Andrey Bout
Toolken+: Improving LLM Tool Usage with Reranking and a Reject Option
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:The recently proposed ToolkenGPT tool learning paradigm demonstrates promising performance but suffers from two major issues: first, it cannot benefit from tool documentation, and second, it often makes mistakes in whether to use a tool at all. We introduce Toolken+ that mitigates the first problem by reranking top $k$ tools selected by ToolkenGPT and the second problem with a special "Reject" option such that the model will generate a vocabulary token if "Reject" is ranked first. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Toolken+ on multistep numerical reasoning and tool selection tasks.
Efficient Grammatical Error Correction Via Multi-Task Training and Optimized Training Schedule
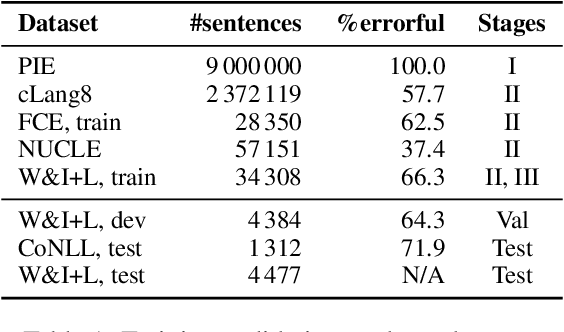
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Progress in neural grammatical error correction (GEC) is hindered by the lack of annotated training data. Sufficient amounts of high-quality manually annotated data are not available, so recent research has relied on generating synthetic data, pretraining on it, and then fine-tuning on real datasets; performance gains have been achieved either by ensembling or by using huge pretrained models such as XXL-T5 as the backbone. In this work, we explore an orthogonal direction: how to use available data more efficiently. First, we propose auxiliary tasks that exploit the alignment between the original and corrected sentences, such as predicting a sequence of corrections. We formulate each task as a sequence-to-sequence problem and perform multi-task training. Second, we discover that the order of datasets used for training and even individual instances within a dataset may have important effects on the final performance, so we set out to find the best training schedule. Together, these two ideas lead to significant improvements, producing results that improve state of the art with much smaller models; in particular, we outperform the best models based on T5-XXL (11B parameters) with a BART-based model (400M parameters).
Sinkhorn Transformations for Single-Query Postprocessing in Text-Video Retrieval
Nov 14, 2023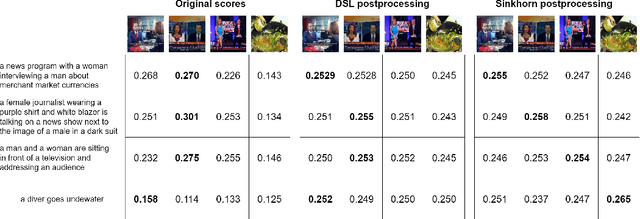
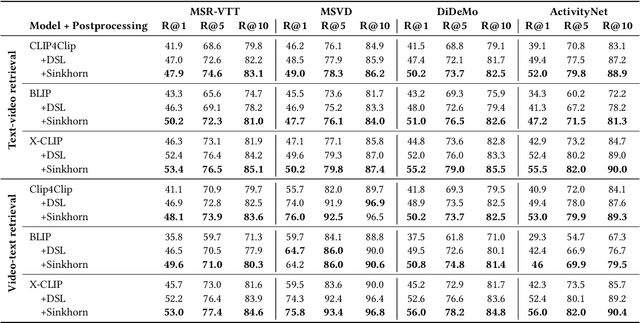
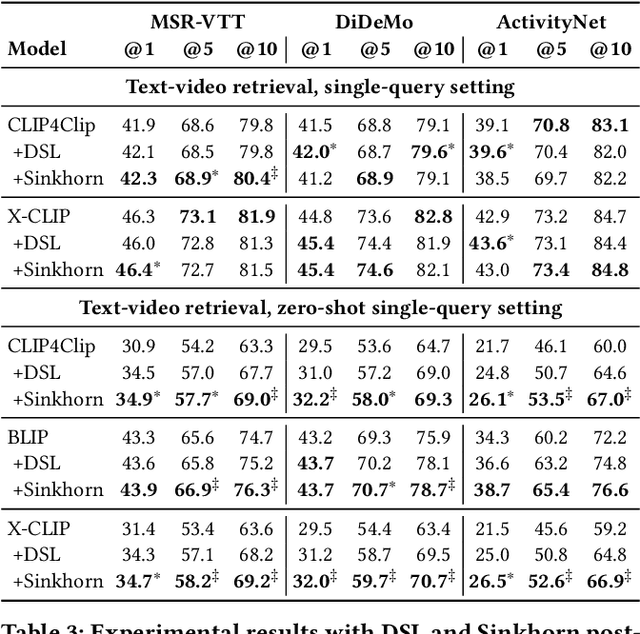
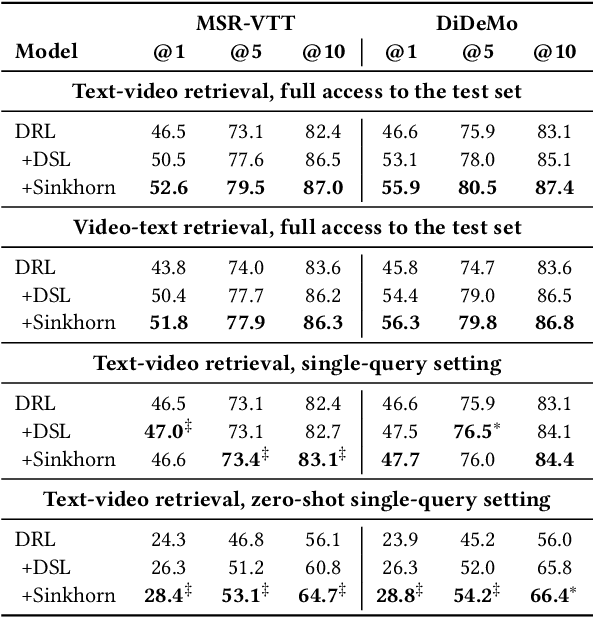
Abstract:A recent trend in multimodal retrieval is related to postprocessing test set results via the dual-softmax loss (DSL). While this approach can bring significant improvements, it usually presumes that an entire matrix of test samples is available as DSL input. This work introduces a new postprocessing approach based on Sinkhorn transformations that outperforms DSL. Further, we propose a new postprocessing setting that does not require access to multiple test queries. We show that our approach can significantly improve the results of state of the art models such as CLIP4Clip, BLIP, X-CLIP, and DRL, thus achieving a new state-of-the-art on several standard text-video retrieval datasets both with access to the entire test set and in the single-query setting.
GEC-DePenD: Non-Autoregressive Grammatical Error Correction with Decoupled Permutation and Decoding
Nov 14, 2023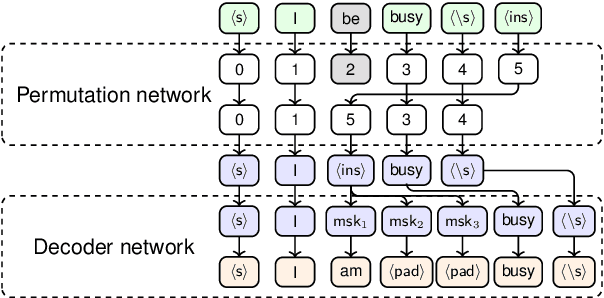
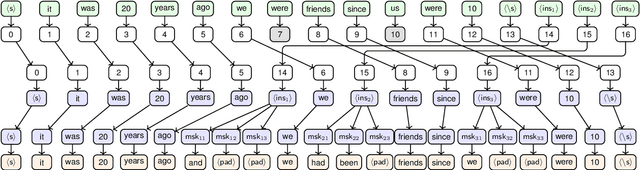
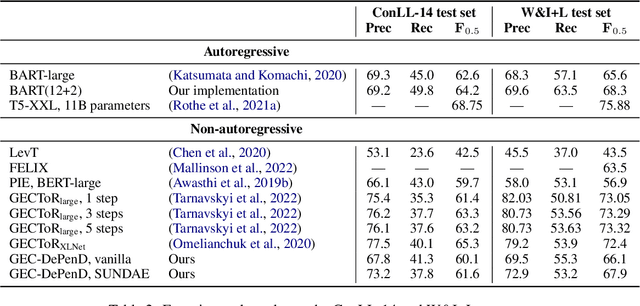
Abstract:Grammatical error correction (GEC) is an important NLP task that is currently usually solved with autoregressive sequence-to-sequence models. However, approaches of this class are inherently slow due to one-by-one token generation, so non-autoregressive alternatives are needed. In this work, we propose a novel non-autoregressive approach to GEC that decouples the architecture into a permutation network that outputs a self-attention weight matrix that can be used in beam search to find the best permutation of input tokens (with auxiliary {ins} tokens) and a decoder network based on a step-unrolled denoising autoencoder that fills in specific tokens. This allows us to find the token permutation after only one forward pass of the permutation network, avoiding autoregressive constructions. We show that the resulting network improves over previously known non-autoregressive methods for GEC and reaches the level of autoregressive methods that do not use language-specific synthetic data generation methods. Our results are supported by a comprehensive experimental validation on the ConLL-2014 and Write&Improve+LOCNESS datasets and an extensive ablation study that supports our architectural and algorithmic choices.
PanGu-Σ: Towards Trillion Parameter Language Model with Sparse Heterogeneous Computing
Mar 20, 2023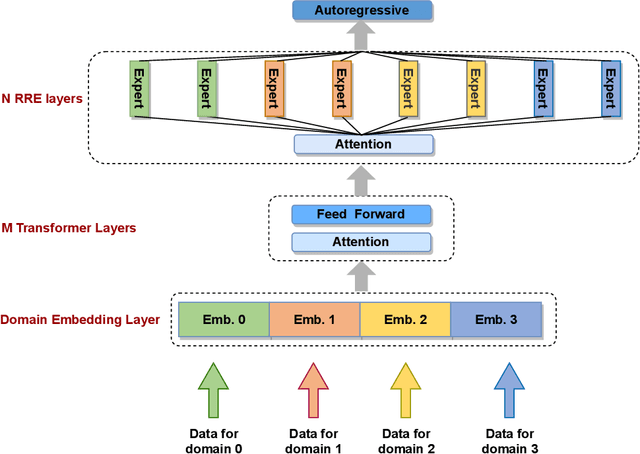
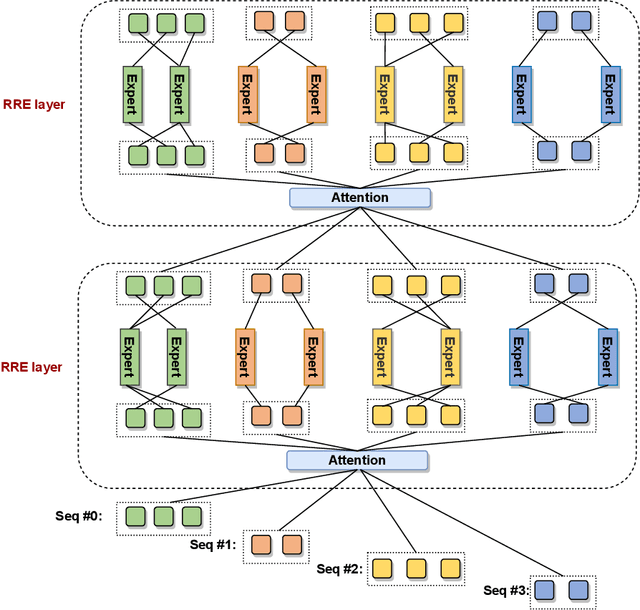
Abstract:The scaling of large language models has greatly improved natural language understanding, generation, and reasoning. In this work, we develop a system that trained a trillion-parameter language model on a cluster of Ascend 910 AI processors and MindSpore framework, and present the language model with 1.085T parameters named PanGu-{\Sigma}. With parameter inherent from PanGu-{\alpha}, we extend the dense Transformer model to sparse one with Random Routed Experts (RRE), and efficiently train the model over 329B tokens by using Expert Computation and Storage Separation(ECSS). This resulted in a 6.3x increase in training throughput through heterogeneous computing. Our experimental findings show that PanGu-{\Sigma} provides state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot learning of various Chinese NLP downstream tasks. Moreover, it demonstrates strong abilities when fine-tuned in application data of open-domain dialogue, question answering, machine translation and code generation.
Template-based Approach to Zero-shot Intent Recognition
Jun 22, 2022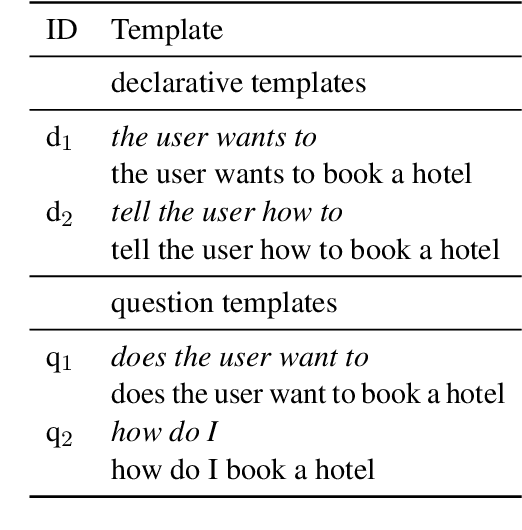
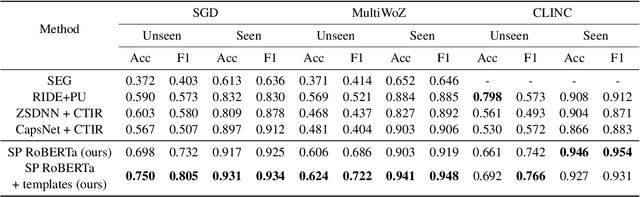
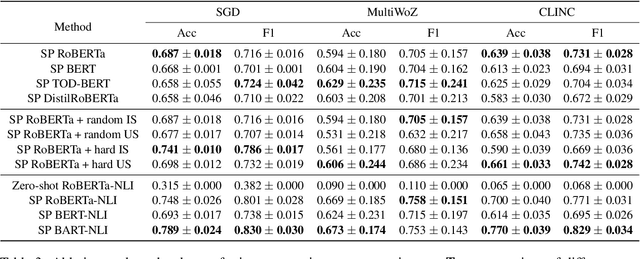
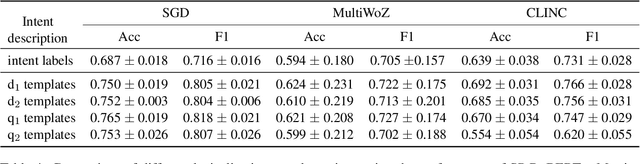
Abstract:The recent advances in transfer learning techniques and pre-training of large contextualized encoders foster innovation in real-life applications, including dialog assistants. Practical needs of intent recognition require effective data usage and the ability to constantly update supported intents, adopting new ones, and abandoning outdated ones. In particular, the generalized zero-shot paradigm, in which the model is trained on the seen intents and tested on both seen and unseen intents, is taking on new importance. In this paper, we explore the generalized zero-shot setup for intent recognition. Following best practices for zero-shot text classification, we treat the task with a sentence pair modeling approach. We outperform previous state-of-the-art f1-measure by up to 16\% for unseen intents, using intent labels and user utterances and without accessing external sources (such as knowledge bases). Further enhancement includes lexicalization of intent labels, which improves performance by up to 7\%. By using task transferring from other sentence pair tasks, such as Natural Language Inference, we gain additional improvements.
A Single Example Can Improve Zero-Shot Data Generation
Aug 16, 2021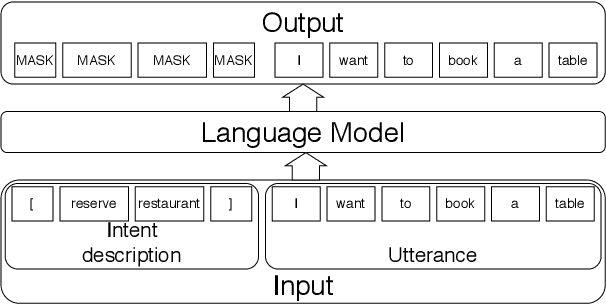
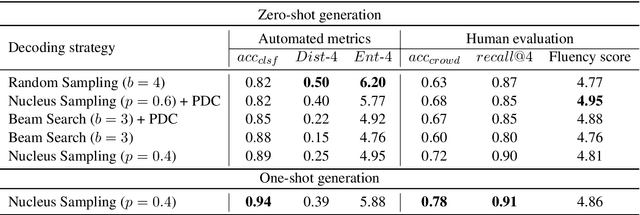
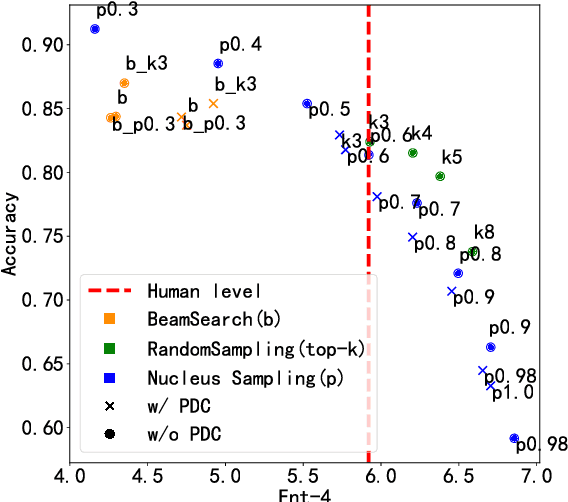
Abstract:Sub-tasks of intent classification, such as robustness to distribution shift, adaptation to specific user groups and personalization, out-of-domain detection, require extensive and flexible datasets for experiments and evaluation. As collecting such datasets is time- and labor-consuming, we propose to use text generation methods to gather datasets. The generator should be trained to generate utterances that belong to the given intent. We explore two approaches to generating task-oriented utterances. In the zero-shot approach, the model is trained to generate utterances from seen intents and is further used to generate utterances for intents unseen during training. In the one-shot approach, the model is presented with a single utterance from a test intent. We perform a thorough automatic, and human evaluation of the dataset generated utilizing two proposed approaches. Our results reveal that the attributes of the generated data are close to original test sets, collected via crowd-sourcing.
Revisiting Mahalanobis Distance for Transformer-Based Out-of-Domain Detection
Jan 11, 2021Abstract:Real-life applications, heavily relying on machine learning, such as dialog systems, demand out-of-domain detection methods. Intent classification models should be equipped with a mechanism to distinguish seen intents from unseen ones so that the dialog agent is capable of rejecting the latter and avoiding undesired behavior. However, despite increasing attention paid to the task, the best practices for out-of-domain intent detection have not yet been fully established. This paper conducts a thorough comparison of out-of-domain intent detection methods. We prioritize the methods, not requiring access to out-of-domain data during training, gathering of which is extremely time- and labor-consuming due to lexical and stylistic variation of user utterances. We evaluate multiple contextual encoders and methods, proven to be efficient, on three standard datasets for intent classification, expanded with out-of-domain utterances. Our main findings show that fine-tuning Transformer-based encoders on in-domain data leads to superior results. Mahalanobis distance, together with utterance representations, derived from Transformer-based encoders, outperforms other methods by a wide margin and establishes new state-of-the-art results for all datasets. The broader analysis shows that the reason for success lies in the fact that the fine-tuned Transformer is capable of constructing homogeneous representations of in-domain utterances, revealing geometrical disparity to out of domain utterances. In turn, the Mahalanobis distance captures this disparity easily.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge