Ruibing Hou
DreamActor-M2: Universal Character Image Animation via Spatiotemporal In-Context Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Character image animation aims to synthesize high-fidelity videos by transferring motion from a driving sequence to a static reference image. Despite recent advancements, existing methods suffer from two fundamental challenges: (1) suboptimal motion injection strategies that lead to a trade-off between identity preservation and motion consistency, manifesting as a "see-saw", and (2) an over-reliance on explicit pose priors (e.g., skeletons), which inadequately capture intricate dynamics and hinder generalization to arbitrary, non-humanoid characters. To address these challenges, we present DreamActor-M2, a universal animation framework that reimagines motion conditioning as an in-context learning problem. Our approach follows a two-stage paradigm. First, we bridge the input modality gap by fusing reference appearance and motion cues into a unified latent space, enabling the model to jointly reason about spatial identity and temporal dynamics by leveraging the generative prior of foundational models. Second, we introduce a self-bootstrapped data synthesis pipeline that curates pseudo cross-identity training pairs, facilitating a seamless transition from pose-dependent control to direct, end-to-end RGB-driven animation. This strategy significantly enhances generalization across diverse characters and motion scenarios. To facilitate comprehensive evaluation, we further introduce AW Bench, a versatile benchmark encompassing a wide spectrum of characters types and motion scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamActor-M2 achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering superior visual fidelity and robust cross-domain generalization. Project Page: https://grisoon.github.io/DreamActor-M2/
CLIP-Guided Adaptable Self-Supervised Learning for Human-Centric Visual Tasks
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Human-centric visual analysis plays a pivotal role in diverse applications, including surveillance, healthcare, and human-computer interaction. With the emergence of large-scale unlabeled human image datasets, there is an increasing need for a general unsupervised pre-training model capable of supporting diverse human-centric downstream tasks. To achieve this goal, we propose CLASP (CLIP-guided Adaptable Self-suPervised learning), a novel framework designed for unsupervised pre-training in human-centric visual tasks. CLASP leverages the powerful vision-language model CLIP to generate both low-level (e.g., body parts) and high-level (e.g., attributes) semantic pseudo-labels. These multi-level semantic cues are then integrated into the learned visual representations, enriching their expressiveness and generalizability. Recognizing that different downstream tasks demand varying levels of semantic granularity, CLASP incorporates a Prompt-Controlled Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) module. MoE dynamically adapts feature extraction based on task-specific prompts, mitigating potential feature conflicts and enhancing transferability. Furthermore, CLASP employs a multi-task pre-training strategy, where part- and attribute-level pseudo-labels derived from CLIP guide the representation learning process. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that CLASP consistently outperforms existing unsupervised pre-training methods, advancing the field of human-centric visual analysis.
Revisiting Multimodal Positional Encoding in Vision-Language Models
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Multimodal position encoding is essential for vision-language models, yet there has been little systematic investigation into multimodal position encoding. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of multimodal Rotary Positional Embedding (RoPE) by examining its two core components: position design and frequency allocation. Through extensive experiments, we identify three key guidelines: positional coherence, full frequency utilization, and preservation of textual priors-ensuring unambiguous layout, rich representation, and faithful transfer from the pre-trained LLM. Based on these insights, we propose Multi-Head RoPE (MHRoPE) and MRoPE-Interleave (MRoPE-I), two simple and plug-and-play variants that require no architectural changes. Our methods consistently outperform existing approaches across diverse benchmarks, with significant improvements in both general and fine-grained multimodal understanding. Code will be avaliable at https://github.com/JJJYmmm/Multimodal-RoPEs.
un$^2$CLIP: Improving CLIP's Visual Detail Capturing Ability via Inverting unCLIP
May 30, 2025Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) has become a foundation model and has been applied to various vision and multimodal tasks. However, recent works indicate that CLIP falls short in distinguishing detailed differences in images and shows suboptimal performance on dense-prediction and vision-centric multimodal tasks. Therefore, this work focuses on improving existing CLIP models, aiming to capture as many visual details in images as possible. We find that a specific type of generative models, unCLIP, provides a suitable framework for achieving our goal. Specifically, unCLIP trains an image generator conditioned on the CLIP image embedding. In other words, it inverts the CLIP image encoder. Compared to discriminative models like CLIP, generative models are better at capturing image details because they are trained to learn the data distribution of images. Additionally, the conditional input space of unCLIP aligns with CLIP's original image-text embedding space. Therefore, we propose to invert unCLIP (dubbed un$^2$CLIP) to improve the CLIP model. In this way, the improved image encoder can gain unCLIP's visual detail capturing ability while preserving its alignment with the original text encoder simultaneously. We evaluate our improved CLIP across various tasks to which CLIP has been applied, including the challenging MMVP-VLM benchmark, the dense-prediction open-vocabulary segmentation task, and multimodal large language model tasks. Experiments show that un$^2$CLIP significantly improves the original CLIP and previous CLIP improvement methods. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/LiYinqi/un2CLIP.
DIVE: Inverting Conditional Diffusion Models for Discriminative Tasks
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable progress in various generative tasks such as image and video generation. This paper studies the problem of leveraging pretrained diffusion models for performing discriminative tasks. Specifically, we extend the discriminative capability of pretrained frozen generative diffusion models from the classification task to the more complex object detection task, by "inverting" a pretrained layout-to-image diffusion model. To this end, a gradient-based discrete optimization approach for replacing the heavy prediction enumeration process, and a prior distribution model for making more accurate use of the Bayes' rule, are proposed respectively. Empirical results show that this method is on par with basic discriminative object detection baselines on COCO dataset. In addition, our method can greatly speed up the previous diffusion-based method for classification without sacrificing accuracy. Code and models are available at https://github.com/LiYinqi/DIVE .
HIS-GPT: Towards 3D Human-In-Scene Multimodal Understanding
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We propose a new task to benchmark human-in-scene understanding for embodied agents: Human-In-Scene Question Answering (HIS-QA). Given a human motion within a 3D scene, HIS-QA requires the agent to comprehend human states and behaviors, reason about its surrounding environment, and answer human-related questions within the scene. To support this new task, we present HIS-Bench, a multimodal benchmark that systematically evaluates HIS understanding across a broad spectrum, from basic perception to commonsense reasoning and planning. Our evaluation of various vision-language models on HIS-Bench reveals significant limitations in their ability to handle HIS-QA tasks. To this end, we propose HIS-GPT, the first foundation model for HIS understanding. HIS-GPT integrates 3D scene context and human motion dynamics into large language models while incorporating specialized mechanisms to capture human-scene interactions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HIS-GPT sets a new state-of-the-art on HIS-QA tasks. We hope this work inspires future research on human behavior analysis in 3D scenes, advancing embodied AI and world models.
MATS: An Audio Language Model under Text-only Supervision
Feb 20, 2025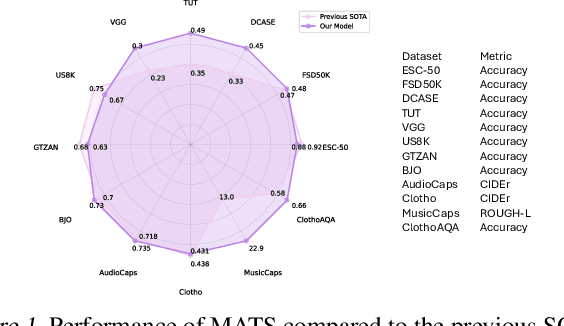
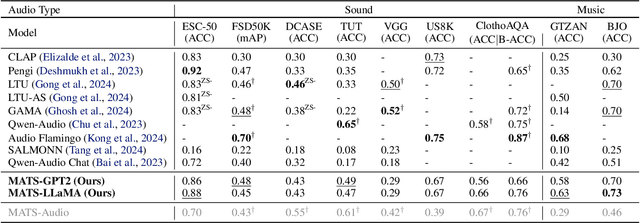
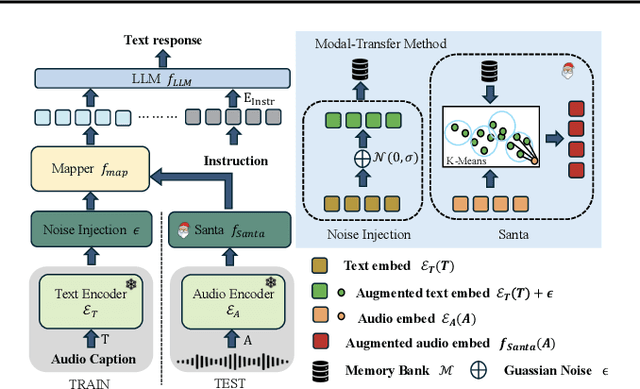
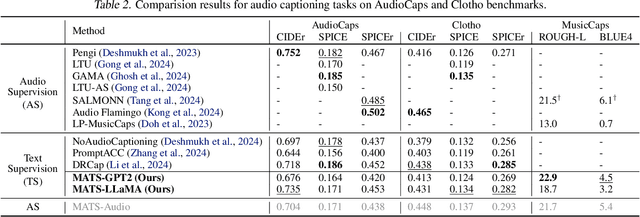
Abstract:Large audio-language models (LALMs), built upon powerful Large Language Models (LLMs), have exhibited remarkable audio comprehension and reasoning capabilities. However, the training of LALMs demands a large corpus of audio-language pairs, which requires substantial costs in both data collection and training resources. In this paper, we propose MATS, an audio-language multimodal LLM designed to handle Multiple Audio task using solely Text-only Supervision. By leveraging pre-trained audio-language alignment models such as CLAP, we develop a text-only training strategy that projects the shared audio-language latent space into LLM latent space, endowing the LLM with audio comprehension capabilities without relying on audio data during training. To further bridge the modality gap between audio and language embeddings within CLAP, we propose the Strongly-related noisy text with audio (Santa) mechanism. Santa maps audio embeddings into CLAP language embedding space while preserving essential information from the audio input. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MATS, despite being trained exclusively on text data, achieves competitive performance compared to recent LALMs trained on large-scale audio-language pairs.
RefHCM: A Unified Model for Referring Perceptions in Human-Centric Scenarios
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Human-centric perceptions play a crucial role in real-world applications. While recent human-centric works have achieved impressive progress, these efforts are often constrained to the visual domain and lack interaction with human instructions, limiting their applicability in broader scenarios such as chatbots and sports analysis. This paper introduces Referring Human Perceptions, where a referring prompt specifies the person of interest in an image. To tackle the new task, we propose RefHCM (Referring Human-Centric Model), a unified framework to integrate a wide range of human-centric referring tasks. Specifically, RefHCM employs sequence mergers to convert raw multimodal data -- including images, text, coordinates, and parsing maps -- into semantic tokens. This standardized representation enables RefHCM to reformulate diverse human-centric referring tasks into a sequence-to-sequence paradigm, solved using a plain encoder-decoder transformer architecture. Benefiting from a unified learning strategy, RefHCM effectively facilitates knowledge transfer across tasks and exhibits unforeseen capabilities in handling complex reasoning. This work represents the first attempt to address referring human perceptions with a general-purpose framework, while simultaneously establishing a corresponding benchmark that sets new standards for the field. Extensive experiments showcase RefHCM's competitive and even superior performance across multiple human-centric referring tasks. The code and data are publicly at https://github.com/JJJYmmm/RefHCM.
UniPose: A Unified Multimodal Framework for Human Pose Comprehension, Generation and Editing
Nov 25, 2024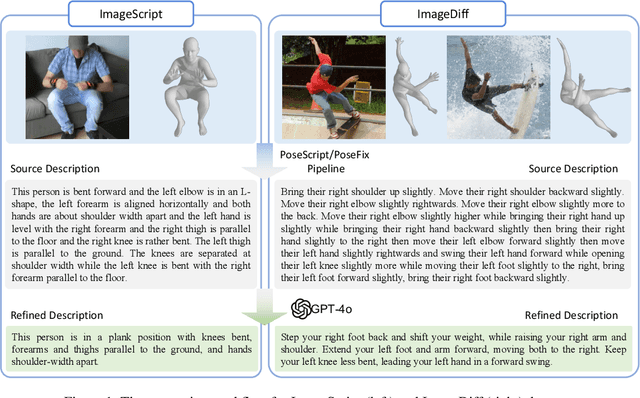
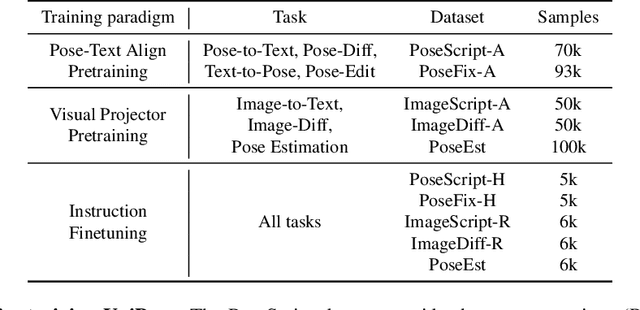
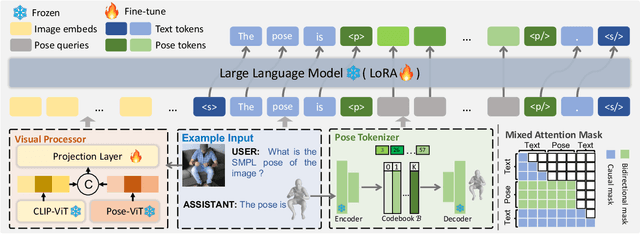
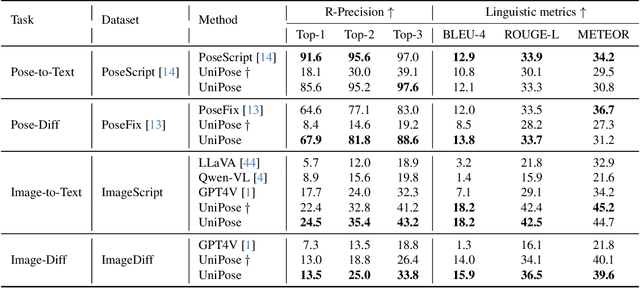
Abstract:Human pose plays a crucial role in the digital age. While recent works have achieved impressive progress in understanding and generating human poses, they often support only a single modality of control signals and operate in isolation, limiting their application in real-world scenarios. This paper presents UniPose, a framework employing Large Language Models (LLMs) to comprehend, generate, and edit human poses across various modalities, including images, text, and 3D SMPL poses. Specifically, we apply a pose tokenizer to convert 3D poses into discrete pose tokens, enabling seamless integration into the LLM within a unified vocabulary. To further enhance the fine-grained pose perception capabilities, we facilitate UniPose with a mixture of visual encoders, among them a pose-specific visual encoder. Benefiting from a unified learning strategy, UniPose effectively transfers knowledge across different pose-relevant tasks, adapts to unseen tasks, and exhibits extended capabilities. This work serves as the first attempt at building a general-purpose framework for pose comprehension, generation, and editing. Extensive experiments highlight UniPose's competitive and even superior performance across various pose-relevant tasks.
Morph: A Motion-free Physics Optimization Framework for Human Motion Generation
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Human motion generation plays a vital role in applications such as digital humans and humanoid robot control. However, most existing approaches disregard physics constraints, leading to the frequent production of physically implausible motions with pronounced artifacts such as floating and foot sliding. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Morph}, a \textbf{Mo}tion-f\textbf{r}ee \textbf{ph}ysics optimization framework, comprising a Motion Generator and a Motion Physics Refinement module, for enhancing physical plausibility without relying on costly real-world motion data. Specifically, the Motion Generator is responsible for providing large-scale synthetic motion data, while the Motion Physics Refinement Module utilizes these synthetic data to train a motion imitator within a physics simulator, enforcing physical constraints to project the noisy motions into a physically-plausible space. These physically refined motions, in turn, are used to fine-tune the Motion Generator, further enhancing its capability. Experiments on both text-to-motion and music-to-dance generation tasks demonstrate that our framework achieves state-of-the-art motion generation quality while improving physical plausibility drastically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge