Shanlan Shen
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Real-World Face Restoration: Methods and Results
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:This paper provides a review of the NTIRE 2025 challenge on real-world face restoration, highlighting the proposed solutions and the resulting outcomes. The challenge focuses on generating natural, realistic outputs while maintaining identity consistency. Its goal is to advance state-of-the-art solutions for perceptual quality and realism, without imposing constraints on computational resources or training data. The track of the challenge evaluates performance using a weighted image quality assessment (IQA) score and employs the AdaFace model as an identity checker. The competition attracted 141 registrants, with 13 teams submitting valid models, and ultimately, 10 teams achieved a valid score in the final ranking. This collaborative effort advances the performance of real-world face restoration while offering an in-depth overview of the latest trends in the field.
Hardware Architecture for Large Parallel Array of Random Feature Extractors applied to Image Recognition
Dec 24, 2015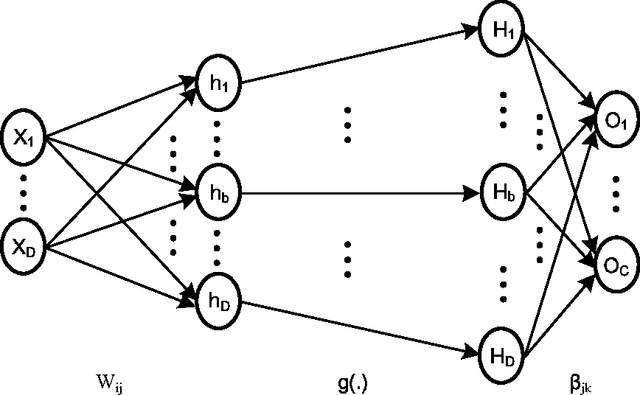

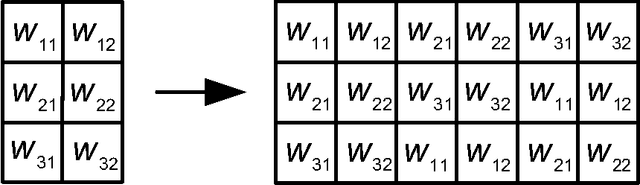

Abstract:We demonstrate a low-power and compact hardware implementation of Random Feature Extractor (RFE) core. With complex tasks like Image Recognition requiring a large set of features, we show how weight reuse technique can allow to virtually expand the random features available from RFE core. Further, we show how to avoid computation cost wasted for propagating "incognizant" or redundant random features. For proof of concept, we validated our approach by using our RFE core as the first stage of Extreme Learning Machine (ELM)--a two layer neural network--and were able to achieve $>97\%$ accuracy on MNIST database of handwritten digits. ELM's first stage of RFE is done on an analog ASIC occupying $5$mm$\times5$mm area in $0.35\mu$m CMOS and consuming $5.95$ $\mu$J/classify while using $\approx 5000$ effective hidden neurons. The ELM second stage consisting of just adders can be implemented as digital circuit with estimated power consumption of $20.9$ nJ/classify. With a total energy consumption of only $5.97$ $\mu$J/classify, this low-power mixed signal ASIC can act as a co-processor in portable electronic gadgets with cameras.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge