Shenggong Ji
Friend Recall in Online Games via Pre-training Edge Transformers
Feb 20, 2023



Abstract:Friend recall is an important way to improve Daily Active Users (DAU) in Tencent games. Traditional friend recall methods focus on rules like friend intimacy or training a classifier for predicting lost players' return probability, but ignore feature information of (active) players and historical friend recall events. In this work, we treat friend recall as a link prediction problem and explore several link prediction methods which can use features of both active and lost players, as well as historical events. Furthermore, we propose a novel Edge Transformer model and pre-train the model via masked auto-encoders. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results in the offline experiments and online A/B Tests of three Tencent games.
Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Graph Relation Learning for Urban Metro Flow Prediction
Apr 06, 2022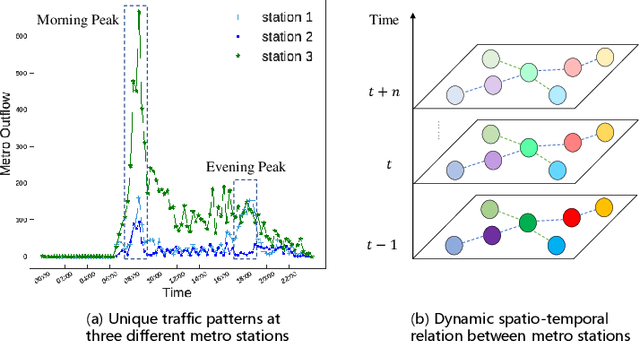
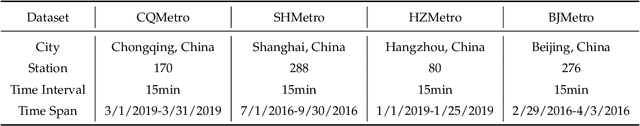
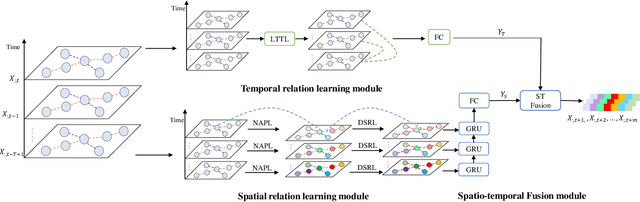
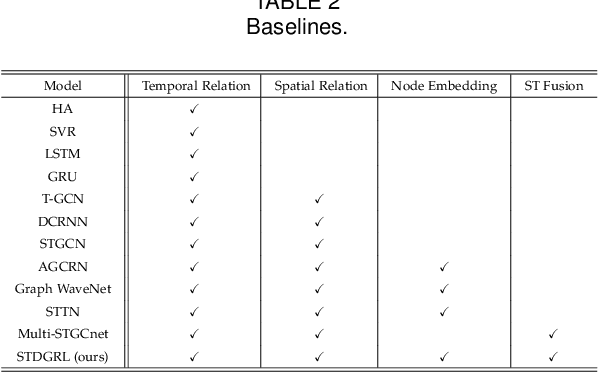
Abstract:Urban metro flow prediction is of great value for metro operation scheduling, passenger flow management and personal travel planning. However, it faces two main challenges. First, different metro stations, e.g. transfer stations and non-transfer stations, have unique traffic patterns. Second, it is challenging to model complex spatio-temporal dynamic relation of metro stations. To address these challenges, we develop a spatio-temporal dynamic graph relational learning model (STDGRL) to predict urban metro station flow. First, we propose a spatio-temporal node embedding representation module to capture the traffic patterns of different stations. Second, we employ a dynamic graph relationship learning module to learn dynamic spatial relationships between metro stations without a predefined graph adjacency matrix. Finally, we provide a transformer-based long-term relationship prediction module for long-term metro flow prediction. Extensive experiments are conducted based on metro data in Beijing, Shanghai, Chongqing and Hangzhou. Experimental results show the advantages of our method beyond 11 baselines for urban metro flow prediction.
HiSTGNN: Hierarchical Spatio-temporal Graph Neural Networks for Weather Forecasting
Jan 22, 2022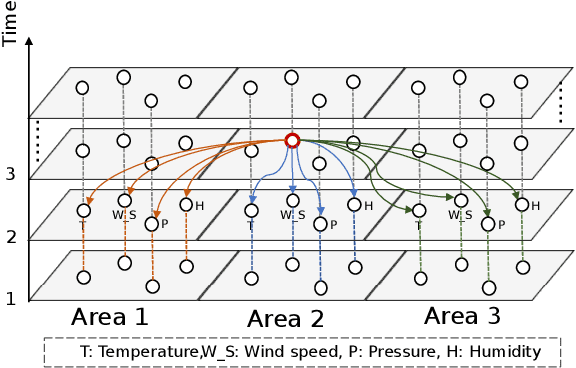

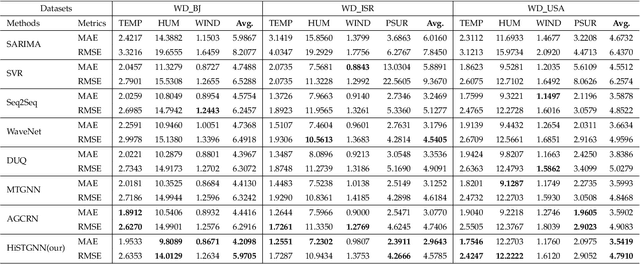
Abstract:Weather Forecasting is an attractive challengeable task due to its influence on human life and complexity in atmospheric motion. Supported by massive historical observed time series data, the task is suitable for data-driven approaches, especially deep neural networks. Recently, the Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) based methods have achieved excellent performance for spatio-temporal forecasting. However, the canonical GNNs-based methods only individually model the local graph of meteorological variables per station or the global graph of whole stations, lacking information interaction between meteorological variables in different stations. In this paper, we propose a novel Hierarchical Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network (HiSTGNN) to model cross-regional spatio-temporal correlations among meteorological variables in multiple stations. An adaptive graph learning layer and spatial graph convolution are employed to construct self-learning graph and study hidden dependency among nodes of variable-level and station-level graph. For capturing temporal pattern, the dilated inception as the backbone of gate temporal convolution is designed to model long and various meteorological trends. Moreover, a dynamic interaction learning is proposed to build bidirectional information passing in hierarchical graph. Experimental results on three real-world meteorological datasets demonstrate the superior performance of HiSTGNN beyond 7 baselines and it reduces the errors by 4.2% to 11.6% especially compared to state-of-the-art weather forecasting method.
ScaleVLAD: Improving Multimodal Sentiment Analysis via Multi-Scale Fusion of Locally Descriptors
Dec 02, 2021



Abstract:Fusion technique is a key research topic in multimodal sentiment analysis. The recent attention-based fusion demonstrates advances over simple operation-based fusion. However, these fusion works adopt single-scale, i.e., token-level or utterance-level, unimodal representation. Such single-scale fusion is suboptimal because that different modality should be aligned with different granularities. This paper proposes a fusion model named ScaleVLAD to gather multi-Scale representation from text, video, and audio with shared Vectors of Locally Aggregated Descriptors to improve unaligned multimodal sentiment analysis. These shared vectors can be regarded as shared topics to align different modalities. In addition, we propose a self-supervised shifted clustering loss to keep the fused feature differentiation among samples. The backbones are three Transformer encoders corresponding to three modalities, and the aggregated features generated from the fusion module are feed to a Transformer plus a full connection to finish task predictions. Experiments on three popular sentiment analysis benchmarks, IEMOCAP, MOSI, and MOSEI, demonstrate significant gains over baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge