Runyi Li
Mirai: Autoregressive Visual Generation Needs Foresight
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) visual generators model images as sequences of discrete tokens and are trained with next token likelihood. This strict causality supervision optimizes each step only by its immediate next token, which diminishes global coherence and slows convergence. We ask whether foresight, training signals that originate from later tokens, can help AR visual generation. We conduct a series of controlled diagnostics along the injection level, foresight layout, and foresight source axes, unveiling a key insight: aligning foresight to AR models' internal representation on the 2D image grids improves causality modeling. We formulate this insight with Mirai (meaning "future" in Japanese), a general framework that injects future information into AR training with no architecture change and no extra inference overhead: Mirai-E uses explicit foresight from multiple future positions of unidirectional representations, whereas Mirai-I leverages implicit foresight from matched bidirectional representations. Extensive experiments show that Mirai significantly accelerates convergence and improves generation quality. For instance, Mirai can speed up LlamaGen-B's convergence by up to 10$\times$ and reduce the generation FID from 5.34 to 4.34 on the ImageNet class-condition image generation benchmark. Our study highlights that visual autoregressive models need foresight.
LAFR: Efficient Diffusion-based Blind Face Restoration via Latent Codebook Alignment Adapter
May 29, 2025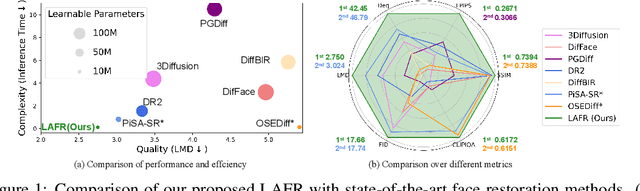
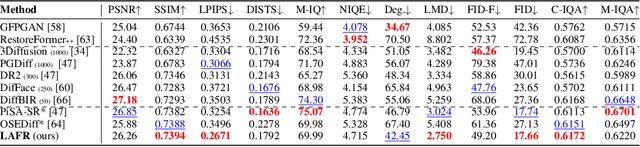
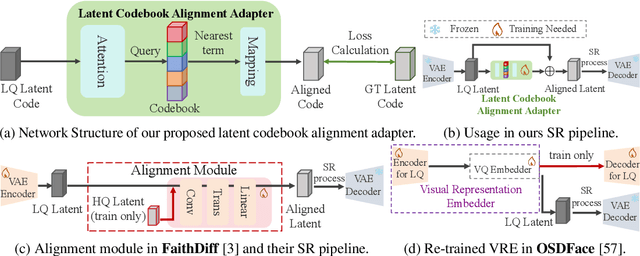
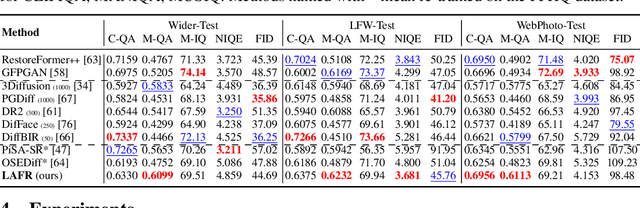
Abstract:Blind face restoration from low-quality (LQ) images is a challenging task that requires not only high-fidelity image reconstruction but also the preservation of facial identity. While diffusion models like Stable Diffusion have shown promise in generating high-quality (HQ) images, their VAE modules are typically trained only on HQ data, resulting in semantic misalignment when encoding LQ inputs. This mismatch significantly weakens the effectiveness of LQ conditions during the denoising process. Existing approaches often tackle this issue by retraining the VAE encoder, which is computationally expensive and memory-intensive. To address this limitation efficiently, we propose LAFR (Latent Alignment for Face Restoration), a novel codebook-based latent space adapter that aligns the latent distribution of LQ images with that of HQ counterparts, enabling semantically consistent diffusion sampling without altering the original VAE. To further enhance identity preservation, we introduce a multi-level restoration loss that combines constraints from identity embeddings and facial structural priors. Additionally, by leveraging the inherent structural regularity of facial images, we show that lightweight finetuning of diffusion prior on just 0.9% of FFHQ dataset is sufficient to achieve results comparable to state-of-the-art methods, reduce training time by 70%. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world face restoration benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of LAFR, achieving high-quality, identity-preserving face reconstruction from severely degraded inputs.
CTSR: Controllable Fidelity-Realness Trade-off Distillation for Real-World Image Super Resolution
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Real-world image super-resolution is a critical image processing task, where two key evaluation criteria are the fidelity to the original image and the visual realness of the generated results. Although existing methods based on diffusion models excel in visual realness by leveraging strong priors, they often struggle to achieve an effective balance between fidelity and realness. In our preliminary experiments, we observe that a linear combination of multiple models outperforms individual models, motivating us to harness the strengths of different models for a more effective trade-off. Based on this insight, we propose a distillation-based approach that leverages the geometric decomposition of both fidelity and realness, alongside the performance advantages of multiple teacher models, to strike a more balanced trade-off. Furthermore, we explore the controllability of this trade-off, enabling a flexible and adjustable super-resolution process, which we call CTSR (Controllable Trade-off Super-Resolution). Experiments conducted on several real-world image super-resolution benchmarks demonstrate that our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior performance across both fidelity and realness metrics.
RealOSR: Latent Unfolding Boosting Diffusion-based Real-world Omnidirectional Image Super-Resolution
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Omnidirectional image super-resolution (ODISR) aims to upscale low-resolution (LR) omnidirectional images (ODIs) to high-resolution (HR), addressing the growing demand for detailed visual content across a $180^{\circ}\times360^{\circ}$ viewport. Existing methods are limited by simple degradation assumptions (e.g., bicubic downsampling), which fail to capture the complex, unknown real-world degradation processes. Recent diffusion-based approaches suffer from slow inference due to their hundreds of sampling steps and frequent pixel-latent space conversions. To tackle these challenges, in this paper, we propose RealOSR, a novel diffusion-based approach for real-world ODISR (Real-ODISR) with single-step diffusion denoising. To sufficiently exploit the input information, RealOSR introduces a lightweight domain alignment module, which facilitates the efficient injection of LR ODI into the single-step latent denoising. Additionally, to better utilize the rich semantic and multi-scale feature modeling ability of denoising UNet, we develop a latent unfolding module that simulates the gradient descent process directly in latent space. Experimental results demonstrate that RealOSR outperforms previous methods in both ODI recovery quality and efficiency. Compared to the recent state-of-the-art diffusion-based ODISR method, OmniSSR, RealOSR achieves significant improvements in visual quality and over \textbf{200$\times$} inference acceleration. Our code and models will be released.
OmniGuard: Hybrid Manipulation Localization via Augmented Versatile Deep Image Watermarking
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid growth of generative AI and its widespread application in image editing, new risks have emerged regarding the authenticity and integrity of digital content. Existing versatile watermarking approaches suffer from trade-offs between tamper localization precision and visual quality. Constrained by the limited flexibility of previous framework, their localized watermark must remain fixed across all images. Under AIGC-editing, their copyright extraction accuracy is also unsatisfactory. To address these challenges, we propose OmniGuard, a novel augmented versatile watermarking approach that integrates proactive embedding with passive, blind extraction for robust copyright protection and tamper localization. OmniGuard employs a hybrid forensic framework that enables flexible localization watermark selection and introduces a degradation-aware tamper extraction network for precise localization under challenging conditions. Additionally, a lightweight AIGC-editing simulation layer is designed to enhance robustness across global and local editing. Extensive experiments show that OmniGuard achieves superior fidelity, robustness, and flexibility. Compared to the recent state-of-the-art approach EditGuard, our method outperforms it by 4.25dB in PSNR of the container image, 20.7% in F1-Score under noisy conditions, and 14.8% in average bit accuracy.
FakeShield: Explainable Image Forgery Detection and Localization via Multi-modal Large Language Models
Oct 03, 2024
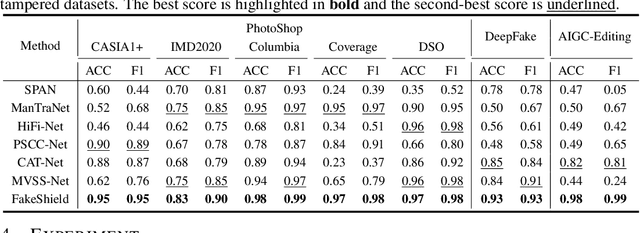
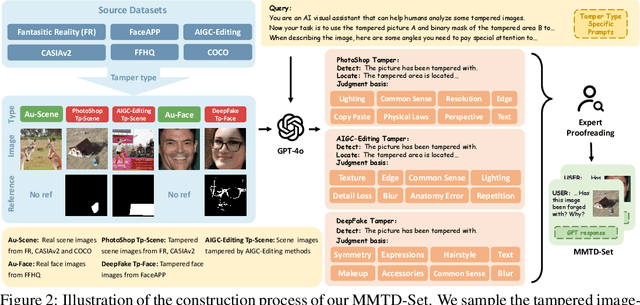

Abstract:The rapid development of generative AI is a double-edged sword, which not only facilitates content creation but also makes image manipulation easier and more difficult to detect. Although current image forgery detection and localization (IFDL) methods are generally effective, they tend to face two challenges: \textbf{1)} black-box nature with unknown detection principle, \textbf{2)} limited generalization across diverse tampering methods (e.g., Photoshop, DeepFake, AIGC-Editing). To address these issues, we propose the explainable IFDL task and design FakeShield, a multi-modal framework capable of evaluating image authenticity, generating tampered region masks, and providing a judgment basis based on pixel-level and image-level tampering clues. Additionally, we leverage GPT-4o to enhance existing IFDL datasets, creating the Multi-Modal Tamper Description dataSet (MMTD-Set) for training FakeShield's tampering analysis capabilities. Meanwhile, we incorporate a Domain Tag-guided Explainable Forgery Detection Module (DTE-FDM) and a Multi-modal Forgery Localization Module (MFLM) to address various types of tamper detection interpretation and achieve forgery localization guided by detailed textual descriptions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FakeShield effectively detects and localizes various tampering techniques, offering an explainable and superior solution compared to previous IFDL methods.
Protect-Your-IP: Scalable Source-Tracing and Attribution against Personalized Generation
May 26, 2024
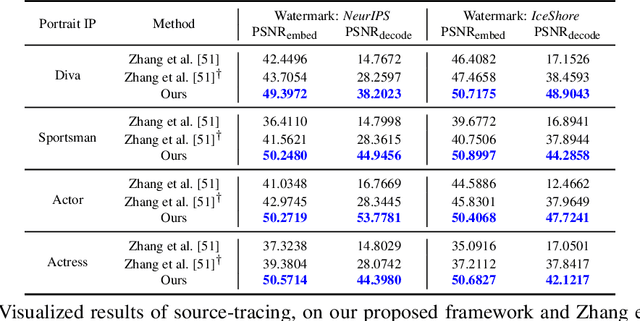
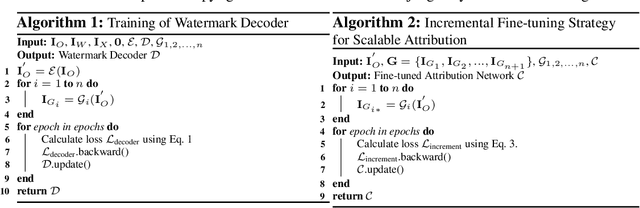

Abstract:With the advent of personalized generation models, users can more readily create images resembling existing content, heightening the risk of violating portrait rights and intellectual property (IP). Traditional post-hoc detection and source-tracing methods for AI-generated content (AIGC) employ proactive watermark approaches; however, these are less effective against personalized generation models. Moreover, attribution techniques for AIGC rely on passive detection but often struggle to differentiate AIGC from authentic images, presenting a substantial challenge. Integrating these two processes into a cohesive framework not only meets the practical demands for protection and forensics but also improves the effectiveness of attribution tasks. Inspired by this insight, we propose a unified approach for image copyright source-tracing and attribution, introducing an innovative watermarking-attribution method that blends proactive and passive strategies. We embed copyright watermarks into protected images and train a watermark decoder to retrieve copyright information from the outputs of personalized models, using this watermark as an initial step for confirming if an image is AIGC-generated. To pinpoint specific generation techniques, we utilize powerful visual backbone networks for classification. Additionally, we implement an incremental learning strategy to adeptly attribute new personalized models without losing prior knowledge, thereby enhancing the model's adaptability to novel generation methods. We have conducted experiments using various celebrity portrait series sourced online, and the results affirm the efficacy of our method in source-tracing and attribution tasks, as well as its robustness against knowledge forgetting.
GS-Hider: Hiding Messages into 3D Gaussian Splatting
May 24, 2024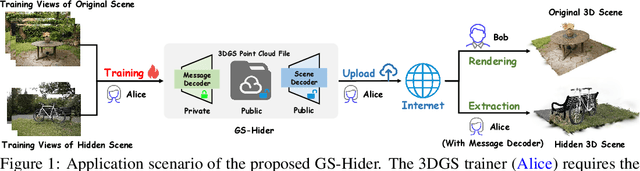
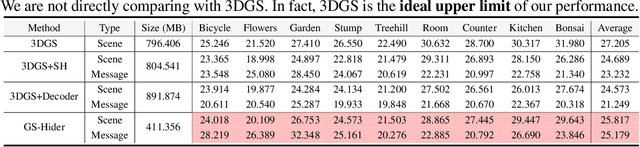

Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has already become the emerging research focus in the fields of 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Given that training a 3DGS requires a significant amount of time and computational cost, it is crucial to protect the copyright, integrity, and privacy of such 3D assets. Steganography, as a crucial technique for encrypted transmission and copyright protection, has been extensively studied. However, it still lacks profound exploration targeted at 3DGS. Unlike its predecessor NeRF, 3DGS possesses two distinct features: 1) explicit 3D representation; and 2) real-time rendering speeds. These characteristics result in the 3DGS point cloud files being public and transparent, with each Gaussian point having a clear physical significance. Therefore, ensuring the security and fidelity of the original 3D scene while embedding information into the 3DGS point cloud files is an extremely challenging task. To solve the above-mentioned issue, we first propose a steganography framework for 3DGS, dubbed GS-Hider, which can embed 3D scenes and images into original GS point clouds in an invisible manner and accurately extract the hidden messages. Specifically, we design a coupled secured feature attribute to replace the original 3DGS's spherical harmonics coefficients and then use a scene decoder and a message decoder to disentangle the original RGB scene and the hidden message. Extensive experiments demonstrated that the proposed GS-Hider can effectively conceal multimodal messages without compromising rendering quality and possesses exceptional security, robustness, capacity, and flexibility. Our project is available at: https://xuanyuzhang21.github.io/project/gshider.
V2A-Mark: Versatile Deep Visual-Audio Watermarking for Manipulation Localization and Copyright Protection
Apr 25, 2024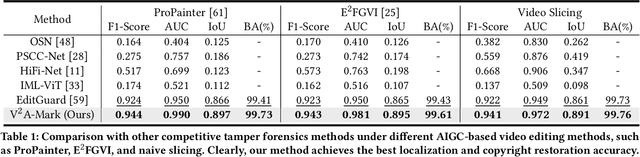
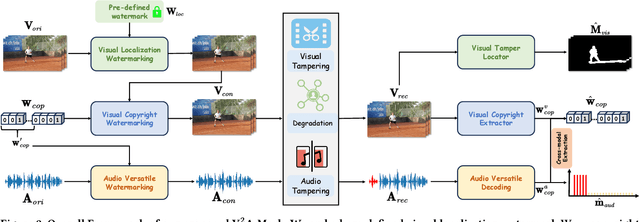
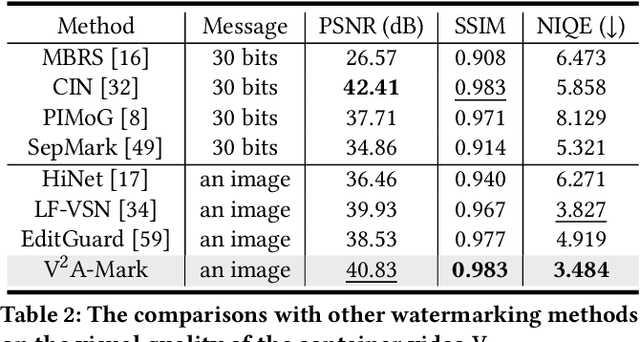
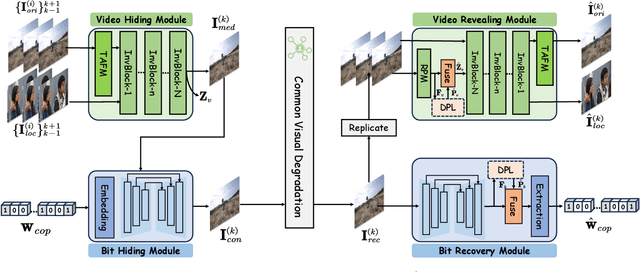
Abstract:AI-generated video has revolutionized short video production, filmmaking, and personalized media, making video local editing an essential tool. However, this progress also blurs the line between reality and fiction, posing challenges in multimedia forensics. To solve this urgent issue, V2A-Mark is proposed to address the limitations of current video tampering forensics, such as poor generalizability, singular function, and single modality focus. Combining the fragility of video-into-video steganography with deep robust watermarking, our method can embed invisible visual-audio localization watermarks and copyright watermarks into the original video frames and audio, enabling precise manipulation localization and copyright protection. We also design a temporal alignment and fusion module and degradation prompt learning to enhance the localization accuracy and decoding robustness. Meanwhile, we introduce a sample-level audio localization method and a cross-modal copyright extraction mechanism to couple the information of audio and video frames. The effectiveness of V2A-Mark has been verified on a visual-audio tampering dataset, emphasizing its superiority in localization precision and copyright accuracy, crucial for the sustainable development of video editing in the AIGC video era.
OmniSSR: Zero-shot Omnidirectional Image Super-Resolution using Stable Diffusion Model
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Omnidirectional images (ODIs) are commonly used in real-world visual tasks, and high-resolution ODIs help improve the performance of related visual tasks. Most existing super-resolution methods for ODIs use end-to-end learning strategies, resulting in inferior realness of generated images and a lack of effective out-of-domain generalization capabilities in training methods. Image generation methods represented by diffusion model provide strong priors for visual tasks and have been proven to be effectively applied to image restoration tasks. Leveraging the image priors of the Stable Diffusion (SD) model, we achieve omnidirectional image super-resolution with both fidelity and realness, dubbed as OmniSSR. Firstly, we transform the equirectangular projection (ERP) images into tangent projection (TP) images, whose distribution approximates the planar image domain. Then, we use SD to iteratively sample initial high-resolution results. At each denoising iteration, we further correct and update the initial results using the proposed Octadecaplex Tangent Information Interaction (OTII) and Gradient Decomposition (GD) technique to ensure better consistency. Finally, the TP images are transformed back to obtain the final high-resolution results. Our method is zero-shot, requiring no training or fine-tuning. Experiments of our method on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge