Sergey Nikolenko
Against Opacity: Explainable AI and Large Language Models for Effective Digital Advertising
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The opaqueness of modern digital advertising, exemplified by platforms such as Meta Ads, raises concerns regarding their autonomous control over audience targeting, pricing structures, and ad relevancy assessments. Locked in their leading positions by network effects, ``Metas and Googles of the world'' attract countless advertisers who rely on intuition, with billions of dollars lost on ineffective social media ads. The platforms' algorithms use huge amounts of data unavailable to advertisers, and the algorithms themselves are opaque as well. This lack of transparency hinders the advertisers' ability to make informed decisions and necessitates efforts to promote transparency, standardize industry metrics, and strengthen regulatory frameworks. In this work, we propose novel ways to assist marketers in optimizing their advertising strategies via machine learning techniques designed to analyze and evaluate content, in particular, predict the click-through rates (CTR) of novel advertising content. Another important problem is that large volumes of data available in the competitive landscape, e.g., competitors' ads, impede the ability of marketers to derive meaningful insights. This leads to a pressing need for a novel approach that would allow us to summarize and comprehend complex data. Inspired by the success of ChatGPT in bridging the gap between large language models (LLMs) and a broader non-technical audience, we propose a novel system that facilitates marketers in data interpretation, called SODA, that merges LLMs with explainable AI, enabling better human-AI collaboration with an emphasis on the domain of digital marketing and advertising. By combining LLMs and explainability features, in particular modern text-image models, we aim to improve the synergy between human marketers and AI systems.
Toolken+: Improving LLM Tool Usage with Reranking and a Reject Option
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:The recently proposed ToolkenGPT tool learning paradigm demonstrates promising performance but suffers from two major issues: first, it cannot benefit from tool documentation, and second, it often makes mistakes in whether to use a tool at all. We introduce Toolken+ that mitigates the first problem by reranking top $k$ tools selected by ToolkenGPT and the second problem with a special "Reject" option such that the model will generate a vocabulary token if "Reject" is ranked first. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Toolken+ on multistep numerical reasoning and tool selection tasks.
Robust AI-Generated Text Detection by Restricted Embeddings
Oct 10, 2024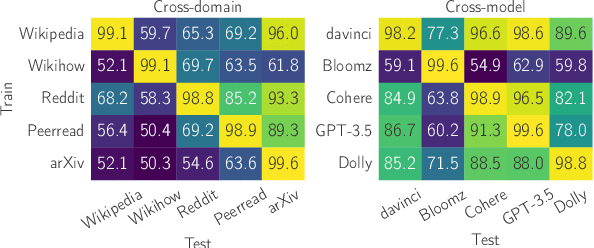
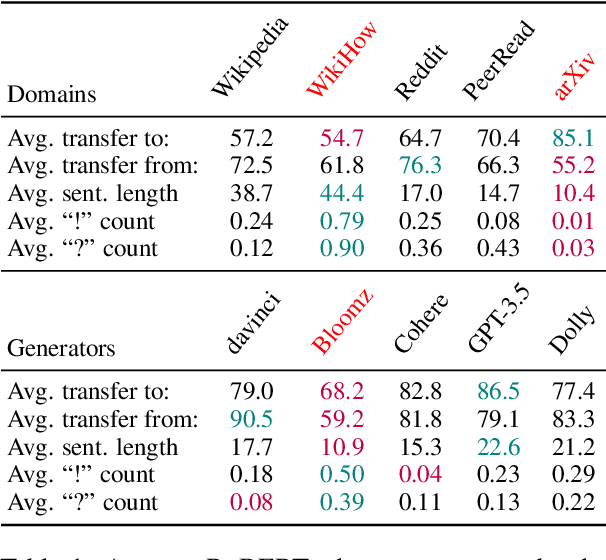
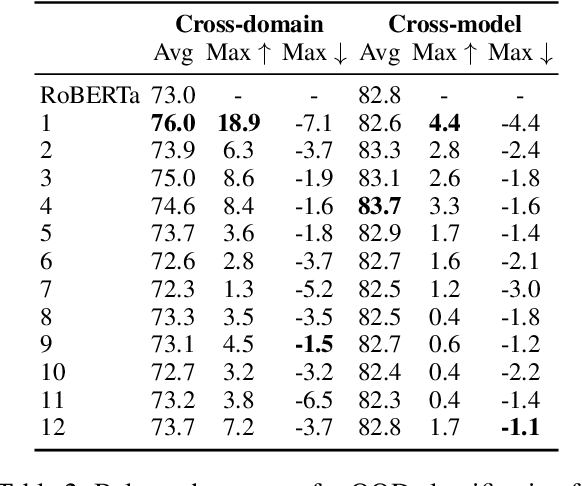
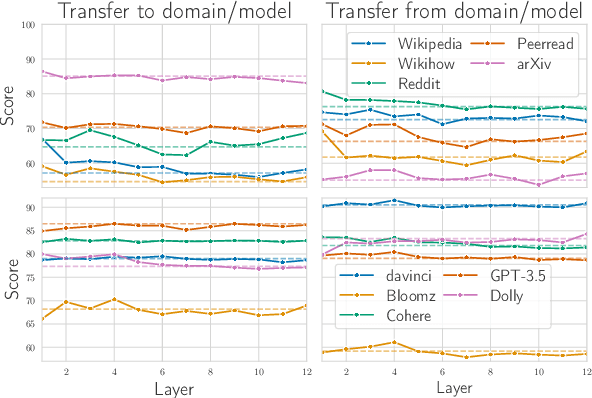
Abstract:Growing amount and quality of AI-generated texts makes detecting such content more difficult. In most real-world scenarios, the domain (style and topic) of generated data and the generator model are not known in advance. In this work, we focus on the robustness of classifier-based detectors of AI-generated text, namely their ability to transfer to unseen generators or semantic domains. We investigate the geometry of the embedding space of Transformer-based text encoders and show that clearing out harmful linear subspaces helps to train a robust classifier, ignoring domain-specific spurious features. We investigate several subspace decomposition and feature selection strategies and achieve significant improvements over state of the art methods in cross-domain and cross-generator transfer. Our best approaches for head-wise and coordinate-based subspace removal increase the mean out-of-distribution (OOD) classification score by up to 9% and 14% in particular setups for RoBERTa and BERT embeddings respectively. We release our code and data: https://github.com/SilverSolver/RobustATD
Neural Click Models for Recommender Systems
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:We develop and evaluate neural architectures to model the user behavior in recommender systems (RS) inspired by click models for Web search but going beyond standard click models. Proposed architectures include recurrent networks, Transformer-based models that alleviate the quadratic complexity of self-attention, adversarial and hierarchical architectures. Our models outperform baselines on the ContentWise and RL4RS datasets and can be used in RS simulators to model user response for RS evaluation and pretraining.
Improving Interpretability and Robustness for the Detection of AI-Generated Images
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:With growing abilities of generative models, artificial content detection becomes an increasingly important and difficult task. However, all popular approaches to this problem suffer from poor generalization across domains and generative models. In this work, we focus on the robustness of AI-generated image (AIGI) detectors. We analyze existing state-of-the-art AIGI detection methods based on frozen CLIP embeddings and show how to interpret them, shedding light on how images produced by various AI generators differ from real ones. Next we propose two ways to improve robustness: based on removing harmful components of the embedding vector and based on selecting the best performing attention heads in the image encoder model. Our methods increase the mean out-of-distribution (OOD) classification score by up to 6% for cross-model transfer. We also propose a new dataset for AIGI detection and use it in our evaluation; we believe this dataset will help boost further research. The dataset and code are provided as a supplement.
$ abla^2$DFT: A Universal Quantum Chemistry Dataset of Drug-Like Molecules and a Benchmark for Neural Network Potentials
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Methods of computational quantum chemistry provide accurate approximations of molecular properties crucial for computer-aided drug discovery and other areas of chemical science. However, high computational complexity limits the scalability of their applications. Neural network potentials (NNPs) are a promising alternative to quantum chemistry methods, but they require large and diverse datasets for training. This work presents a new dataset and benchmark called $\nabla^2$DFT that is based on the nablaDFT. It contains twice as much molecular structures, three times more conformations, new data types and tasks, and state-of-the-art models. The dataset includes energies, forces, 17 molecular properties, Hamiltonian and overlap matrices, and a wavefunction object. All calculations were performed at the DFT level ($\omega$B97X-D/def2-SVP) for each conformation. Moreover, $\nabla^2$DFT is the first dataset that contains relaxation trajectories for a substantial number of drug-like molecules. We also introduce a novel benchmark for evaluating NNPs in molecular property prediction, Hamiltonian prediction, and conformational optimization tasks. Finally, we propose an extendable framework for training NNPs and implement 10 models within it.
ImplicitSLIM and How it Improves Embedding-based Collaborative Filtering
May 31, 2024



Abstract:We present ImplicitSLIM, a novel unsupervised learning approach for sparse high-dimensional data, with applications to collaborative filtering. Sparse linear methods (SLIM) and their variations show outstanding performance, but they are memory-intensive and hard to scale. ImplicitSLIM improves embedding-based models by extracting embeddings from SLIM-like models in a computationally cheap and memory-efficient way, without explicit learning of heavy SLIM-like models. We show that ImplicitSLIM improves performance and speeds up convergence for both state of the art and classical collaborative filtering methods. The source code for ImplicitSLIM, related models, and applications is available at https://github.com/ilya-shenbin/ImplicitSLIM.
Efficient Grammatical Error Correction Via Multi-Task Training and Optimized Training Schedule
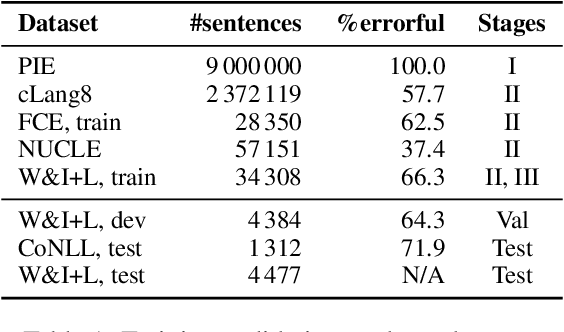
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Progress in neural grammatical error correction (GEC) is hindered by the lack of annotated training data. Sufficient amounts of high-quality manually annotated data are not available, so recent research has relied on generating synthetic data, pretraining on it, and then fine-tuning on real datasets; performance gains have been achieved either by ensembling or by using huge pretrained models such as XXL-T5 as the backbone. In this work, we explore an orthogonal direction: how to use available data more efficiently. First, we propose auxiliary tasks that exploit the alignment between the original and corrected sentences, such as predicting a sequence of corrections. We formulate each task as a sequence-to-sequence problem and perform multi-task training. Second, we discover that the order of datasets used for training and even individual instances within a dataset may have important effects on the final performance, so we set out to find the best training schedule. Together, these two ideas lead to significant improvements, producing results that improve state of the art with much smaller models; in particular, we outperform the best models based on T5-XXL (11B parameters) with a BART-based model (400M parameters).
GEC-DePenD: Non-Autoregressive Grammatical Error Correction with Decoupled Permutation and Decoding
Nov 14, 2023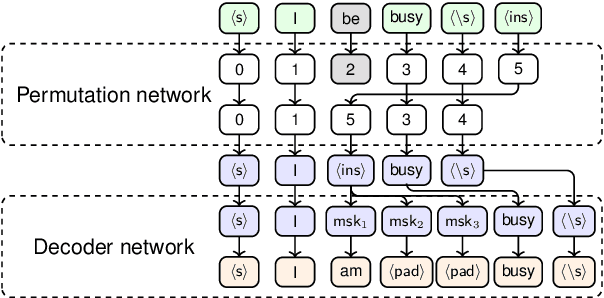
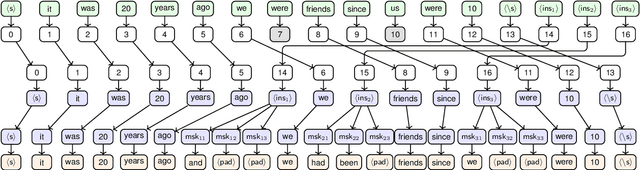
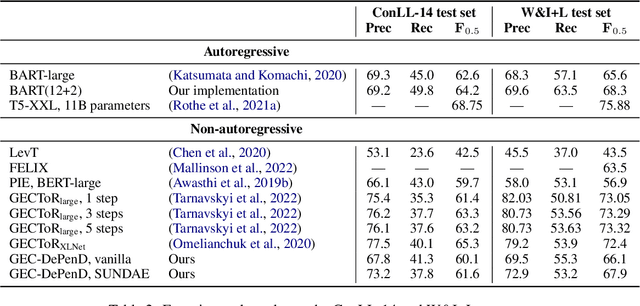
Abstract:Grammatical error correction (GEC) is an important NLP task that is currently usually solved with autoregressive sequence-to-sequence models. However, approaches of this class are inherently slow due to one-by-one token generation, so non-autoregressive alternatives are needed. In this work, we propose a novel non-autoregressive approach to GEC that decouples the architecture into a permutation network that outputs a self-attention weight matrix that can be used in beam search to find the best permutation of input tokens (with auxiliary {ins} tokens) and a decoder network based on a step-unrolled denoising autoencoder that fills in specific tokens. This allows us to find the token permutation after only one forward pass of the permutation network, avoiding autoregressive constructions. We show that the resulting network improves over previously known non-autoregressive methods for GEC and reaches the level of autoregressive methods that do not use language-specific synthetic data generation methods. Our results are supported by a comprehensive experimental validation on the ConLL-2014 and Write&Improve+LOCNESS datasets and an extensive ablation study that supports our architectural and algorithmic choices.
Artificial Text Boundary Detection with Topological Data Analysis and Sliding Window Techniques
Nov 14, 2023
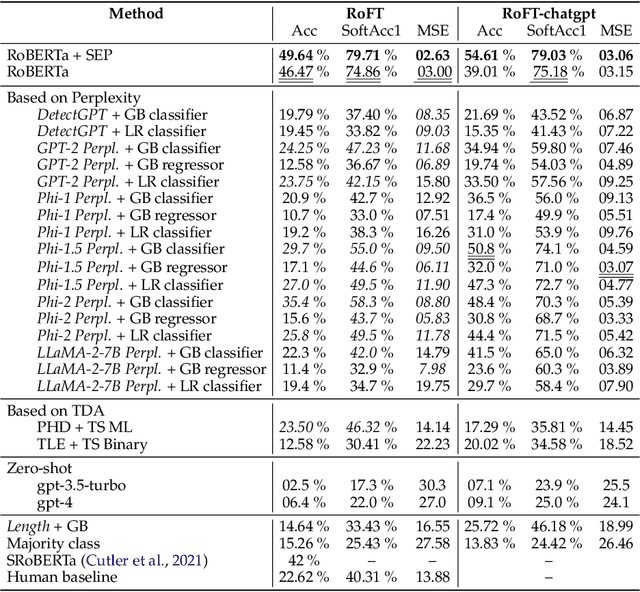
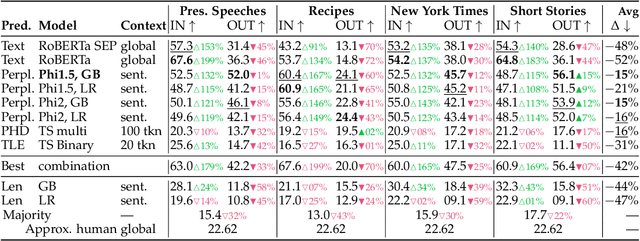
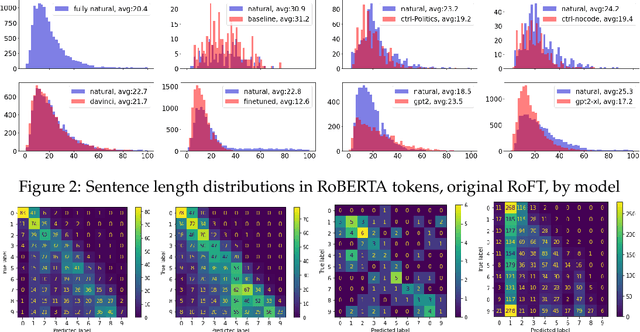
Abstract:Due to the rapid development of text generation models, people increasingly often encounter texts that may start out as written by a human but then continue as machine-generated results of large language models. Detecting the boundary between human-written and machine-generated parts of such texts is a very challenging problem that has not received much attention in literature. In this work, we consider and compare a number of different approaches for this artificial text boundary detection problem, comparing several predictors over features of different nature. We show that supervised fine-tuning of the RoBERTa model works well for this task in general but fails to generalize in important cross-domain and cross-generator settings, demonstrating a tendency to overfit to spurious properties of the data. Then, we propose novel approaches based on features extracted from a frozen language model's embeddings that are able to outperform both the human accuracy level and previously considered baselines on the Real or Fake Text benchmark. Moreover, we adapt perplexity-based approaches for the boundary detection task and analyze their behaviour. We analyze the robustness of all proposed classifiers in cross-domain and cross-model settings, discovering important properties of the data that can negatively influence the performance of artificial text boundary detection algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge