Rui Liao
GRAM-TDI: adaptive multimodal representation learning for drug target interaction prediction
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Drug target interaction (DTI) prediction is a cornerstone of computational drug discovery, enabling rational design, repurposing, and mechanistic insights. While deep learning has advanced DTI modeling, existing approaches primarily rely on SMILES protein pairs and fail to exploit the rich multimodal information available for small molecules and proteins. We introduce GRAMDTI, a pretraining framework that integrates multimodal molecular and protein inputs into unified representations. GRAMDTI extends volume based contrastive learning to four modalities, capturing higher-order semantic alignment beyond conventional pairwise approaches. To handle modality informativeness, we propose adaptive modality dropout, dynamically regulating each modality's contribution during pre-training. Additionally, IC50 activity measurements, when available, are incorporated as weak supervision to ground representations in biologically meaningful interaction strengths. Experiments on four publicly available datasets demonstrate that GRAMDTI consistently outperforms state of the art baselines. Our results highlight the benefits of higher order multimodal alignment, adaptive modality utilization, and auxiliary supervision for robust and generalizable DTI prediction.
TRIDENT: Tri-Modal Molecular Representation Learning with Taxonomic Annotations and Local Correspondence
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Molecular property prediction aims to learn representations that map chemical structures to functional properties. While multimodal learning has emerged as a powerful paradigm to learn molecular representations, prior works have largely overlooked textual and taxonomic information of molecules for representation learning. We introduce TRIDENT, a novel framework that integrates molecular SMILES, textual descriptions, and taxonomic functional annotations to learn rich molecular representations. To achieve this, we curate a comprehensive dataset of molecule-text pairs with structured, multi-level functional annotations. Instead of relying on conventional contrastive loss, TRIDENT employs a volume-based alignment objective to jointly align tri-modal features at the global level, enabling soft, geometry-aware alignment across modalities. Additionally, TRIDENT introduces a novel local alignment objective that captures detailed relationships between molecular substructures and their corresponding sub-textual descriptions. A momentum-based mechanism dynamically balances global and local alignment, enabling the model to learn both broad functional semantics and fine-grained structure-function mappings. TRIDENT achieves state-of-the-art performance on 11 downstream tasks, demonstrating the value of combining SMILES, textual, and taxonomic functional annotations for molecular property prediction.
Multimodal Modeling of CRISPR-Cas12 Activity Using Foundation Models and Chromatin Accessibility Data
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Predicting guide RNA (gRNA) activity is critical for effective CRISPR-Cas12 genome editing but remains challenging due to limited data, variation across protospacer adjacent motifs (PAMs-short sequence requirements for Cas binding), and reliance on large-scale training. We investigate whether pre-trained biological foundation model originally trained on transcriptomic data can improve gRNA activity estimation even without domain-specific pre-training. Using embeddings from existing RNA foundation model as input to lightweight regressor, we show substantial gains over traditional baselines. We also integrate chromatin accessibility data to capture regulatory context, improving performance further. Our results highlight the effectiveness of pre-trained foundation models and chromatin accessibility data for gRNA activity prediction.
BioLangFusion: Multimodal Fusion of DNA, mRNA, and Protein Language Models
Jun 10, 2025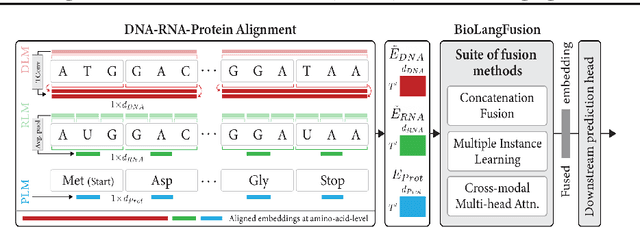
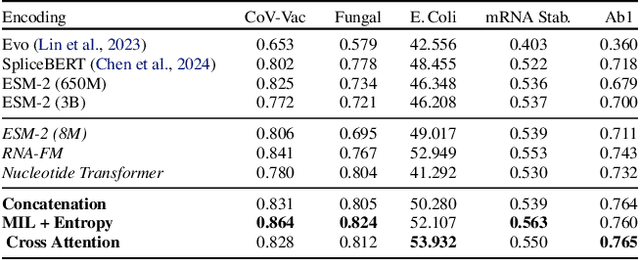
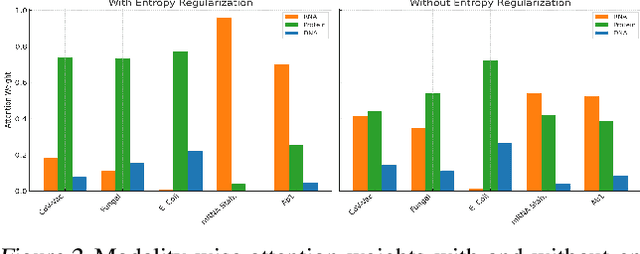
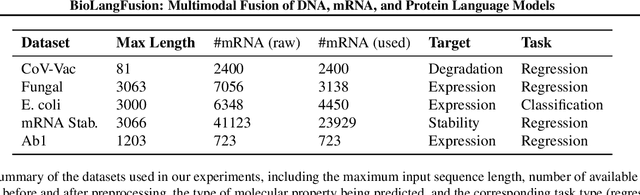
Abstract:We present BioLangFusion, a simple approach for integrating pre-trained DNA, mRNA, and protein language models into unified molecular representations. Motivated by the central dogma of molecular biology (information flow from gene to transcript to protein), we align per-modality embeddings at the biologically meaningful codon level (three nucleotides encoding one amino acid) to ensure direct cross-modal correspondence. BioLangFusion studies three standard fusion techniques: (i) codon-level embedding concatenation, (ii) entropy-regularized attention pooling inspired by multiple-instance learning, and (iii) cross-modal multi-head attention -- each technique providing a different inductive bias for combining modality-specific signals. These methods require no additional pre-training or modification of the base models, allowing straightforward integration with existing sequence-based foundation models. Across five molecular property prediction tasks, BioLangFusion outperforms strong unimodal baselines, showing that even simple fusion of pre-trained models can capture complementary multi-omic information with minimal overhead.
Geometric Hyena Networks for Large-scale Equivariant Learning
May 28, 2025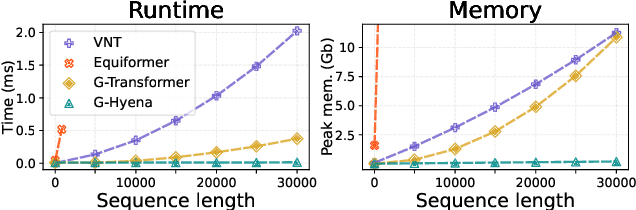
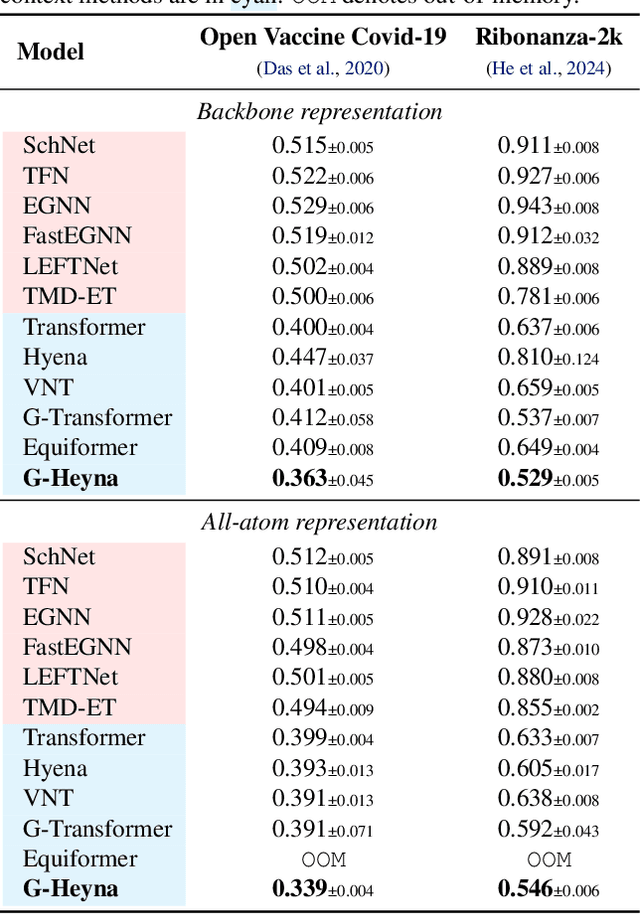
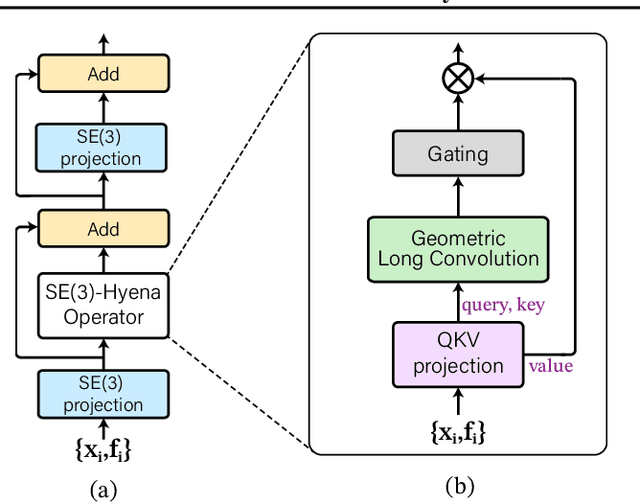
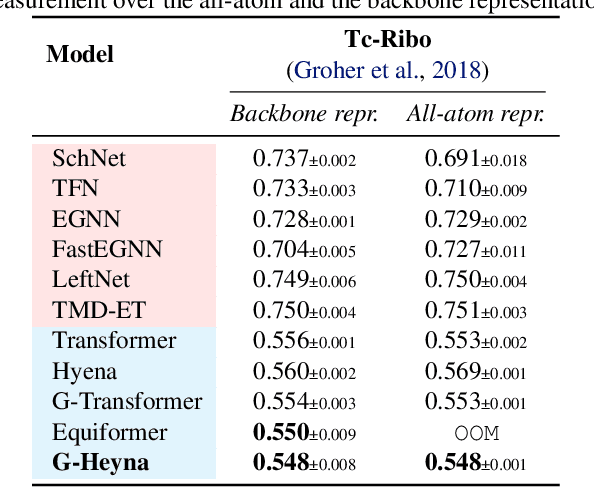
Abstract:Processing global geometric context while preserving equivariance is crucial when modeling biological, chemical, and physical systems. Yet, this is challenging due to the computational demands of equivariance and global context at scale. Standard methods such as equivariant self-attention suffer from quadratic complexity, while local methods such as distance-based message passing sacrifice global information. Inspired by the recent success of state-space and long-convolutional models, we introduce Geometric Hyena, the first equivariant long-convolutional model for geometric systems. Geometric Hyena captures global geometric context at sub-quadratic complexity while maintaining equivariance to rotations and translations. Evaluated on all-atom property prediction of large RNA molecules and full protein molecular dynamics, Geometric Hyena outperforms existing equivariant models while requiring significantly less memory and compute that equivariant self-attention. Notably, our model processes the geometric context of 30k tokens 20x faster than the equivariant transformer and allows 72x longer context within the same budget.
InfoSEM: A Deep Generative Model with Informative Priors for Gene Regulatory Network Inference
Mar 06, 2025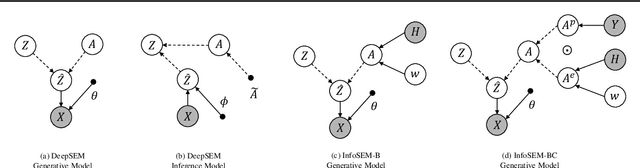
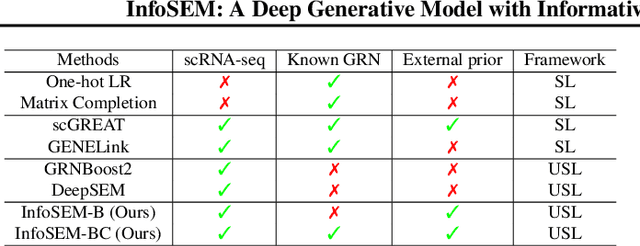
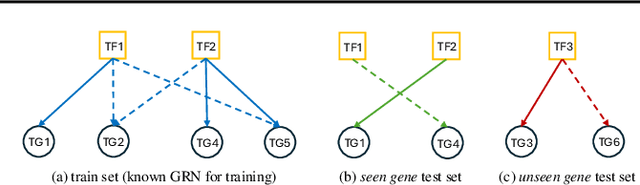
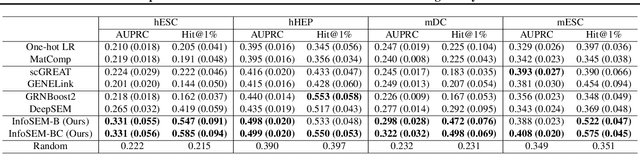
Abstract:Inferring Gene Regulatory Networks (GRNs) from gene expression data is crucial for understanding biological processes. While supervised models are reported to achieve high performance for this task, they rely on costly ground truth (GT) labels and risk learning gene-specific biases, such as class imbalances of GT interactions, rather than true regulatory mechanisms. To address these issues, we introduce InfoSEM, an unsupervised generative model that leverages textual gene embeddings as informative priors, improving GRN inference without GT labels. InfoSEM can also integrate GT labels as an additional prior when available, avoiding biases and further enhancing performance. Additionally, we propose a biologically motivated benchmarking framework that better reflects real-world applications such as biomarker discovery and reveals learned biases of existing supervised methods. InfoSEM outperforms existing models by 38.5% across four datasets using textual embeddings prior and further boosts performance by 11.1% when integrating labeled data as priors.
GoBERT: Gene Ontology Graph Informed BERT for Universal Gene Function Prediction
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:Exploring the functions of genes and gene products is crucial to a wide range of fields, including medical research, evolutionary biology, and environmental science. However, discovering new functions largely relies on expensive and exhaustive wet lab experiments. Existing methods of automatic function annotation or prediction mainly focus on protein function prediction with sequence, 3D-structures or protein family information. In this study, we propose to tackle the gene function prediction problem by exploring Gene Ontology graph and annotation with BERT (GoBERT) to decipher the underlying relationships among gene functions. Our proposed novel function prediction task utilizes existing functions as inputs and generalizes the function prediction to gene and gene products. Specifically, two pre-train tasks are designed to jointly train GoBERT to capture both explicit and implicit relations of functions. Neighborhood prediction is a self-supervised multi-label classification task that captures the explicit function relations. Specified masking and recovering task helps GoBERT in finding implicit patterns among functions. The pre-trained GoBERT possess the ability to predict novel functions for various gene and gene products based on known functional annotations. Extensive experiments, biological case studies, and ablation studies are conducted to demonstrate the superiority of our proposed GoBERT.
HELM: Hierarchical Encoding for mRNA Language Modeling
Oct 16, 2024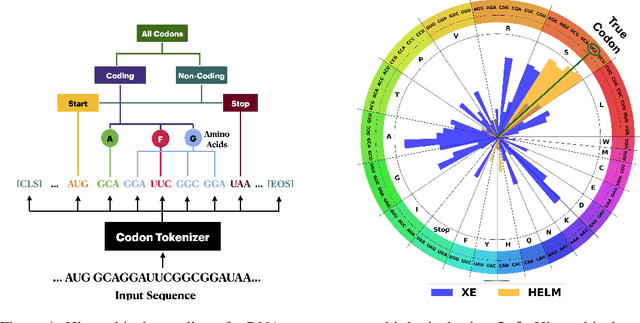
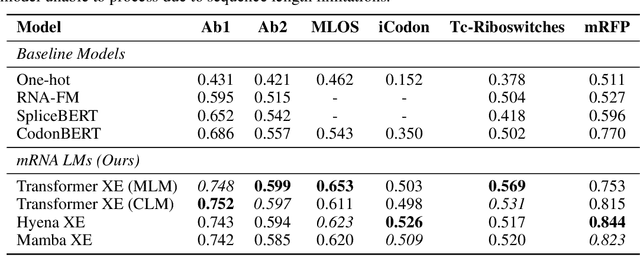
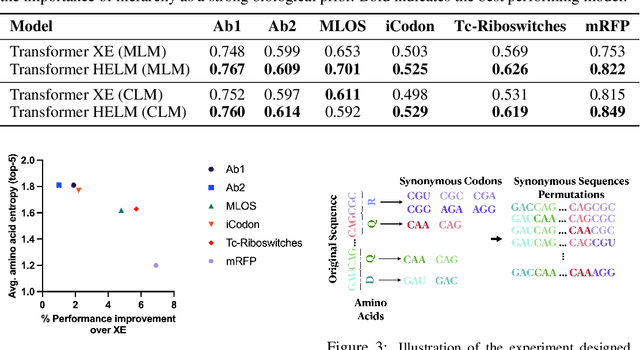
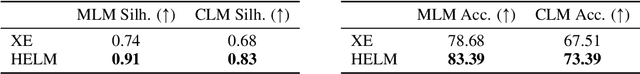
Abstract:Messenger RNA (mRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, with its codon structure directly impacting biological properties. While Language Models (LMs) have shown promise in analyzing biological sequences, existing approaches fail to account for the hierarchical nature of mRNA's codon structure. We introduce Hierarchical Encoding for mRNA Language Modeling (HELM), a novel pre-training strategy that incorporates codon-level hierarchical structure into language model training. HELM modulates the loss function based on codon synonymity, aligning the model's learning process with the biological reality of mRNA sequences. We evaluate HELM on diverse mRNA datasets and tasks, demonstrating that HELM outperforms standard language model pre-training as well as existing foundation model baselines on six diverse downstream property prediction tasks and an antibody region annotation tasks on average by around 8\%. Additionally, HELM enhances the generative capabilities of language model, producing diverse mRNA sequences that better align with the underlying true data distribution compared to non-hierarchical baselines.
Beyond Sequence: Impact of Geometric Context for RNA Property Prediction
Oct 15, 2024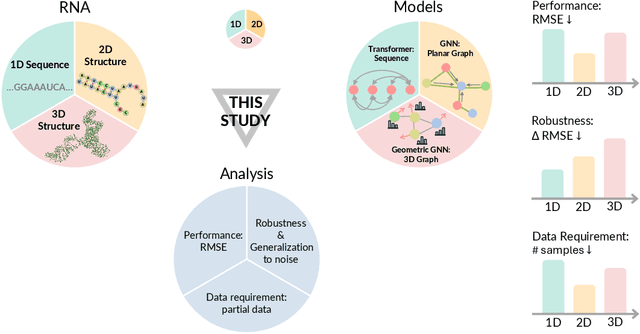
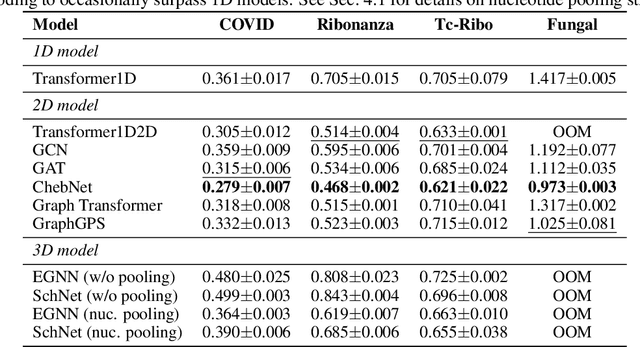
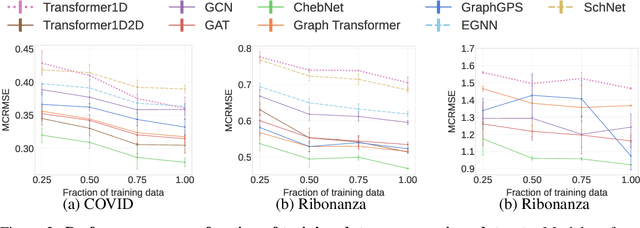
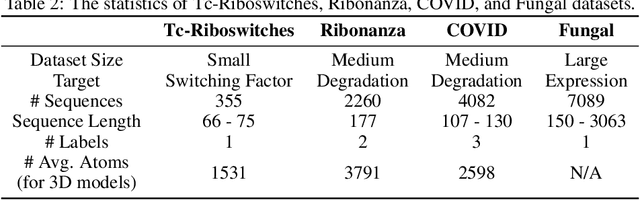
Abstract:Accurate prediction of RNA properties, such as stability and interactions, is crucial for advancing our understanding of biological processes and developing RNA-based therapeutics. RNA structures can be represented as 1D sequences, 2D topological graphs, or 3D all-atom models, each offering different insights into its function. Existing works predominantly focus on 1D sequence-based models, which overlook the geometric context provided by 2D and 3D geometries. This study presents the first systematic evaluation of incorporating explicit 2D and 3D geometric information into RNA property prediction, considering not only performance but also real-world challenges such as limited data availability, partial labeling, sequencing noise, and computational efficiency. To this end, we introduce a newly curated set of RNA datasets with enhanced 2D and 3D structural annotations, providing a resource for model evaluation on RNA data. Our findings reveal that models with explicit geometry encoding generally outperform sequence-based models, with an average prediction RMSE reduction of around 12% across all various RNA tasks and excelling in low-data and partial labeling regimes, underscoring the value of explicitly incorporating geometric context. On the other hand, geometry-unaware sequence-based models are more robust under sequencing noise but often require around 2-5x training data to match the performance of geometry-aware models. Our study offers further insights into the trade-offs between different RNA representations in practical applications and addresses a significant gap in evaluating deep learning models for RNA tasks.
SE(3)-Hyena Operator for Scalable Equivariant Learning
Jul 01, 2024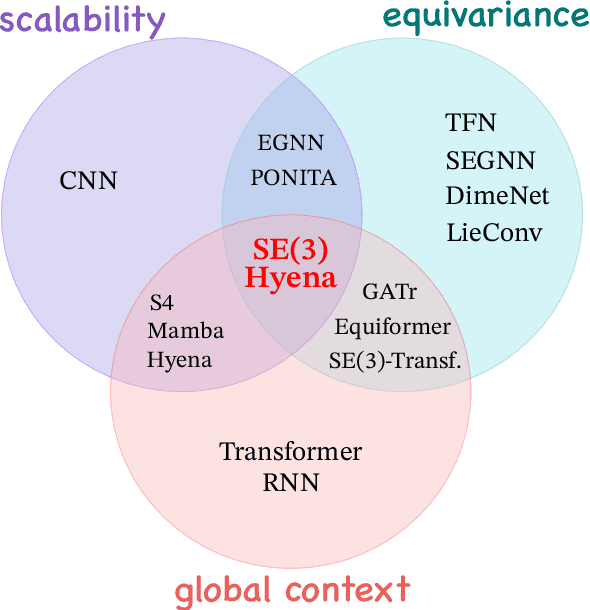
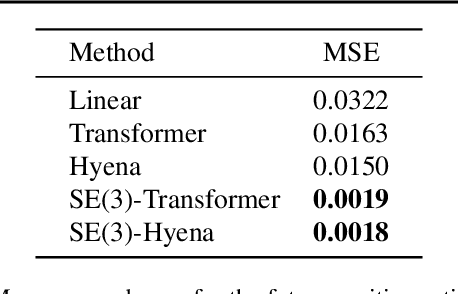
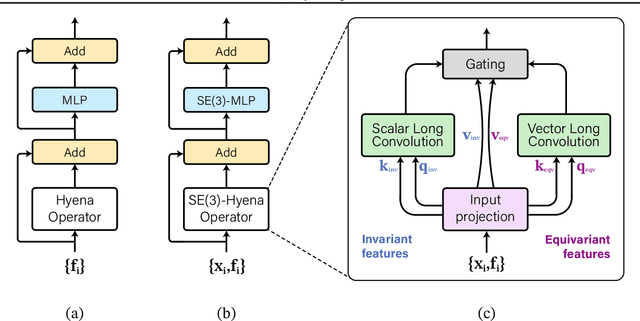
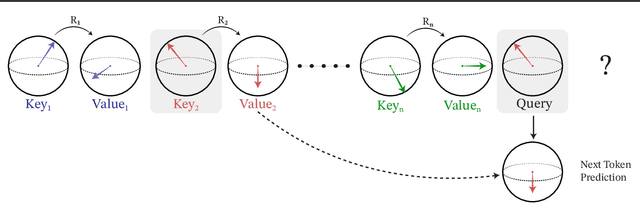
Abstract:Modeling global geometric context while maintaining equivariance is crucial for accurate predictions in many fields such as biology, chemistry, or vision. Yet, this is challenging due to the computational demands of processing high-dimensional data at scale. Existing approaches such as equivariant self-attention or distance-based message passing, suffer from quadratic complexity with respect to sequence length, while localized methods sacrifice global information. Inspired by the recent success of state-space and long-convolutional models, in this work, we introduce SE(3)-Hyena operator, an equivariant long-convolutional model based on the Hyena operator. The SE(3)-Hyena captures global geometric context at sub-quadratic complexity while maintaining equivariance to rotations and translations. Evaluated on equivariant associative recall and n-body modeling, SE(3)-Hyena matches or outperforms equivariant self-attention while requiring significantly less memory and computational resources for long sequences. Our model processes the geometric context of 20k tokens x3.5 times faster than the equivariant transformer and allows x175 longer a context within the same memory budget.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge