episodic \emph{thin-slices}, and a peak F1 of 0.72 over videos for AVEC2013.
Robust Multiview Multimodal Driver Monitoring System Using Masked Multi-Head Self-Attention
Apr 13, 2023Abstract:Driver Monitoring Systems (DMSs) are crucial for safe hand-over actions in Level-2+ self-driving vehicles. State-of-the-art DMSs leverage multiple sensors mounted at different locations to monitor the driver and the vehicle's interior scene and employ decision-level fusion to integrate these heterogenous data. However, this fusion method may not fully utilize the complementarity of different data sources and may overlook their relative importance. To address these limitations, we propose a novel multiview multimodal driver monitoring system based on feature-level fusion through multi-head self-attention (MHSA). We demonstrate its effectiveness by comparing it against four alternative fusion strategies (Sum, Conv, SE, and AFF). We also present a novel GPU-friendly supervised contrastive learning framework SuMoCo to learn better representations. Furthermore, We fine-grained the test split of the DAD dataset to enable the multi-class recognition of drivers' activities. Experiments on this enhanced database demonstrate that 1) the proposed MHSA-based fusion method (AUC-ROC: 97.0\%) outperforms all baselines and previous approaches, and 2) training MHSA with patch masking can improve its robustness against modality/view collapses. The code and annotations are publicly available.
Heterogeneous Graph Learning for Acoustic Event Classification
Mar 12, 2023


Abstract:Heterogeneous graphs provide a compact, efficient, and scalable way to model data involving multiple disparate modalities. This makes modeling audiovisual data using heterogeneous graphs an attractive option. However, graph structure does not appear naturally in audiovisual data. Graphs for audiovisual data are constructed manually which is both difficult and sub-optimal. In this work, we address this problem by (i) proposing a parametric graph construction strategy for the intra-modal edges, and (ii) learning the crossmodal edges. To this end, we develop a new model, heterogeneous graph crossmodal network (HGCN) that learns the crossmodal edges. Our proposed model can adapt to various spatial and temporal scales owing to its parametric construction, while the learnable crossmodal edges effectively connect the relevant nodes across modalities. Experiments on a large benchmark dataset (AudioSet) show that our model is state-of-the-art (0.53 mean average precision), outperforming transformer-based models and other graph-based models.
Explainable Human-centered Traits from Head Motion and Facial Expression Dynamics
Feb 23, 2023



Abstract:We explore the efficacy of multimodal behavioral cues for explainable prediction of personality and interview-specific traits. We utilize elementary head-motion units named kinemes, atomic facial movements termed action units and speech features to estimate these human-centered traits. Empirical results confirm that kinemes and action units enable discovery of multiple trait-specific behaviors while also enabling explainability in support of the predictions. For fusing cues, we explore decision and feature-level fusion, and an additive attention-based fusion strategy which quantifies the relative importance of the three modalities for trait prediction. Examining various long-short term memory (LSTM) architectures for classification and regression on the MIT Interview and First Impressions Candidate Screening (FICS) datasets, we note that: (1) Multimodal approaches outperform unimodal counterparts; (2) Efficient trait predictions and plausible explanations are achieved with both unimodal and multimodal approaches, and (3) Following the thin-slice approach, effective trait prediction is achieved even from two-second behavioral snippets.
Real-Time Driver Monitoring Systems through Modality and View Analysis
Oct 17, 2022
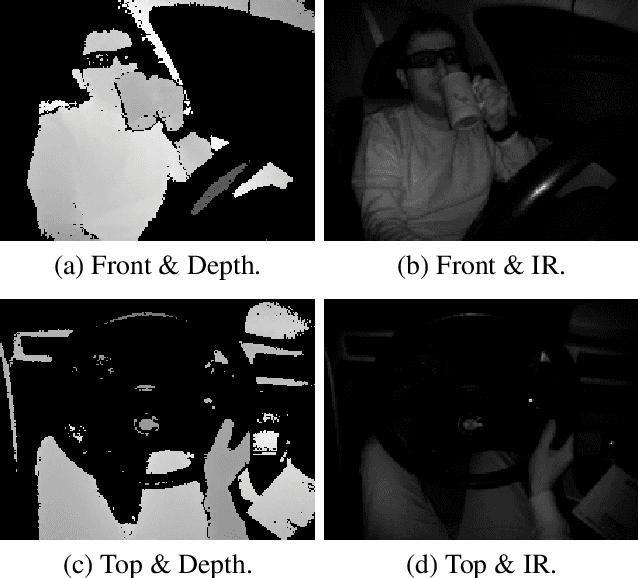

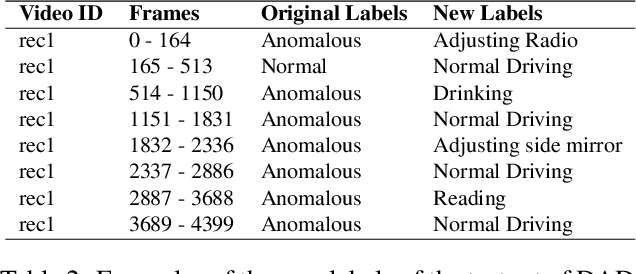
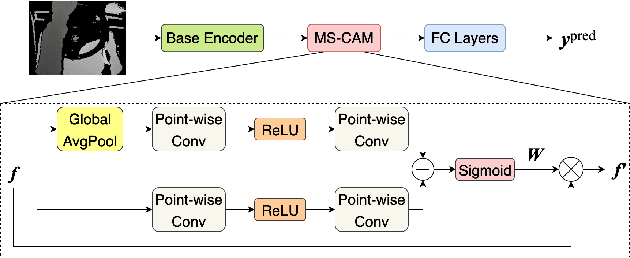
Abstract:Driver distractions are known to be the dominant cause of road accidents. While monitoring systems can detect non-driving-related activities and facilitate reducing the risks, they must be accurate and efficient to be applicable. Unfortunately, state-of-the-art methods prioritize accuracy while ignoring latency because they leverage cross-view and multimodal videos in which consecutive frames are highly similar. Thus, in this paper, we pursue time-effective detection models by neglecting the temporal relation between video frames and investigate the importance of each sensing modality in detecting drives' activities. Experiments demonstrate that 1) our proposed algorithms are real-time and can achieve similar performances (97.5\% AUC-PR) with significantly reduced computation compared with video-based models; 2) the top view with the infrared channel is more informative than any other single modality. Furthermore, we enhance the DAD dataset by manually annotating its test set to enable multiclassification. We also thoroughly analyze the influence of visual sensor types and their placements on the prediction of each class. The code and the new labels will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge