Soran Parsa
Optimising robotic operation speed with edge computing over 5G networks: Insights from selective harvesting robots
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:Selective harvesting by autonomous robots will be a critical enabling technology for future farming. Increases in inflation and shortages of skilled labour are driving factors that can help encourage user acceptability of robotic harvesting. For example, robotic strawberry harvesting requires real-time high-precision fruit localisation, 3D mapping and path planning for 3-D cluster manipulation. Whilst industry and academia have developed multiple strawberry harvesting robots, none have yet achieved human-cost parity. Achieving this goal requires increased picking speed (perception, control and movement), accuracy and the development of low-cost robotic system designs. We propose the edge-server over 5G for Selective Harvesting (E5SH) system, which is an integration of high bandwidth and low latency Fifth Generation (5G) mobile network into a crop harvesting robotic platform, which we view as an enabler for future robotic harvesting systems. We also consider processing scale and speed in conjunction with system environmental and energy costs. A system architecture is presented and evaluated with support from quantitative results from a series of experiments that compare the performance of the system in response to different architecture choices, including image segmentation models, network infrastructure (5G vs WiFi) and messaging protocols such as Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) and Transport Control Protocol Robot Operating System (TCPROS). Our results demonstrate that the E5SH system delivers step-change peak processing performance speedup of above 18-fold than a stand-alone embedded computing Nvidia Jetson Xavier NX (NJXN) system.
Towards Autonomous Selective Harvesting: A Review of Robot Perception, Robot Design, Motion Planning and Control
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:This paper provides an overview of the current state-of-the-art in selective harvesting robots (SHRs) and their potential for addressing the challenges of global food production. SHRs have the potential to increase productivity, reduce labour costs, and minimise food waste by selectively harvesting only ripe fruits and vegetables. The paper discusses the main components of SHRs, including perception, grasping, cutting, motion planning, and control. It also highlights the challenges in developing SHR technologies, particularly in the areas of robot design, motion planning and control. The paper also discusses the potential benefits of integrating AI and soft robots and data-driven methods to enhance the performance and robustness of SHR systems. Finally, the paper identifies several open research questions in the field and highlights the need for further research and development efforts to advance SHR technologies to meet the challenges of global food production. Overall, this paper provides a starting point for researchers and practitioners interested in developing SHRs and highlights the need for more research in this field.
Autonomous Strawberry Picking Robotic System (Robofruit)
Jan 10, 2023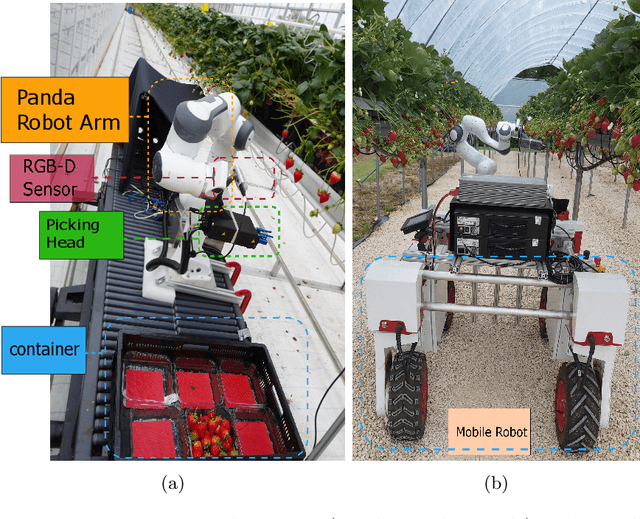
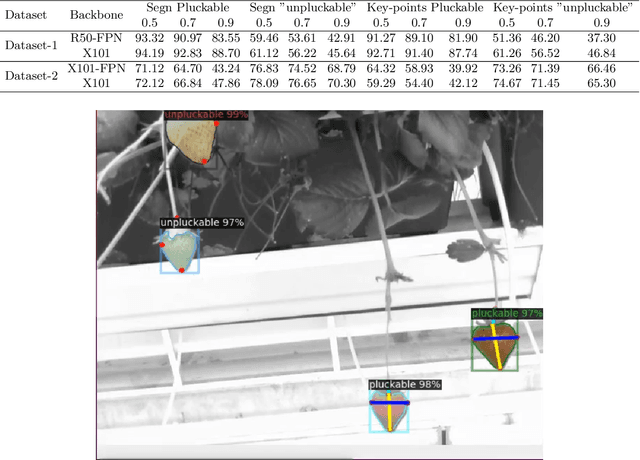
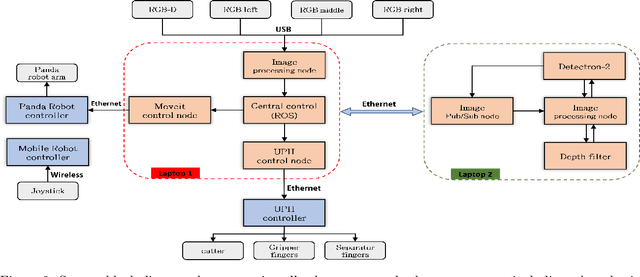
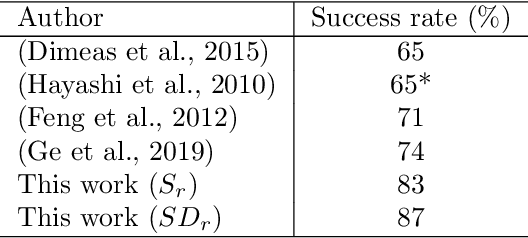
Abstract:Challenges in strawberry picking made selective harvesting robotic technology demanding. However, selective harvesting of strawberries is complicated forming a few scientific research questions. Most available solutions only deal with a specific picking scenario, e.g., picking only a single variety of fruit in isolation. Nonetheless, most economically viable (e.g. high-yielding and/or disease-resistant) varieties of strawberry are grown in dense clusters. The current perception technology in such use cases is inefficient. In this work, we developed a novel system capable of harvesting strawberries with several unique features. The features allow the system to deal with very complex picking scenarios, e.g. dense clusters. Our concept of a modular system makes our system reconfigurable to adapt to different picking scenarios. We designed, manufactured, and tested a picking head with 2.5 DOF (2 independent mechanisms and 1 dependent cutting system) capable of removing possible occlusions and harvesting targeted strawberries without contacting fruit flesh to avoid damage and bruising. In addition, we developed a novel perception system to localise strawberries and detect their key points, picking points, and determine their ripeness. For this purpose, we introduced two new datasets. Finally, we tested the system in a commercial strawberry growing field and our research farm with three different strawberry varieties. The results show the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed system. The designed picking head was able to remove occlusions and harvest strawberries effectively. The perception system was able to detect and determine the ripeness of strawberries with 95% accuracy. In total, the system was able to harvest 87% of all detected strawberries with a success rate of 83% for all pluckable fruits. We also discuss a series of open research questions in the discussion section.
Peduncle Gripping and Cutting Force for Strawberry Harvesting Robotic End-effector Design
Jul 25, 2022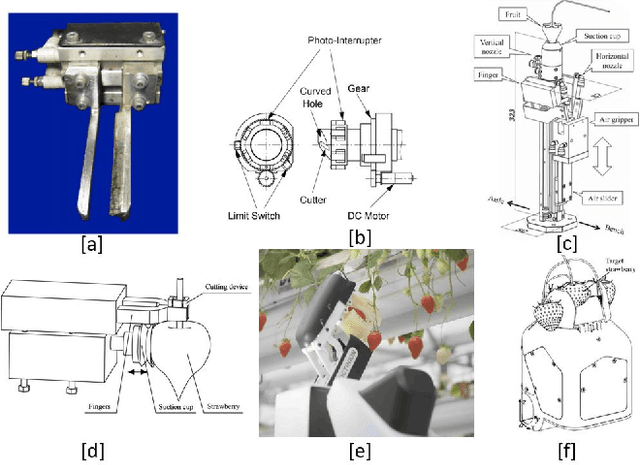
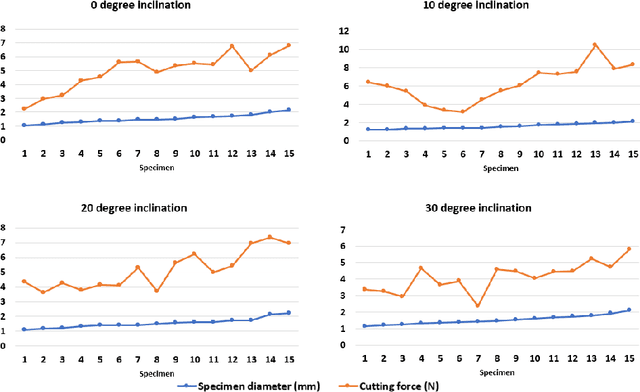
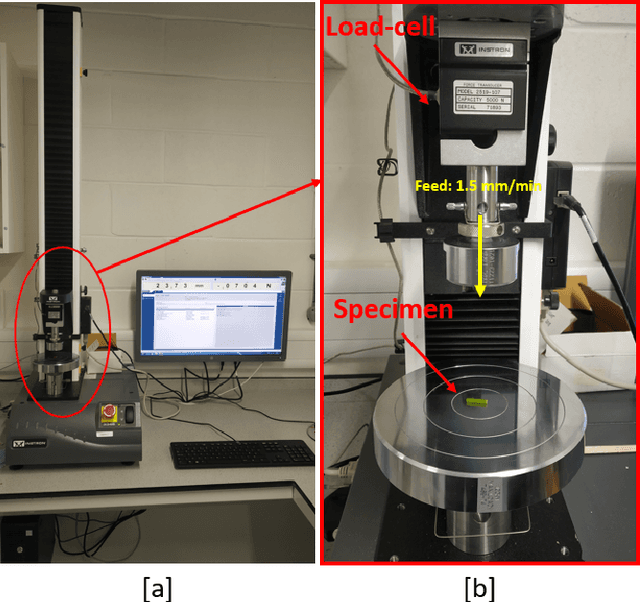
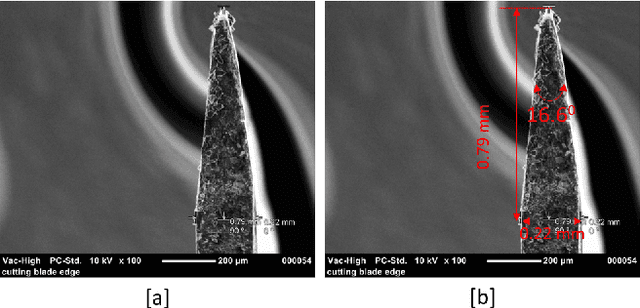
Abstract:Robotic harvesting of strawberries has gained much interest in the recent past. Although there are many innovations, they haven't yet reached a level that is comparable to an expert human picker. The end effector unit plays a major role in defining the efficiency of such a robotic harvesting system. Even though there are reports on various end effectors for strawberry harvesting, but there they lack a picture of certain parameters that the researchers can rely upon to develop new end effectors. These parameters include the limit of gripping force that can be applied on the peduncle for effective gripping, the force required to cut the strawberry peduncle, etc. These estimations would be helpful in the design cycle of the end effectors that target to grip and cut the strawberry peduncle during the harvesting action. This paper studies the estimation and analysis of these parameters experimentally. It has been estimated that the peduncle gripping force can be limited to 10 N. This enables an end effector to grip a strawberry of mass up to 50 grams with a manipulation acceleration of 50 m/s$^2$ without squeezing the peduncle. The study on peduncle cutting force reveals that a force of 15 N is sufficient to cut a strawberry peduncle using a blade with a wedge angle of 16.6 degrees at a 30-degree orientation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge