Sichen Liu
Stable-DiffCoder: Pushing the Frontier of Code Diffusion Large Language Model
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Diffusion-based language models (DLLMs) offer non-sequential, block-wise generation and richer data reuse compared to autoregressive (AR) models, but existing code DLLMs still lag behind strong AR baselines under comparable budgets. We revisit this setting in a controlled study and introduce Stable-DiffCoder, a block diffusion code model that reuses the Seed-Coder architecture, data, and training pipeline. To enable efficient knowledge learning and stable training, we incorporate a block diffusion continual pretraining (CPT) stage enhanced by a tailored warmup and block-wise clipped noise schedule. Under the same data and architecture, Stable-DiffCoder overall outperforms its AR counterpart on a broad suite of code benchmarks. Moreover, relying only on the CPT and supervised fine-tuning stages, Stable-DiffCoder achieves stronger performance than a wide range of \~8B ARs and DLLMs, demonstrating that diffusion-based training can improve code modeling quality beyond AR training alone. Moreover, diffusion-based any-order modeling improves structured code modeling for editing and reasoning, and through data augmentation, benefits low-resource coding languages.
Extrapolating and Decoupling Image-to-Video Generation Models: Motion Modeling is Easier Than You Think
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Image-to-Video (I2V) generation aims to synthesize a video clip according to a given image and condition (e.g., text). The key challenge of this task lies in simultaneously generating natural motions while preserving the original appearance of the images. However, current I2V diffusion models (I2V-DMs) often produce videos with limited motion degrees or exhibit uncontrollable motion that conflicts with the textual condition. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Extrapolating and Decoupling framework, which introduces model merging techniques to the I2V domain for the first time. Specifically, our framework consists of three separate stages: (1) Starting with a base I2V-DM, we explicitly inject the textual condition into the temporal module using a lightweight, learnable adapter and fine-tune the integrated model to improve motion controllability. (2) We introduce a training-free extrapolation strategy to amplify the dynamic range of the motion, effectively reversing the fine-tuning process to enhance the motion degree significantly. (3) With the above two-stage models excelling in motion controllability and degree, we decouple the relevant parameters associated with each type of motion ability and inject them into the base I2V-DM. Since the I2V-DM handles different levels of motion controllability and dynamics at various denoising time steps, we adjust the motion-aware parameters accordingly over time. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments have been conducted to demonstrate the superiority of our framework over existing methods.
* Accepted by CVPR2025
Make LoRA Great Again: Boosting LoRA with Adaptive Singular Values and Mixture-of-Experts Optimization Alignment
Feb 26, 2025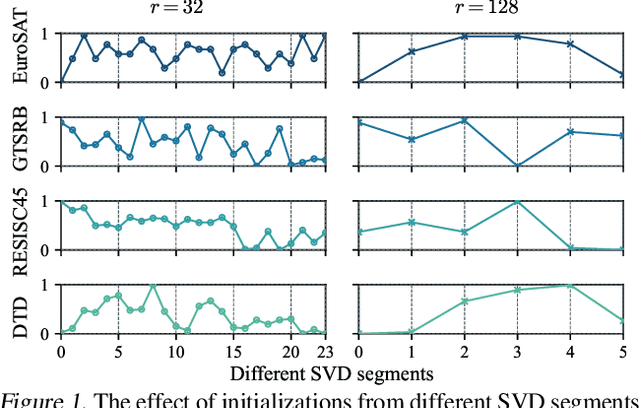
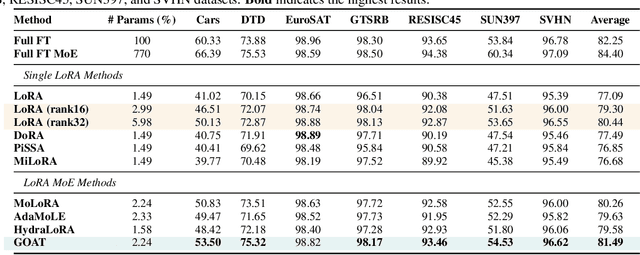
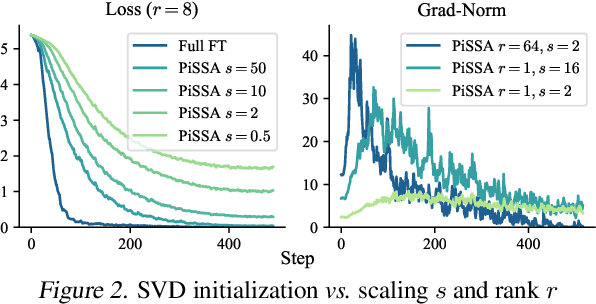
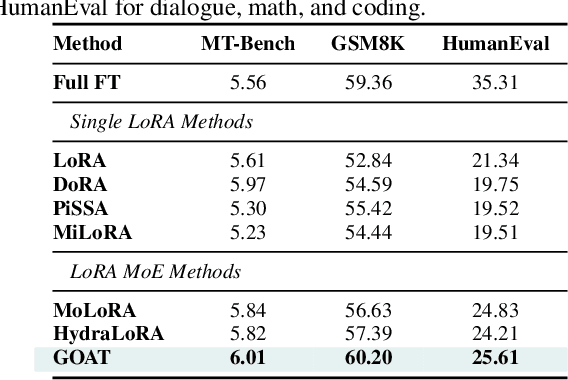
Abstract:While Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) enables parameter-efficient fine-tuning for Large Language Models (LLMs), its performance often falls short of Full Fine-Tuning (Full FT). Current methods optimize LoRA by initializing with static singular value decomposition (SVD) subsets, leading to suboptimal leveraging of pre-trained knowledge. Another path for improving LoRA is incorporating a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. However, weight misalignment and complex gradient dynamics make it challenging to adopt SVD prior to the LoRA MoE architecture. To mitigate these issues, we propose \underline{G}reat L\underline{o}R\underline{A} Mixture-of-Exper\underline{t} (GOAT), a framework that (1) adaptively integrates relevant priors using an SVD-structured MoE, and (2) aligns optimization with full fine-tuned MoE by deriving a theoretical scaling factor. We demonstrate that proper scaling, without modifying the architecture or training algorithms, boosts LoRA MoE's efficiency and performance. Experiments across 25 datasets, including natural language understanding, commonsense reasoning, image classification, and natural language generation, demonstrate GOAT's state-of-the-art performance, closing the gap with Full FT.
FormulaQA: A Question Answering Dataset for Formula-Based Numerical Reasoning
Feb 21, 2024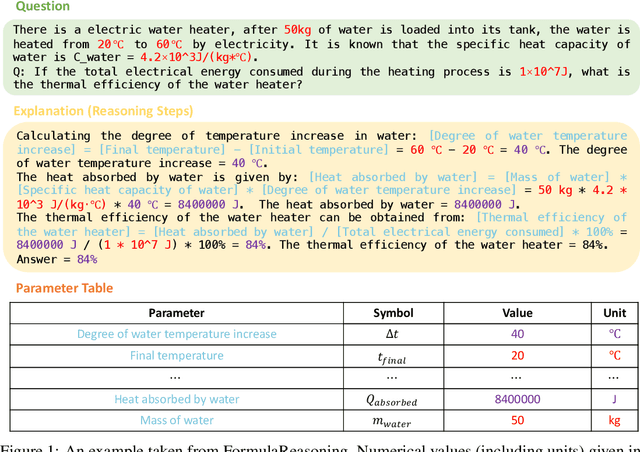
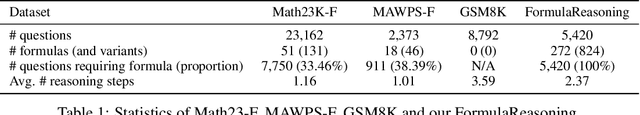


Abstract:The application of formulas is a fundamental ability of humans when addressing numerical reasoning problems. However, existing numerical reasoning datasets seldom explicitly indicate the formulas employed during the reasoning steps. To bridge this gap, we propose a question answering dataset for formula-based numerical reasoning called FormulaQA, from junior high school physics examinations. We further conduct evaluations on LLMs with size ranging from 7B to over 100B parameters utilizing zero-shot and few-shot chain-of-thoughts methods and we explored the approach of using retrieval-augmented LLMs when providing an external formula database. We also fine-tune on smaller models with size not exceeding 2B. Our empirical findings underscore the significant potential for improvement in existing models when applied to our complex, formula-driven FormulaQA.
LLM-Mini-CEX: Automatic Evaluation of Large Language Model for Diagnostic Conversation
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:There is an increasing interest in developing LLMs for medical diagnosis to improve diagnosis efficiency. Despite their alluring technological potential, there is no unified and comprehensive evaluation criterion, leading to the inability to evaluate the quality and potential risks of medical LLMs, further hindering the application of LLMs in medical treatment scenarios. Besides, current evaluations heavily rely on labor-intensive interactions with LLMs to obtain diagnostic dialogues and human evaluation on the quality of diagnosis dialogue. To tackle the lack of unified and comprehensive evaluation criterion, we first initially establish an evaluation criterion, termed LLM-specific Mini-CEX to assess the diagnostic capabilities of LLMs effectively, based on original Mini-CEX. To address the labor-intensive interaction problem, we develop a patient simulator to engage in automatic conversations with LLMs, and utilize ChatGPT for evaluating diagnosis dialogues automatically. Experimental results show that the LLM-specific Mini-CEX is adequate and necessary to evaluate medical diagnosis dialogue. Besides, ChatGPT can replace manual evaluation on the metrics of humanistic qualities and provides reproducible and automated comparisons between different LLMs.
DyRRen: A Dynamic Retriever-Reranker-Generator Model for Numerical Reasoning over Tabular and Textual Data
Nov 23, 2022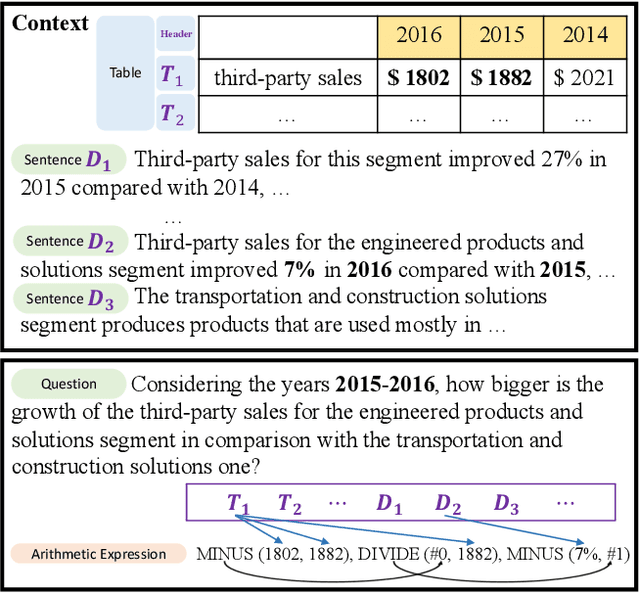
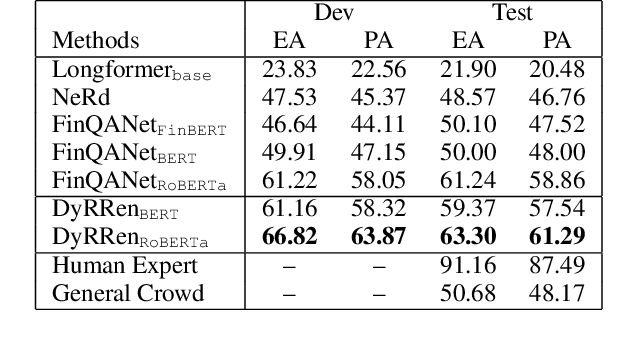
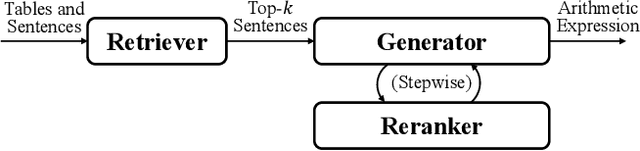
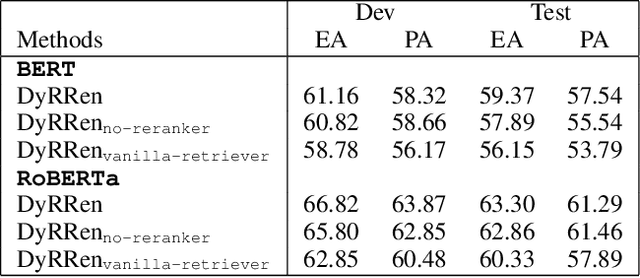
Abstract:Numerical reasoning over hybrid data containing tables and long texts has recently received research attention from the AI community. To generate an executable reasoning program consisting of math and table operations to answer a question, state-of-the-art methods use a retriever-generator pipeline. However, their retrieval results are static, while different generation steps may rely on different sentences. To attend to the retrieved information that is relevant to each generation step, in this paper, we propose DyRRen, an extended retriever-reranker-generator framework where each generation step is enhanced by a dynamic reranking of retrieved sentences. It outperforms existing baselines on the FinQA dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge