Shifeng Pan
Drop the beat! Freestyler for Accompaniment Conditioned Rapping Voice Generation
Aug 28, 2024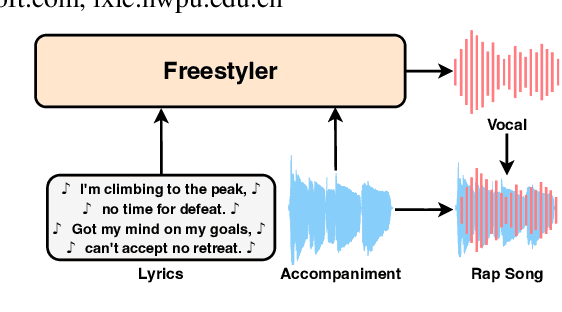

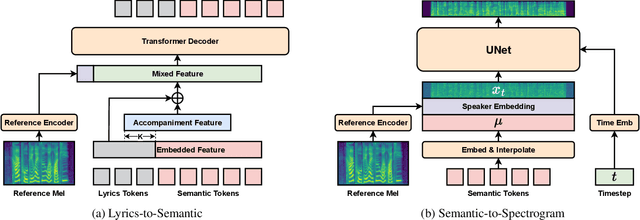
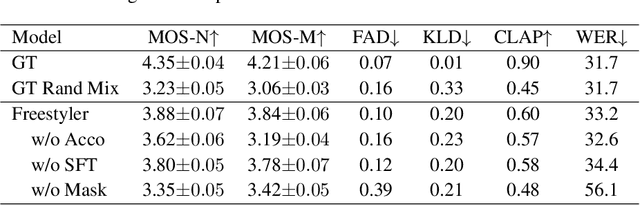
Abstract:Rap, a prominent genre of vocal performance, remains underexplored in vocal generation. General vocal synthesis depends on precise note and duration inputs, requiring users to have related musical knowledge, which limits flexibility. In contrast, rap typically features simpler melodies, with a core focus on a strong rhythmic sense that harmonizes with accompanying beats. In this paper, we propose Freestyler, the first system that generates rapping vocals directly from lyrics and accompaniment inputs. Freestyler utilizes language model-based token generation, followed by a conditional flow matching model to produce spectrograms and a neural vocoder to restore audio. It allows a 3-second prompt to enable zero-shot timbre control. Due to the scarcity of publicly available rap datasets, we also present RapBank, a rap song dataset collected from the internet, alongside a meticulously designed processing pipeline. Experimental results show that Freestyler produces high-quality rapping voice generation with enhanced naturalness and strong alignment with accompanying beats, both stylistically and rhythmically.
InferGrad: Improving Diffusion Models for Vocoder by Considering Inference in Training
Feb 08, 2022



Abstract:Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (diffusion models for short) require a large number of iterations in inference to achieve the generation quality that matches or surpasses the state-of-the-art generative models, which invariably results in slow inference speed. Previous approaches aim to optimize the choice of inference schedule over a few iterations to speed up inference. However, this results in reduced generation quality, mainly because the inference process is optimized separately, without jointly optimizing with the training process. In this paper, we propose InferGrad, a diffusion model for vocoder that incorporates inference process into training, to reduce the inference iterations while maintaining high generation quality. More specifically, during training, we generate data from random noise through a reverse process under inference schedules with a few iterations, and impose a loss to minimize the gap between the generated and ground-truth data samples. Then, unlike existing approaches, the training of InferGrad considers the inference process. The advantages of InferGrad are demonstrated through experiments on the LJSpeech dataset showing that InferGrad achieves better voice quality than the baseline WaveGrad under same conditions while maintaining the same voice quality as the baseline but with $3$x speedup ($2$ iterations for InferGrad vs $6$ iterations for WaveGrad).
Cross-speaker Style Transfer with Prosody Bottleneck in Neural Speech Synthesis
Jul 27, 2021



Abstract:Cross-speaker style transfer is crucial to the applications of multi-style and expressive speech synthesis at scale. It does not require the target speakers to be experts in expressing all styles and to collect corresponding recordings for model training. However, the performances of existing style transfer methods are still far behind real application needs. The root causes are mainly twofold. Firstly, the style embedding extracted from single reference speech can hardly provide fine-grained and appropriate prosody information for arbitrary text to synthesize. Secondly, in these models the content/text, prosody, and speaker timbre are usually highly entangled, it's therefore not realistic to expect a satisfied result when freely combining these components, such as to transfer speaking style between speakers. In this paper, we propose a cross-speaker style transfer text-to-speech (TTS) model with explicit prosody bottleneck. The prosody bottleneck builds up the kernels accounting for speaking style robustly, and disentangles the prosody from content and speaker timbre, therefore guarantees high quality cross-speaker style transfer. Evaluation result shows the proposed method even achieves on-par performance with source speaker's speaker-dependent (SD) model in objective measurement of prosody, and significantly outperforms the cycle consistency and GMVAE-based baselines in objective and subjective evaluations.
Forward-Backward Decoding for Regularizing End-to-End TTS
Jul 18, 2019



Abstract:Neural end-to-end TTS can generate very high-quality synthesized speech, and even close to human recording within similar domain text. However, it performs unsatisfactory when scaling it to challenging test sets. One concern is that the encoder-decoder with attention-based network adopts autoregressive generative sequence model with the limitation of "exposure bias" To address this issue, we propose two novel methods, which learn to predict future by improving agreement between forward and backward decoding sequence. The first one is achieved by introducing divergence regularization terms into model training objective to reduce the mismatch between two directional models, namely L2R and R2L (which generates targets from left-to-right and right-to-left, respectively). While the second one operates on decoder-level and exploits the future information during decoding. In addition, we employ a joint training strategy to allow forward and backward decoding to improve each other in an interactive process. Experimental results show our proposed methods especially the second one (bidirectional decoder regularization), leads a significantly improvement on both robustness and overall naturalness, as outperforming baseline (the revised version of Tacotron2) with a MOS gap of 0.14 in a challenging test, and achieving close to human quality (4.42 vs. 4.49 in MOS) on general test.
Learning latent representations for style control and transfer in end-to-end speech synthesis
Dec 11, 2018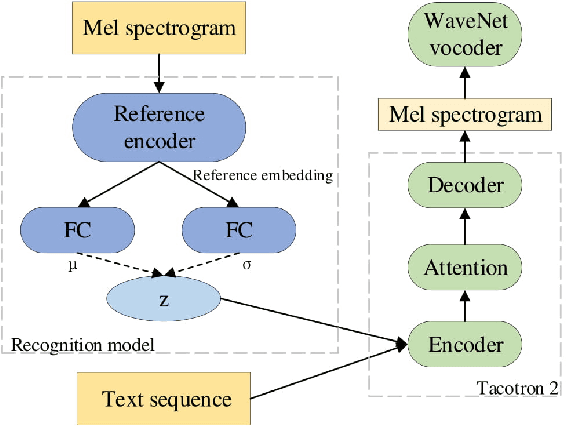
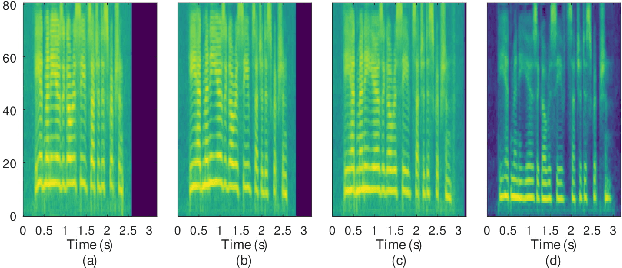


Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to an end-to-end speech synthesis model, to learn the latent representation of speaking styles in an unsupervised manner. The style representation learned through VAE shows good properties such as disentangling, scaling, and combination, which makes it easy for style control. Style transfer can be achieved in this framework by first inferring style representation through the recognition network of VAE, then feeding it into TTS network to guide the style in synthesizing speech. To avoid Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence collapse in training, several techniques are adopted. Finally, the proposed model shows good performance of style control and outperforms Global Style Token (GST) model in ABX preference tests on style transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge