Shaoyang Xu
Training Data Efficiency in Multimodal Process Reward Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Process Reward Models (MPRMs) are central to step-level supervision for visual reasoning in MLLMs. Training MPRMs typically requires large-scale Monte Carlo (MC)-annotated corpora, incurring substantial training cost. This paper studies the data efficiency for MPRM training. Our preliminary experiments reveal that MPRM training quickly saturates under random subsampling of the training data, indicating substantial redundancy within existing MC-annotated corpora. To explain this, we formalize a theoretical framework and reveal that informative gradient updates depend on two factors: label mixtures of positive/negative steps and label reliability (average MC scores of positive steps). Guided by these insights, we propose the Balanced-Information Score (BIS), which prioritizes both mixture and reliability based on existing MC signals at the rollout level, without incurring any additional cost. Across two backbones (InternVL2.5-8B and Qwen2.5-VL-7B) on VisualProcessBench, BIS-selected subsets consistently match and even surpass the full-data performance at small fractions. Notably, the BIS subset reaches full-data performance using only 10% of the training data, improving over random subsampling by a relative 4.1%.
Language of Thought Shapes Output Diversity in Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Output diversity is crucial for Large Language Models as it underpins pluralism and creativity. In this work, we reveal that controlling the language used during model thinking-the language of thought-provides a novel and structural source of output diversity. Our preliminary study shows that different thinking languages occupy distinct regions in a model's thinking space. Based on this observation, we study two repeated sampling strategies under multilingual thinking-Single-Language Sampling and Mixed-Language Sampling-and conduct diversity evaluation on outputs that are controlled to be in English, regardless of the thinking language used. Across extensive experiments, we demonstrate that switching the thinking language from English to non-English languages consistently increases output diversity, with a clear and consistent positive correlation such that languages farther from English in the thinking space yield larger gains. We further show that aggregating samples across multiple thinking languages yields additional improvements through compositional effects, and that scaling sampling with linguistic heterogeneity expands the model's diversity ceiling. Finally, we show that these findings translate into practical benefits in pluralistic alignment scenarios, leading to broader coverage of cultural knowledge and value orientations in LLM outputs. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/iNLP-Lab/Multilingual-LoT-Diversity.
DCIS: Efficient Length Extrapolation of LLMs via Divide-and-Conquer Scaling Factor Search
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) based on the Transformer architecture usually have their context length limited due to the high training cost. Recent advancements extend the context window by adjusting the scaling factors of RoPE and fine-tuning. However, suboptimal initialization of these factors results in increased fine-tuning costs and reduced performance at target length. To address these challenges, we propose an innovative RoPE-based fine-tuning framework that diverges from conventional scaling factors search. Specifically, we present a Divide-and-Conquer Incremental Search (DCIS) algorithm that strategically determines the better scaling factors. Further fine-tuning with the identified scaling factors effectively extends the context window of LLMs. Empirical results demonstrate that our methodology not only mitigates performance decay at extended target lengths but also allows the model to fine-tune on short contexts and generalize to long contexts, thereby reducing the cost of fine-tuning. The scaling factors obtained through DCIS can even perform effectively without fine-tuning. Further analysis of the search space reveals that DCIS achieves twice the search efficiency compared to other methods. We also examine the impact of the non-strictly increasing scaling factors utilized in DCIS and evaluate the general capabilities of LLMs across various context lengths.
Multilingual Large Language Models: A Systematic Survey
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the latest research on multilingual large language models (MLLMs). MLLMs not only are able to understand and generate language across linguistic boundaries, but also represent an important advancement in artificial intelligence. We first discuss the architecture and pre-training objectives of MLLMs, highlighting the key components and methodologies that contribute to their multilingual capabilities. We then discuss the construction of multilingual pre-training and alignment datasets, underscoring the importance of data quality and diversity in enhancing MLLM performance. An important focus of this survey is on the evaluation of MLLMs. We present a detailed taxonomy and roadmap covering the assessment of MLLMs' cross-lingual knowledge, reasoning, alignment with human values, safety, interpretability and specialized applications. Specifically, we extensively discuss multilingual evaluation benchmarks and datasets, and explore the use of LLMs themselves as multilingual evaluators. To enhance MLLMs from black to white boxes, we also address the interpretability of multilingual capabilities, cross-lingual transfer and language bias within these models. Finally, we provide a comprehensive review of real-world applications of MLLMs across diverse domains, including biology, medicine, computer science, mathematics and law. We showcase how these models have driven innovation and improvements in these specialized fields while also highlighting the challenges and opportunities in deploying MLLMs within diverse language communities and application scenarios. We listed the paper related in this survey and publicly available at https://github.com/tjunlp-lab/Awesome-Multilingual-LLMs-Papers.
Self-Pluralising Culture Alignment for Large Language Models
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly accessible in many countries, it is essential to align them to serve pluralistic human values across cultures. However, pluralistic culture alignment in LLMs remain an open problem. In this paper, we propose CultureSPA, a Self-Pluralising Culture Alignment framework that allows LLMs to simultaneously align to pluralistic cultures. The framework first generates questions on various culture topics, then yields LLM outputs in response to these generated questions under both culture-aware and culture-unaware settings. By comparing culture-aware/unaware outputs, we are able to detect and collect culture-related instances. These instances are employed to fine-tune LLMs to serve pluralistic cultures in either a culture-joint or culture-specific way. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CultureSPA significantly improves the alignment of LLMs to diverse cultures without compromising general abilities. And further improvements can be achieved if CultureSPA is combined with advanced prompt engineering techniques. Comparisons between culture-joint and culture-specific tuning strategies, along with variations in data quality and quantity, illustrate the robustness of our method. We also explore the mechanisms underlying CultureSPA and the relations between different cultures it reflects.
FuxiTranyu: A Multilingual Large Language Model Trained with Balanced Data
Aug 13, 2024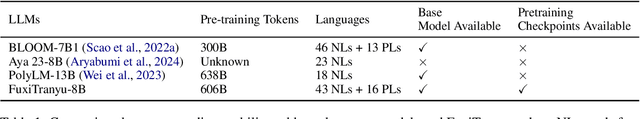
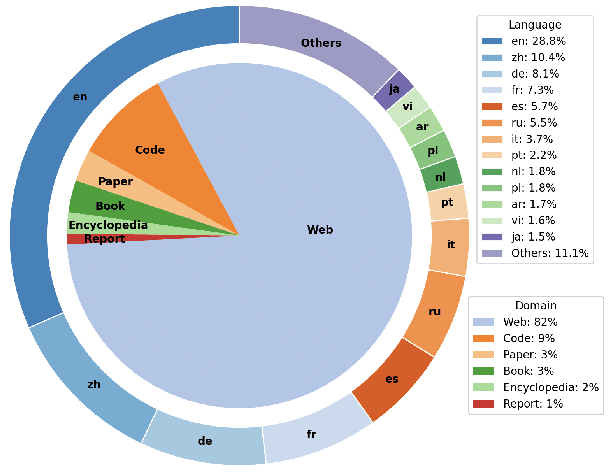
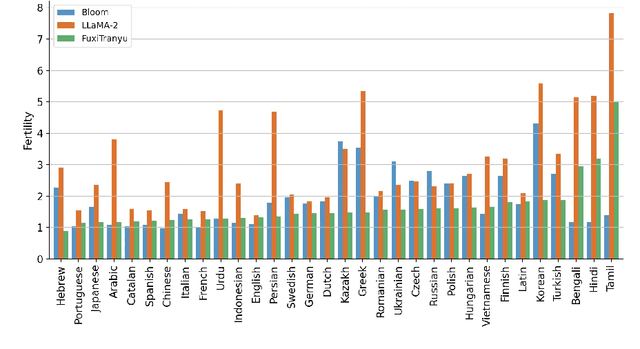
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated prowess in a wide range of tasks. However, many LLMs exhibit significant performance discrepancies between high- and low-resource languages. To mitigate this challenge, we present FuxiTranyu, an open-source multilingual LLM, which is designed to satisfy the need of the research community for balanced and high-performing multilingual capabilities. FuxiTranyu-8B, the base model with 8 billion parameters, is trained from scratch on a meticulously balanced multilingual data repository that contains 600 billion tokens covering 43 natural languages and 16 programming languages. In addition to the base model, we also develop two instruction-tuned models: FuxiTranyu-8B-SFT that is fine-tuned on a diverse multilingual instruction dataset, and FuxiTranyu-8B-DPO that is further refined with DPO on a preference dataset for enhanced alignment ability. Extensive experiments on a wide range of multilingual benchmarks demonstrate the competitive performance of FuxiTranyu against existing multilingual LLMs, e.g., BLOOM-7B, PolyLM-13B, Llama-2-Chat-7B and Mistral-7B-Instruct. Interpretability analyses at both the neuron and representation level suggest that FuxiTranyu is able to learn consistent multilingual representations across different languages. To promote further research into multilingual LLMs and their working mechanisms, we release both the base and instruction-tuned FuxiTranyu models together with 58 pretraining checkpoints at HuggingFace and Github.
ConTrans: Weak-to-Strong Alignment Engineering via Concept Transplantation
May 22, 2024Abstract:Ensuring large language models (LLM) behave consistently with human goals, values, and intentions is crucial for their safety but yet computationally expensive. To reduce the computational cost of alignment training of LLMs, especially for those with a huge number of parameters, and to reutilize learned value alignment, we propose ConTrans, a novel framework that enables weak-to-strong alignment transfer via concept transplantation. From the perspective of representation engineering, ConTrans refines concept vectors in value alignment from a source LLM (usually a weak yet aligned LLM). The refined concept vectors are then reformulated to adapt to the target LLM (usually a strong yet unaligned base LLM) via affine transformation. In the third step, ConTrans transplants the reformulated concept vectors into the residual stream of the target LLM. Experiments demonstrate the successful transplantation of a wide range of aligned concepts from 7B models to 13B and 70B models across multiple LLMs and LLM families. Remarkably, ConTrans even surpasses instruction-tuned models in terms of truthfulness. Experiment results validate the effectiveness of both inter-LLM-family and intra-LLM-family concept transplantation. Our work successfully demonstrates an alternative way to achieve weak-to-strong alignment generalization and control.
Exploring Multilingual Human Value Concepts in Large Language Models: Is Value Alignment Consistent, Transferable and Controllable across Languages?
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Prior research in representation engineering has revealed that LLMs encode concepts within their representation spaces, predominantly centered around English. In this study, we extend this philosophy to a multilingual scenario, delving into multilingual human value concepts in LLMs. Through our comprehensive exploration covering 7 types of human values, 16 languages and 3 LLM series with distinct multilinguality, we empirically substantiate the existence of multilingual human values in LLMs. Further cross-lingual analysis on these concepts discloses 3 traits arising from language resource disparities: cross-lingual inconsistency, distorted linguistic relationships, and unidirectional cross-lingual transfer between high- and low-resource languages, all in terms of human value concepts. Additionally, we validate the feasibility of cross-lingual control over value alignment capabilities of LLMs, leveraging the dominant language as a source language. Drawing from our findings on multilingual value alignment, we prudently provide suggestions on the composition of multilingual data for LLMs pre-training: including a limited number of dominant languages for cross-lingual alignment transfer while avoiding their excessive prevalence, and keeping a balanced distribution of non-dominant languages. We aspire that our findings would contribute to enhancing the safety and utility of multilingual AI.
Language Representation Projection: Can We Transfer Factual Knowledge across Languages in Multilingual Language Models?
Nov 07, 2023



Abstract:Multilingual pretrained language models serve as repositories of multilingual factual knowledge. Nevertheless, a substantial performance gap of factual knowledge probing exists between high-resource languages and low-resource languages, suggesting limited implicit factual knowledge transfer across languages in multilingual pretrained language models. This paper investigates the feasibility of explicitly transferring relatively rich factual knowledge from English to non-English languages. To accomplish this, we propose two parameter-free $\textbf{L}$anguage $\textbf{R}$epresentation $\textbf{P}$rojection modules (LRP2). The first module converts non-English representations into English-like equivalents, while the second module reverts English-like representations back into representations of the corresponding non-English language. Experimental results on the mLAMA dataset demonstrate that LRP2 significantly improves factual knowledge retrieval accuracy and facilitates knowledge transferability across diverse non-English languages. We further investigate the working mechanism of LRP2 from the perspectives of representation space and cross-lingual knowledge neuron.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge