Yuwei Miao
LTS-VoiceAgent: A Listen-Think-Speak Framework for Efficient Streaming Voice Interaction via Semantic Triggering and Incremental Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Real-time voice agents face a dilemma: end-to-end models often lack deep reasoning, while cascaded pipelines incur high latency by executing ASR, LLM reasoning, and TTS strictly in sequence, unlike human conversation where listeners often start thinking before the speaker finishes. Since cascaded architectures remain the dominant choice for complex tasks, existing cascaded streaming strategies attempt to reduce this latency via mechanical segmentation (e.g., fixed chunks, VAD-based splitting) or speculative generation, but they frequently either break semantic units or waste computation on predictions that must be rolled back. To address these challenges, we propose LTS-VoiceAgent, a Listen-Think-Speak framework that explicitly separates when to think from how to reason incrementally. It features a Dynamic Semantic Trigger to detect meaningful prefixes, and a Dual-Role Stream Orchestrator that coordinates a background Thinker (for state maintenance) and a foreground Speaker (for speculative solving). This parallel design enables "thinking while speaking" without blocking responses. We also introduce a Pause-and-Repair benchmark containing natural disfluencies to stress-test streaming robustness. Experiments across VERA, Spoken-MQA, BigBenchAudio, and our benchmark show that LTS-VoiceAgent achieves a stronger accuracy-latency-efficiency trade-off than serial cascaded baselines and existing streaming strategies.
GenePheno: Interpretable Gene Knockout-Induced Phenotype Abnormality Prediction from Gene Sequences
Nov 14, 2025
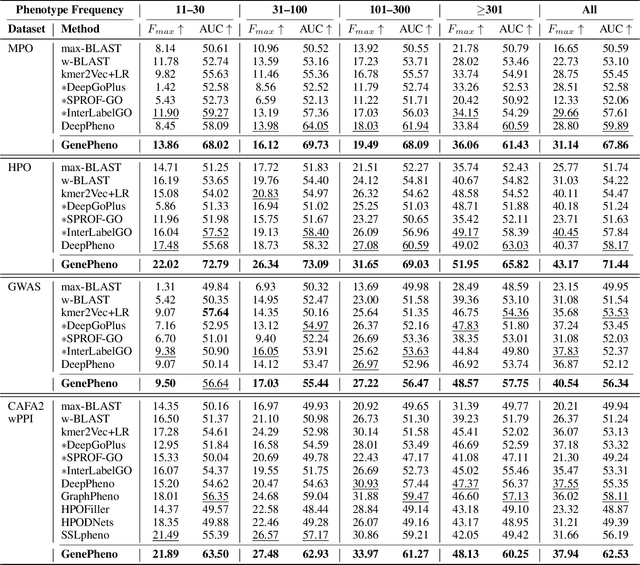
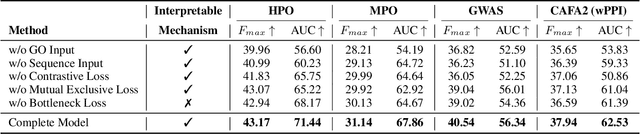
Abstract:Exploring how genetic sequences shape phenotypes is a fundamental challenge in biology and a key step toward scalable, hypothesis-driven experimentation. The task is complicated by the large modality gap between sequences and phenotypes, as well as the pleiotropic nature of gene-phenotype relationships. Existing sequence-based efforts focus on the degree to which variants of specific genes alter a limited set of phenotypes, while general gene knockout induced phenotype abnormality prediction methods heavily rely on curated genetic information as inputs, which limits scalability and generalizability. As a result, the task of broadly predicting the presence of multiple phenotype abnormalities under gene knockout directly from gene sequences remains underexplored. We introduce GenePheno, the first interpretable multi-label prediction framework that predicts knockout induced phenotypic abnormalities from gene sequences. GenePheno employs a contrastive multi-label learning objective that captures inter-phenotype correlations, complemented by an exclusive regularization that enforces biological consistency. It further incorporates a gene function bottleneck layer, offering human interpretable concepts that reflect functional mechanisms behind phenotype formation. To support progress in this area, we curate four datasets with canonical gene sequences as input and multi-label phenotypic abnormalities induced by gene knockouts as targets. Across these datasets, GenePheno achieves state-of-the-art gene-centric $F_{\text{max}}$ and phenotype-centric AUC, and case studies demonstrate its ability to reveal gene functional mechanisms.
GoBERT: Gene Ontology Graph Informed BERT for Universal Gene Function Prediction
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:Exploring the functions of genes and gene products is crucial to a wide range of fields, including medical research, evolutionary biology, and environmental science. However, discovering new functions largely relies on expensive and exhaustive wet lab experiments. Existing methods of automatic function annotation or prediction mainly focus on protein function prediction with sequence, 3D-structures or protein family information. In this study, we propose to tackle the gene function prediction problem by exploring Gene Ontology graph and annotation with BERT (GoBERT) to decipher the underlying relationships among gene functions. Our proposed novel function prediction task utilizes existing functions as inputs and generalizes the function prediction to gene and gene products. Specifically, two pre-train tasks are designed to jointly train GoBERT to capture both explicit and implicit relations of functions. Neighborhood prediction is a self-supervised multi-label classification task that captures the explicit function relations. Specified masking and recovering task helps GoBERT in finding implicit patterns among functions. The pre-trained GoBERT possess the ability to predict novel functions for various gene and gene products based on known functional annotations. Extensive experiments, biological case studies, and ablation studies are conducted to demonstrate the superiority of our proposed GoBERT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge