Shida Wei
Hunyuan3D 2.1: From Images to High-Fidelity 3D Assets with Production-Ready PBR Material
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:3D AI-generated content (AIGC) is a passionate field that has significantly accelerated the creation of 3D models in gaming, film, and design. Despite the development of several groundbreaking models that have revolutionized 3D generation, the field remains largely accessible only to researchers, developers, and designers due to the complexities involved in collecting, processing, and training 3D models. To address these challenges, we introduce Hunyuan3D 2.1 as a case study in this tutorial. This tutorial offers a comprehensive, step-by-step guide on processing 3D data, training a 3D generative model, and evaluating its performance using Hunyuan3D 2.1, an advanced system for producing high-resolution, textured 3D assets. The system comprises two core components: the Hunyuan3D-DiT for shape generation and the Hunyuan3D-Paint for texture synthesis. We will explore the entire workflow, including data preparation, model architecture, training strategies, evaluation metrics, and deployment. By the conclusion of this tutorial, you will have the knowledge to finetune or develop a robust 3D generative model suitable for applications in gaming, virtual reality, and industrial design.
QAEncoder: Towards Aligned Representation Learning in Question Answering System
Sep 30, 2024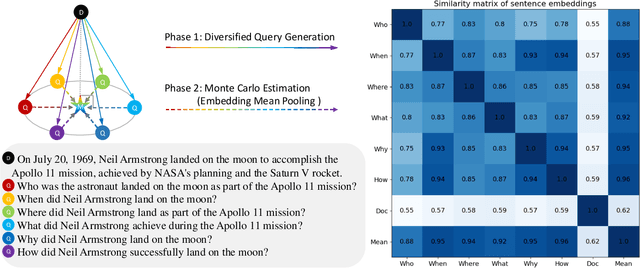
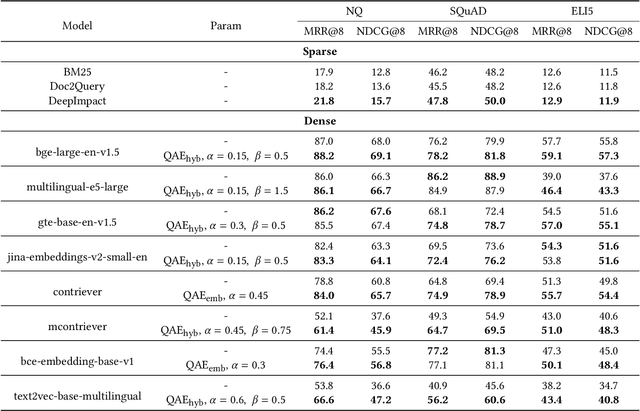
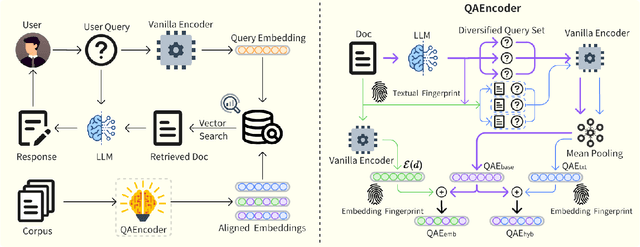
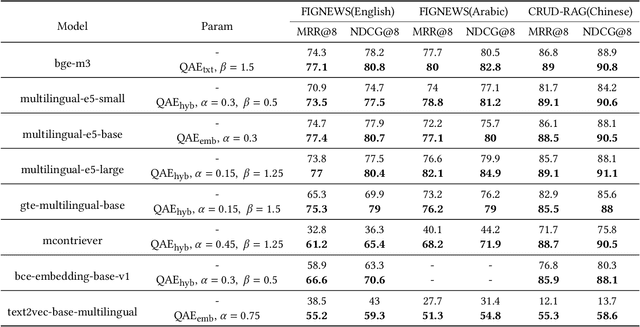
Abstract:Modern QA systems entail retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for accurate and trustworthy responses. However, the inherent gap between user queries and relevant documents hinders precise matching. Motivated by our conical distribution hypothesis, which posits that potential queries and documents form a cone-like structure in the embedding space, we introduce QAEncoder, a training-free approach to bridge this gap. Specifically, QAEncoder estimates the expectation of potential queries in the embedding space as a robust surrogate for the document embedding, and attaches document fingerprints to effectively distinguish these embeddings. Extensive experiments on fourteen embedding models across six languages and eight datasets validate QAEncoder's alignment capability, which offers a plug-and-play solution that seamlessly integrates with existing RAG architectures and training-based methods.
DiffPop: Plausibility-Guided Object Placement Diffusion for Image Composition
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of plausible object placement for the challenging task of realistic image composition. We propose DiffPop, the first framework that utilizes plausibility-guided denoising diffusion probabilistic model to learn the scale and spatial relations among multiple objects and the corresponding scene image. First, we train an unguided diffusion model to directly learn the object placement parameters in a self-supervised manner. Then, we develop a human-in-the-loop pipeline which exploits human labeling on the diffusion-generated composite images to provide the weak supervision for training a structural plausibility classifier. The classifier is further used to guide the diffusion sampling process towards generating the plausible object placement. Experimental results verify the superiority of our method for producing plausible and diverse composite images on the new Cityscapes-OP dataset and the public OPA dataset, as well as demonstrate its potential in applications such as data augmentation and multi-object placement tasks. Our dataset and code will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge